
Robohub.org
Evaluating what’s easy and what’s hard to automate in your workshop
 If you haven’t already introduced a robot into your workshop, or if you are in the process of introducing such a device, you may be wondering … what is the best place to start? What is easy and what is hard to automate? Perhaps there are hundreds — or even thousands — of applications in your workshop. What should be automated first? Here is how we evaluate an application.
If you haven’t already introduced a robot into your workshop, or if you are in the process of introducing such a device, you may be wondering … what is the best place to start? What is easy and what is hard to automate? Perhaps there are hundreds — or even thousands — of applications in your workshop. What should be automated first? Here is how we evaluate an application.
Every time we attend a meeting with robot newbies, they always have very slick ideas about what a robot should be able to do and how it will be done. The ideas are usually all really great and there is certainly a way to achieve them, however, it might take more time, energy and money with less return on investment than might be desirable. You have to be realistic too.
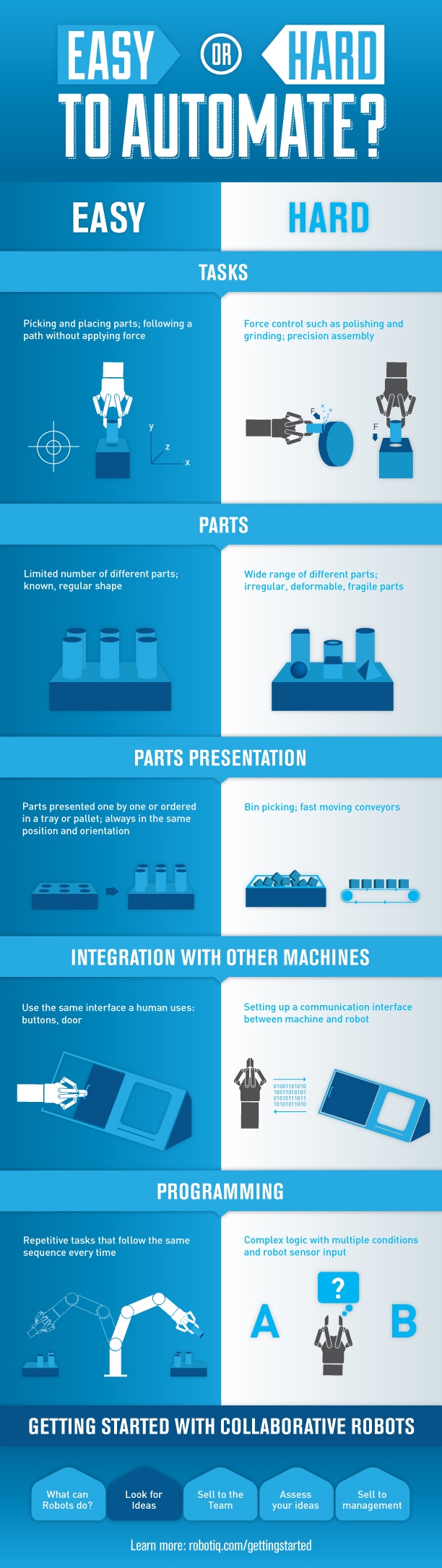
The bottom line is, robots are still pretty complex in general, but there are some applications that are easier than others. This is why we have split the image in our graphic into two sections with an easy and hard side. It is not that the hard side is impossible to do; it is just more complex and requires more effort.
Tasks
Robots are extremely accurate and repeatable in terms of position. It is easy even for a robot that is not very precise to repeat a position within 0.01 mm. So you don’t have to be worried about placing an object at the very same spot each and every time.
However, robots are still hard to automate when their environment is not very repeatable. For example, if an assembly requires hole localization using force feedback, or if you need to polish a part at a precise dimension. Having force feedback adds another level in terms of programming and is tougher to integrate into a first application. You may want to look for applications that can be done without using any input from workers, for example pick-and-place.
Parts
The choice of the part you will handle is critical in a robotic application. The more square or flat surfaces you have, the easier it is. The rigidity of the part will also make a huge difference. Handling the same part or the same family of parts is also a lot easier, because there will be fewer adjustments to make during production. Having a large range of part shapes and sizes will increase the complexity of the grasp.
Having the right kind of gripper can ease your robotic integration. Grippers like the Robotiq Adaptive Gripper are able to handle fragile or deformable objects and even different types of objects, but very few grippers can do this.
Part presentation
The way you present your parts to the robot is critical to the success of your robotic integration. Trays and fixed locations are the easiest to automate.
Bin picking, conveyors and other moving devices are harder to automate, since they require a superior level of intelligence, integration or sensors. This means you will need vision or encoders to determine the part position before grasping it.
Integration with other machines
Using your preexisting machine setup will remain your easiest option. In fact, when integrating a robot into a machine shop, the interface between the machine and the robot is always the hardest part. Robots don’t usually speak the same “language” as your other machines, which can make the connectivity quite complex. Remember that you should start small, with fewer devices to automate. For example, start by closing a door with the robot instead of introducing an automatic door with I/O’s.
Programming
Robots are good for redundant, boring things, but they are not yet good at decision making. This is why in your program you should reduce the level of logic required to the most basic sequence.
For more information on how to integrate your first robot in your workshop, you may want to take a look at the series: Getting Started with Collaborative Robots. This series will guide you through the different steps of integrating a collaborative robot in a workshop.
tags: c-Industrial-Automation, Industrial Automation, Infographics







