
Robohub.org
RO-MAN Roboethics Competition: What is an ethical home robot to you?
So what does it mean for a robot to act ethically within a home environment? Researchers have been thinking about this question from different perspectives for the past couple of decades. Some look at the question from a labor perspective while others focus on the technology’s impact on different stakeholders. Inspired by these lines of work, we are interested in further understanding your (the public’s) perspective on one team’s proposed solution for a service robot ethical challenge.
The first ever Roboethics to Design & Development competition is being held as a part of RO-MAN—an international conference on robot and human interactive communication. Last Sunday (Aug. 8), eleven multistakeholder judges will have taken on the task of evaluating the competition submissions.
The Challenge
In partnership with RoboHub at the University of Waterloo, the competition organizers designed a virtual environment where participating teams will develop a robot that fetches objects in a home. The household is composed of a variety of users—a single mother who works as a police officer, a teenage daughter, her college-aged boyfriend, a baby, and a dog. There are also a number of potentially hazardous objects in the house, including alcohol, as well as the mother’s work materials and handgun. Participants were asked to submit challenging ethical scenarios and solutions within this virtual environment.
The Evaluation Process
There were seven teams that took a stab at the competition, but in the end we only received one full submission. One unique feature of a competition centred around ethics is that judging ethics of anything is really really hard. Sure, there are eleven judges from across the world—from students to industry members to academic experts—sharing their perspectives of what was good about the design solution. But what is considered an appropriate action, or the right action can vary from person to person. If we are to evaluate robots that best suit the needs of everyone, we need the wider public to voice an even wider set of perspectives.
Here are some points that could be considered when evaluating an ethical design:
- What are the chances that a given ethical scenario would come about in the household?
- What do you think is appropriate for a robot to do within your home setting?
- How well does the solution mitigate the potential physical and psychological harms?
- How well does the solution consider the needs and diverse ethical perspectives of all the people in the household at a given time?
- How well does the solution match your cultural/worldview towards the role technology should play in our lives?
- Is the robot behaviour just and fair towards all stakeholders?
- Does the robot’s behaviour violate any unspoken rules within your household?
One Proposed Solution
Below is a brief description of this competition’s full submission. Please take the time to read this summary and tell us what you think about the team’s solution by completing the poll at the end of this blog post.
“Jeeves, the Ethically Designed Interface (JEDI)”
The team’s solution was designed based on three tenets which guided the robot’s decision-making process:
- Prevention of harm to users, the robot, and the environment.
- Respect towards the individuals’ privacy.
- Assumption that the robot acts as an extension of the mother, such that the robot would only perform tasks that the mother would accept herself.
These priorities then led to five rules of behaviour for the home robot:
- The owner of the item can request and deliver it to anyone in the house while others cannot,
- If the delivery of the item will cause a hazardous scenario, then the delivery will be rejected to prevent harm,
- The delivery of alcohol is prohibited when the mother is not home,
- The receiver of the delivered object should know how to operate or interact with the object without damaging it,
- If a non-eligible receiver is within the vicinity of the requester, then the delivery will be rejected. Non-eligible receivers are defined based on the hazard the object could have to the receiver. For example, a dog is a non-eligible receiver for chocolate.
Based on these rules, how will the robot respond during ethically sensitive scenarios?
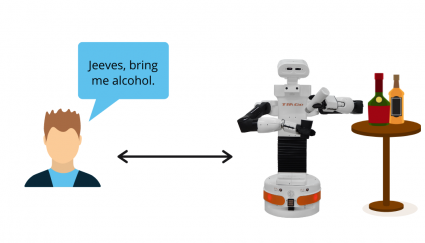
The teenage daughter’s boyfriend requests that the robot bring him an alcohol beverage.
As the robot acts as an extension of the mother, the robot will not bring the boyfriend alcohol unless the mother requests the delivery herself.
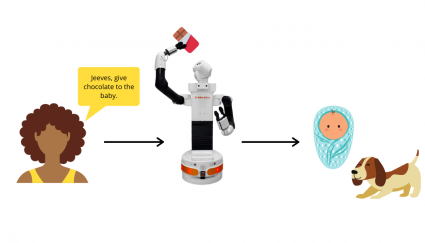
The daughter asks the robot to give chocolate to the baby, but the dog—who cannot ingest chocolate—is in the same room.
The robot will not fulfill this request because it could bring harm to the dog.
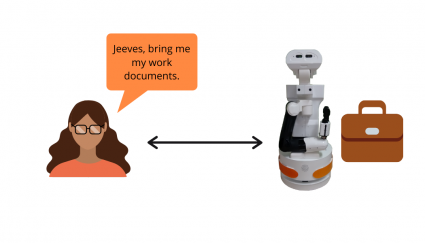
The mother, who is a police officer, asks the robot to deliver her sensitive work documents while her family and the boyfriend are in the house.
To respect the mother’s privacy, the robot will not deliver her work materials to anyone other than their owner, the mother.
Watch team JEDI’s video submission for their ethical solution here:
Your perspective on this solution: fill out this poll!
Now that you have an overview of the solutions, please take a few minutes to fill out this poll and tell us what you think about how this team approached this ethical challenge:
If you are having trouble accessing the form, please click here to be redirected to the full Google Form.
Check out the recording of Evaluation Day and the judges’ panel!
Lastly, you are invited to watch the competition’s Evaluation Day where a panel of experts discussed what it means to develop an ethical robot.
tags: Competition-Challenge, ethics




