
Robohub.org
Teaching robots how to move objects
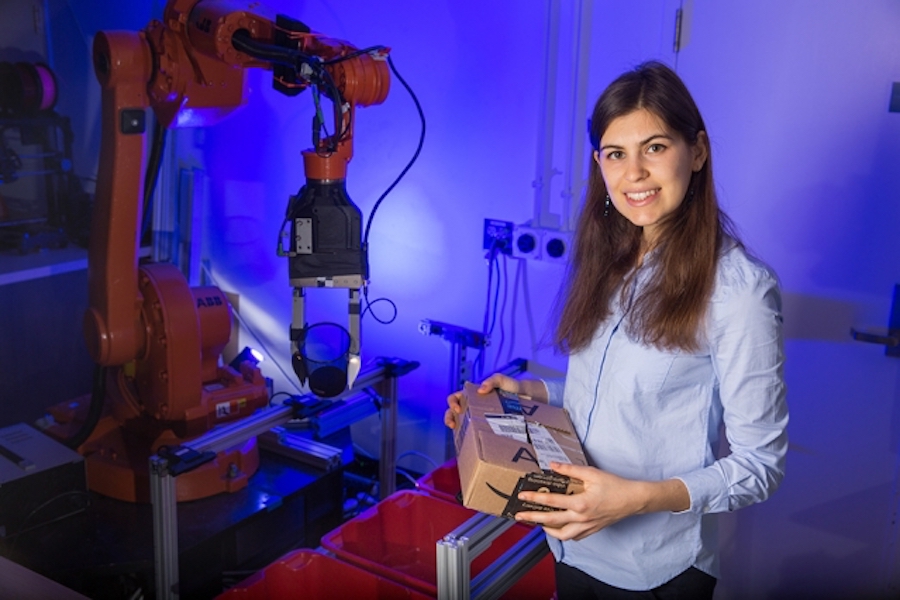
Doctoral student Maria Bauza has been exploring the notion of uncertainty when robots pick up, grasp, or push an object. “If the robot could touch the object, have a notion of tactile information, and be able to react to that information, it will have much more success,” she says.
Photo: Tony Pulsone
By Mary Beth O’Leary
With the push of a button, months of hard work were about to be put to the test. Sixteen teams of engineers convened in a cavernous exhibit hall in Nagoya, Japan, for the 2017 Amazon Robotics Challenge. The robotic systems they built were tasked with removing items from bins and placing them into boxes. For graduate student Maria Bauza, who served as task-planning lead for the MIT-Princeton Team, the moment was particularly nerve-wracking.
“It was super stressful when the competition started,” recalls Bauza. “You just press play and the robot is autonomous. It’s going to do whatever you code it for, but you have no control. If something is broken, then that’s it.”
Robotics has been a major focus for Bauza since her undergraduate career. She studied mathematics and engineering physics at the Polytechnic University of Catalonia in Barcelona. During a year as a visiting student at MIT, Bauza was able to put her interest in computer science and artificial intelligence into practice. “When I came to MIT for that year, I starting applying the tools I had learned in machine learning to real problems in robotics,” she adds.
Two creative undergraduate projects gave her even more practice in this area. In one project, she hacked the controller of a toy remote control car to make it drive in a straight line. In another, she developed a portable robot that could draw on the blackboard for teachers. The robot was given an image of Mona Lisa and, after going through an algorithm, it drew that image on the blackboard. “That was the first small success in my robotics career,” says Bauza.
After graduating with her bachelor’s degree in 2016, she joined the Manipulation and Mechanisms Laboratory at MIT (known as MCube Lab) under Assistant Professor Alberto Rodriguez’s guidance. “Maria brings together experience in machine learning and a strong background in mathematics, computer science, and mechanics, which makes her a great candidate to grow into a leader in the fields of machine learning and robotics,” says Rodriguez.
For her PhD thesis, Bauza is developing machine-learning algorithms and software to improve how robots interact with the world. MCube’s multidisciplinary team provides the support needed to pursue this goal.
“In the end, machine learning can’t work if you don’t have good data,” Bauza explains. “Good data comes from good hardware, good sensors, good cameras — so in MCube we all collaborate to make sure the systems we build are powerful enough to be autonomous.”
To create these robust autonomous systems, Bauza has been exploring the notion of uncertainty when robots pick up, grasp, or push an object. “If the robot could touch the object, have a notion of tactile information, and be able to react to that information, it will have much more success,” explains Bauza.
Improving how robots interact with the world and reason to find the best possible outcome was crucial to the Amazon Robotics Challenge. Bauza built the code that helped the MIT-Princeton Team robot understand what object it was interacting with, and where to place that object. “Maria was in charge of developing the software for high-level decision making,” explains Rodriguez. “She did it without having prior experience in big robotic systems and it worked out fantastic.”
Bauza’s mind was at ease within a few minutes of 2017 Amazon Robotics Challenge. “After a few objects that you do well, you start to relax,” she remembers. “You realize the system is working. By the end it was such a good feeling!”
Bauza and the rest of the MCube team walked away with first place in the “stow task” portion of the challenge. They will continue to work with Amazon on perfecting the technology they developed.
While Bauza tackles the challenge of developing software to help robots interact with their environments, she has her own personal challenge to tackle: surviving winter in Boston. “I’m from the island of Menorca off the coast of Spain, so Boston winters have definitely been an adjustment,” she adds. “Every year I buy warmer clothes. But I’m really lucky to be here and be able to collaborate with Professor Rodriguez and the MCube team on developing smart robots that interact with their environment.”




