
Robohub.org
Exploring ROS2 with a wheeled robot – #4 – Obstacle avoidance
By Marco Arruda
In this post you’ll learn how to program a robot to avoid obstacles using ROS2 and C++. Up to the end of the post, the Dolly robot moves autonomously in a scene with many obstacles, simulated using Gazebo 11.
You’ll learn:
- How to publish AND subscribe topics in the same ROS2 Node
- How to avoid obstacles
- How to implement your own algorithm in ROS2 and C++
1 – Setup environment – Launch simulation
Before anything else, make sure you have the rosject from the previous post, you can copy it from here.
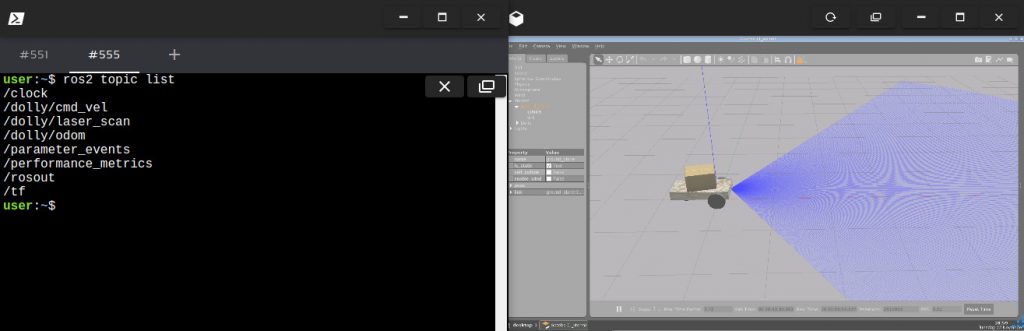
Launch the simulation in one webshell and in a different tab, checkout the topics we have available. You must get something similar to the image below:
2 – Create the node
In order to have our obstacle avoidance algorithm, let’s create a new executable in the file ~/ros2_ws/src/my_package/obstacle_avoidance.cpp:
#include "geometry_msgs/msg/twist.hpp" // Twist
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp" // ROS Core Libraries
#include "sensor_msgs/msg/laser_scan.hpp" // Laser Scan
using std::placeholders::_1;
class ObstacleAvoidance : public rclcpp::Node {
public:
ObstacleAvoidance() : Node("ObstacleAvoidance") {
auto default_qos = rclcpp::QoS(rclcpp::SystemDefaultsQoS());
subscription_ = this->create_subscription(
"laser_scan", default_qos,
std::bind(&ObstacleAvoidance::topic_callback, this, _1));
publisher_ =
this->create_publisher("cmd_vel", 10);
}
private:
void topic_callback(const sensor_msgs::msg::LaserScan::SharedPtr _msg) {
// 200 readings, from right to left, from -57 to 57 degress
// calculate new velocity cmd
float min = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) { float current = _msg->ranges[i];
if (current < min) { min = current; } }
auto message = this->calculateVelMsg(min);
publisher_->publish(message);
}
geometry_msgs::msg::Twist calculateVelMsg(float distance) {
auto msg = geometry_msgs::msg::Twist();
// logic
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Distance is: '%f'", distance);
if (distance < 1) {
// turn around
msg.linear.x = 0;
msg.angular.z = 0.3;
} else {
// go straight ahead
msg.linear.x = 0.3;
msg.angular.z = 0;
}
return msg;
}
rclcpp::Publisher::SharedPtr publisher_;
rclcpp::Subscription::SharedPtr subscription_;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
rclcpp::spin(std::make_shared());
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}
In the main function we have:
- Initialize node rclcpp::init
- Keep it running rclcpp::spin
Inside the class constructor:
- Subcribe to the laser scan messages: subscription_
- Publish to the robot diff driver: publisher_
The obstacle avoidance intelligence goes inside the method calculateVelMsg. This is where decisions are made based on the laser readings. Notice that is depends purely on the minimum distance read from the message.
If you want to customize it, for example, consider only the readings in front of the robot, or even check if it is better to turn left or right, this is the place you need to work on! Remember to adjust the parameters, because the way it is, only the minimum value comes to this method.
3 – Compile the node
This executable depends on both geometry_msgs and sensor_msgs, that we have added in the two previous posts of this series. Make sure you have them at the beginning of the ~/ros2_ws/src/my_package/CMakeLists.txt file:
# find dependencies find_package(ament_cmake REQUIRED) find_package(rclcpp REQUIRED) find_package(geometry_msgs REQUIRED) find_package(sensor_msgs REQUIRED)
And finally, add the executable and install it:
# obstacle avoidance
add_executable(obstacle_avoidance src/obstacle_avoidance.cpp)
ament_target_dependencies(obstacle_avoidance rclcpp sensor_msgs geometry_msgs)
...
install(TARGETS
reading_laser
moving_robot
obstacle_avoidance
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME}/
)
Compile the package:
colcon build --symlink-install --packages-select my_package
4 – Run the node
In order to run, use the following command:
ros2 run my_package obstacle_avoidance
It will not work for this robot! Why is that? We are subscribing and publishing to generic topics: cmd_vel and laser_scan.
We need a launch file to remap these topics, let’s create one at ~/ros2_ws/src/my_package/launch/obstacle_avoidance.launch.py:
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch_ros.actions import Node
def generate_launch_description():
obstacle_avoidance = Node(
package='my_package',
executable='obstacle_avoidance',
output='screen',
remappings=[
('laser_scan', '/dolly/laser_scan'),
('cmd_vel', '/dolly/cmd_vel'),
]
)
return LaunchDescription([obstacle_avoidance])
Recompile the package, source the workspace once more and launch it:
colcon build --symlink-install --packages-select my_package
source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
ros2 launch my_package obstacle_avoidance.launch.py

Related courses & extra links:
The post Exploring ROS2 with a wheeled robot – #4 – Obstacle Avoidance appeared first on The Construct.



