
Robohub.org
Grasping with robots – which object is in reach?
This post is part of our ongoing efforts to make the latest papers in robotics accessible to a general audience.
Imagine a robot reaching for a mug on the table, only to realize that it is too far, or that it would need to bend its arm joint backwards to get there. Understanding which objects are within reach and how to grasp them is an essential requirement if robots are to operate in our everyday environments. To solve this problem, a recent Autonomous Robots paper by Vahrenkamp et al. proposes a new approach to build a comprehensive representation of the capabilities of a robot related to reaching and grasping.
The “manipulability” representation shown below allows the robot to know where it can reach in 6D with its right arm. That means it knows which x,y,z positions it can reach, as well as the orientation of the robot hand that is best for manipulation. The representation takes into account constraints due to joints in the arm. The manipulability is encoded by color (blue: low, red: high).
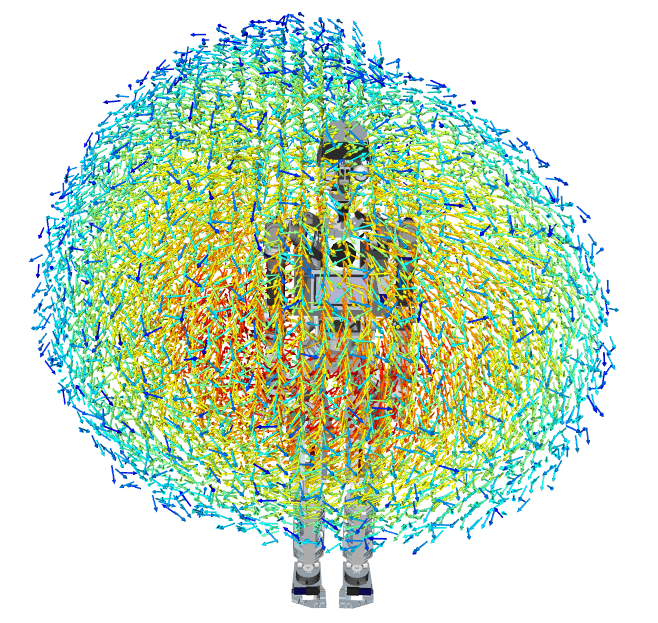
A cut through one of these vector clouds looks like this.
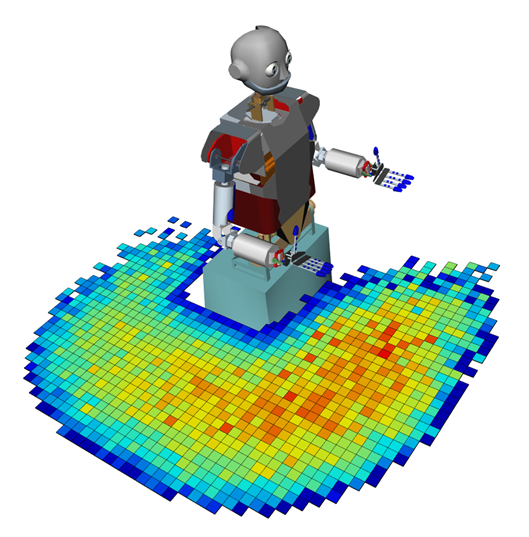
In addition to single handed grasping, the authors discuss how the approach can be extended to grasping with two arms. Experiments were run in simulation on the humanoid robots ARMAR-III and ARMAR-IV.
And in case you want to try this at home, there is an open source version of this work here.
For more information, you can read the paper Representing the robot’s workspace through constrained manipulability analysis (Nikolaus Vahrenkamp and Tamim Asfour, Autonomous Robots – Springer US, July 2014) or ask questions below!
tags: c-Research-Innovation





