
Robohub.org
Autonomous robot evolution: from cradle to grave
A few weeks ago we had the kick-off meeting, in York, of our new 4 year EPSRC funded project Autonomous Robot Evolution (ARE): cradle to grave. We – Andy Tyrrell and Jon Timmis (York), Emma Hart (Edinburgh Napier), Gusti Eiben (Free University of Amsterdam) and myself – are all super excited. We’ve been trying to win support for this project for five years or so, and only now succeeded. This is a project that we’ve been thinking, and writing about, for a long time – so to have the opportunity to try out our ideas for real is wonderful.
In ARE we aim to investigate the artificial evolution of robots for unknown or extreme environments. In a radical new approach we will co-evolve robot bodies and brains in real-time and real-space. Using techniques from 3D printing new robot designs will literally be printed, before being trained in a nursery, then fitness tested in a target environment (a mock nuclear plant). The genomes of the fittest robots will then be combined to create the next generation of ‘child’ robots, so that – over successive generations – we will breed new robot designs in a process that mirrors the way farmers have artificially selected new varieties of plants and animals for thousands of years. Because evolving real robots is slow and resource hungry we will run a parallel process of simulated evolution in a virtual environment, in which the real world environment is used to calibrate the virtual world, and reduce the reality gap*. A hybrid real-virtual process under the control of an ecosystem manager will allow real and virtual robots to mate, and the child robots to be printed and tested in either the virtual or real environments.
The project will be divided into five work packages, each led by a different partner: WP1 Evolution (York), WP2 Physical Environment (UWE), WP3 Virtual Environment (York), WP4 Ecosystem Manager (Napier) and WP5 Integration and Demonstration (UWE).
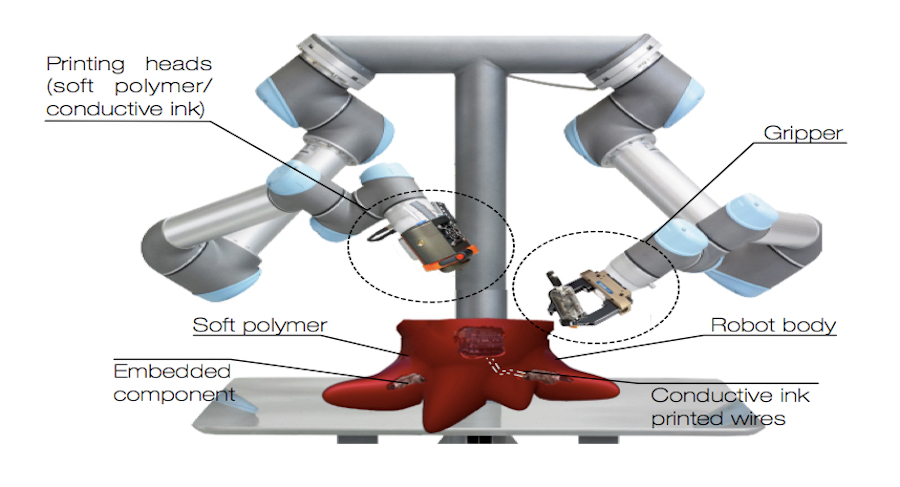
Here in the Bristol Robotics Lab we will focus on work packages 2 and 5. The goal of WP 2 is the development of a purpose designed 3D printing system – which we call a birth clinic – capable of printing small mobile robots, according to a specification determined by a genome designed in WP1. The birth clinic will need to pick and place a number of pre designed and fabricated electronics, sensing and actuation modules (the robot’s ‘organs’) into the printing work area which will be over printed with hot plastic to form the complete robot. The goal of WP5 will be to integrate all components, including the real world birth clinic, nursery, and mock nuclear environment with the virtual environment (WP3) and the ecosystem manager (WP4) into a working demonstrator and undertake evaluation and analysis.
You can see an impression of what the birth clinic might look like above.
One of the most interesting aspects of the project is that we have no idea what the robots we breed will look like. The evolutionary process could come up with almost any body shape and structure (morphology). The same process will also determine which and how many organs (sensors, actuators, etc) are selected, and their positions and orientation within the body. Our evolved robot bodies could be very surprising indeed.
And who knows – maybe we can take a step towards Walterian Creatures?
*Anyone who uses simulation as a tool to develop robots is well aware that robots which appear to work perfectly well in a simulated virtual world often don’t work very well at all when the same design is tested in the real robot. This problem is especially acute when we are artificially evolving those robots. The reason for these problems is that the model of the real world and the robot(s) in it inside our simulation is an approximation. The Reality Gap refers to the less-than-perfect fidelity of the simulation; a better (higher fidelity) simulator would reduce the reality gap.
Related materials:
Article in de Volkskrant (in Dutch) De robotevolutie kan beginnen. Hoe? Moeder Natuur vervangen door virtuele kraamkamer (The robot evolution can begin. How? Replacing Mother Nature with virtual nursery), May 2018.
Eiben and Smith (2015) From evolutionary computing to the evolution of things, Nature.
Winfield and Timmis (2015) Evolvable Robot Hardware, in Evolvable Hardware, Springer.
Eiben et al. (2013) The Triangle of Life, European Conference on Artificial Life (ECAL 2013).





