Robohub.org
Hello Pepper: Getting started to program robots on Android
I didn’t get to meet Pepper the humanoid Robot at Google I/O but I watched the video afterwards: A new development frontier: Android + Pepper the interactive robot. Love the robots’ dance! I was super excited to hear that Pepper will become available in the U.S. later this year, and Android developers can now program robots!
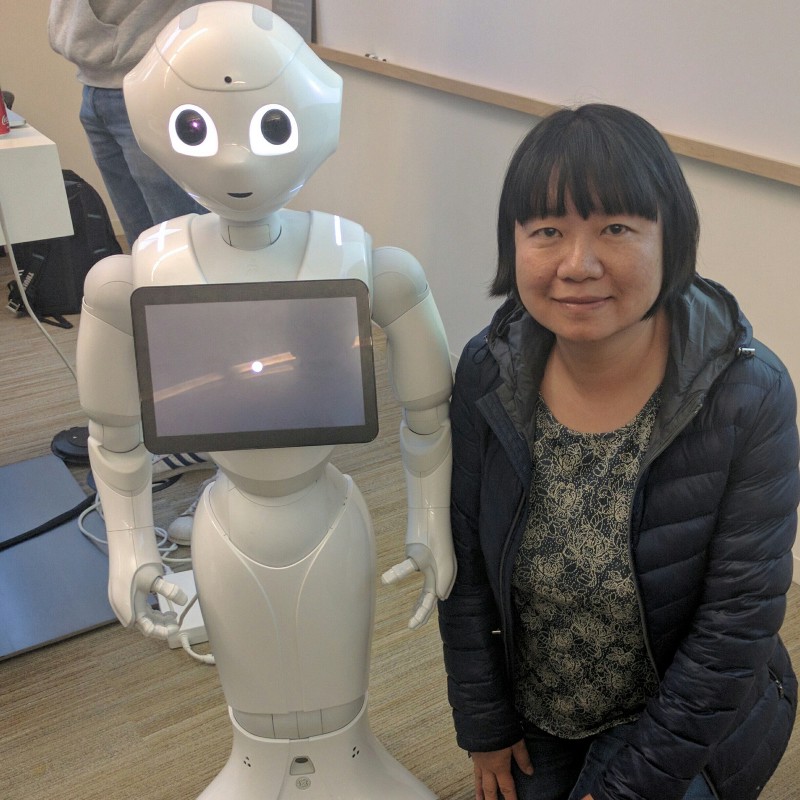
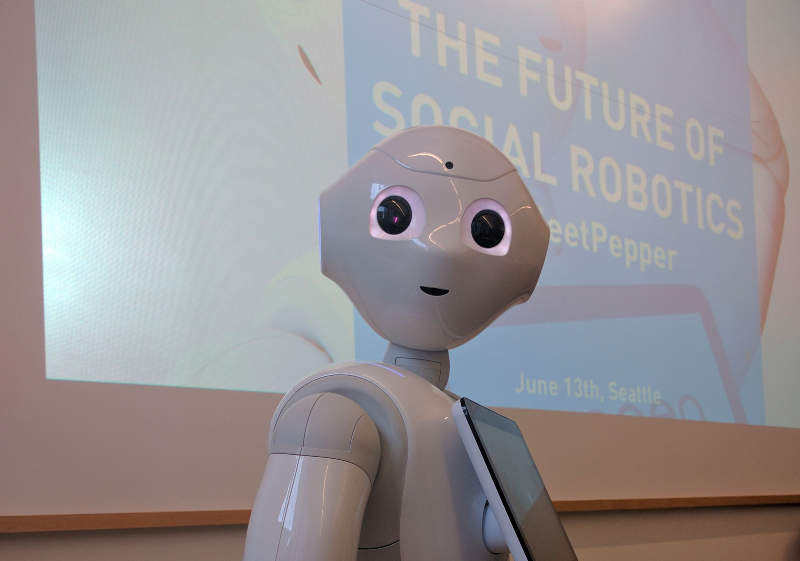
A few weeks after I/O, I attended a Seattle Java User Group meetup. That evening I met Pepper in person, and I learned about the Future of Social Robotics from Nicolas Rigaud (slides here).
Equipped with microphones, cameras, sensors and an intelligence to perceive emotions, Pepper was designed for social interactions. He has an Android tablet on his chest which is very convenient for displaying image, video and texts. Pepper is 4 feet tall (1.2 meters) and can connect to the network with either Wi-Fi or Ethernet. Pepper is multi-lingual in English, French, Japanese and Chinese.
I wanted to learn more about Pepper. So I followed the instructions from the Pepper SDK for Android and was able to quickly get set up and create my first robot Application with Android Studio.
Since I already have Android Studio installed, all I had to do was to install the Pepper SDK plugin before creating my first “Hello World” robot application. You can follow the official Getting Started guide for detailed instructions, and here I’m sharing with you a brief summary of the steps I took (note I already had JDK and Android Studio installed):
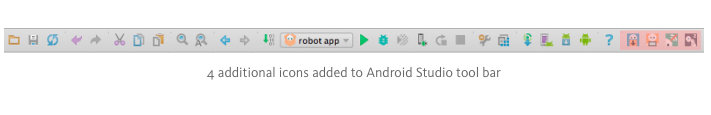
- In Android Studio, install the Pepper SDK plugin; then the Robot SDK Manager icon appears on the Android Studio main tool bar
- Click the Robot SDK Manager icon to get the Robot SDK and tools
- Creating my first robot application
- First create a regular Android application with minSDK = API 22 Android 5.1 Lollipop.
- Then click File > New > Robot Application. Then notice these changes:
These two robot development related icons in Android Studio become enabled: Emulator and Connect/Disconnect. The 4th icon Wakeup is still grayed out since I don’t have a real robot to connect to.
The Android project structure gets updated to the Robot Project Structure. Dependencies are automatically added in build.gradle file:
compile 'com.aldebaran:libqi-java-android:sdk-2016-05-16' compile 'com.aldebaran:qisdk:0.7' compile 'com.aldebaran:qichatplayer:1.0.1'
- I set CPU/ABI as x86 and checked “Use Host GPU” under Run/Debug Configuration/AVD option. Make sure to launch the emulator by clicking on the Robot Emulator icon, instead of using a virtual device from the Android Studio AVD Manager.
- When the Robot emulator launches, the Robot Viewer also gets launched.
Without an actual robot I was still able to follow the first 3 of the tutorials: Say “Hello, world!”, Go to one meter forward and Mimic the elephant.
I will share more as I continue to learn about Pepper. Hopefully in the near future, we all can make apps that work with Pepper the humanoid robot.
tags: c-Education-DIY, Pepper