
Robohub.org
Machine-learning method used for self-driving cars could improve lives of type-1 diabetes patients
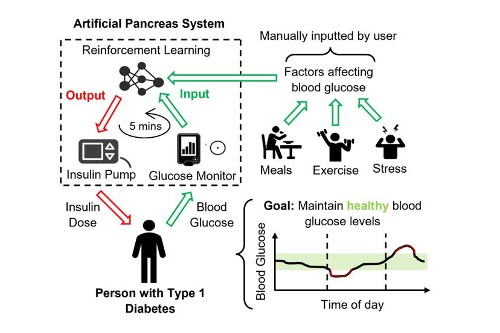
Artificial Pancreas System with Reinforcement Learning. Image credit: Harry Emerson
Scientists at the University of Bristol have shown that reinforcement learning, a type of machine learning in which a computer program learns to make decisions by trying different actions, significantly outperforms commercial blood glucose controllers in terms of safety and effectiveness. By using offline reinforcement learning, where the algorithm learns from patient records, the researchers improve on prior work, showing that good blood glucose control can be achieved by learning from the decisions of the patient rather than by trial and error.
Type 1 diabetes is one of the most prevalent auto-immune conditions in the UK and is characterised by an insufficiency of the hormone insulin, which is responsible for blood glucose regulation.
Many factors affect a person’s blood glucose and therefore it can be a challenging and burdensome task to select the correct insulin dose for a given scenario. Current artificial pancreas devices provide automated insulin dosing but are limited by their simplistic decision-making algorithms.
However a new study, published in the Journal of Biomedical Informatics, shows offline reinforcement learning could represent an important milestone of care for people living with the condition. The largest improvement was in children, who experienced an additional one-and-a-half hours in the target glucose range per day.
Children represent a particularly important group as they are often unable to manage their diabetes without assistance and an improvement of this size would result in markedly better long-term health outcomes.
Lead author Harry Emerson from Bristol’s Department of Engineering Mathematics, explained: “My research explores whether reinforcement learning could be used to develop safer and more effective insulin dosing strategies.
“These machine learning driven algorithms have demonstrated superhuman performance in playing chess and piloting self-driving cars, and therefore could feasibly learn to perform highly personalised insulin dosing from pre-collected blood glucose data.
“This particular piece of work focuses specifically on offline reinforcement learning, in which the algorithm learns to act by observing examples of good and bad blood glucose control.
“Prior reinforcement learning methods in this area predominantly utilise a process of trial-and-error to identify good actions, which could expose a real-world patient to unsafe insulin doses.”
Due to the high risk associated with incorrect insulin dosing, experiments were performed using the FDA-approved UVA/Padova simulator, which creates a suite of virtual patients to test type 1 diabetes control algorithms. State-of-the-art offline reinforcement learning algorithms were evaluated against one of the most widely used artificial pancreas control algorithms. This comparison was conducted across 30 virtual patients (adults, adolescents and children) and considered 7,000 days of data, with performance being evaluated in accordance with current clinical guidelines. The simulator was also extended to consider realistic implementation challenges, such as measurement errors, incorrect patient information and limited quantities of available data.
This work provides a basis for continued reinforcement learning research in glucose control; demonstrating the potential of the approach to improve the health outcomes of people with type 1 diabetes, while highlighting the method’s shortcomings and areas of necessary future development.
The researchers’ ultimate goal is to deploy reinforcement learning in real-world artificial pancreas systems. These devices operate with limited patient oversight and consequently will require significant evidence of safety and effectiveness to achieve regulatory approval.
Harry added: ”This research demonstrates machine learning’s potential to learn effective insulin dosing strategies from the pre-collected type 1 diabetes data. The explored method outperforms one of the most widely used commercial artificial pancreas algorithms and demonstrates an ability to leverage a person’s habits and schedule to respond more quickly to dangerous events.”





