
Robohub.org
Next-generation cockroach-inspired robot is small but mighty
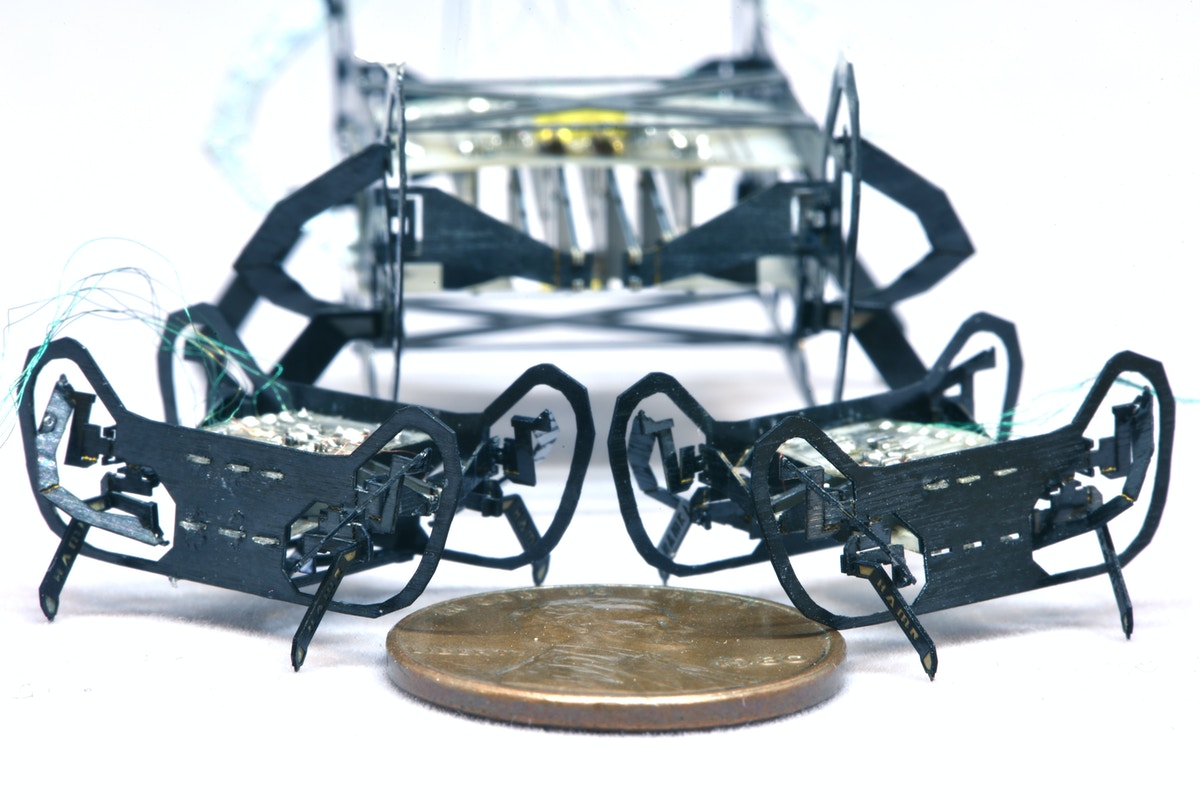
The newly designed HAMR-Jr alongside its predecessor, HAMR-VI. HAMR-Jr is only slightly bigger in length and width than a penny, making it one of the smallest yet highly capable, high-speed insect-scale robots. Credit: Kaushik Jayaram/Harvard SEAS
By Leah Burrows
This itsy-bitsy robot can’t climb up the waterspout yet but it can run, jump, carry heavy payloads and turn on a dime. Dubbed HAMR-JR, this microrobot developed by researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) and Harvard’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering, is a half-scale version of the cockroach-inspired Harvard Ambulatory Microrobot or HAMR.
About the size of a penny, HAMR-JR can perform almost all of the feats of its larger-scale predecessor, making it one of the most dexterous microrobots to date.
“Most robots at this scale are pretty simple and only demonstrate basic mobility,” said Kaushik Jayaram, Ph.D., a former postdoctoral fellow at SEAS and the Wyss Institute, and first author of the paper. “We have shown that you don’t have to compromise dexterity or control for size.”
Jayaram is currently an Assistant Professor at the University of Colorado, Boulder.
The research was presented virtually at the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2020) this week.
One of the big questions going into this research was whether or not the pop-up manufacturing process used to build previous versions of HAMR and other microbots, including the RoboBee, could be used to build robots at multiple scales — from tiny surgical bots to large-scale industrial robots.
PC-MEMS (short for printed circuit microelectromechanical systems) is a fabrication process in which the robot’s components are etched into a 2D sheet and then popped out in its 3D structure. To build HAMR-JR, the researchers simply shrunk the 2D sheet design of the robot — along with the actuators and onboard circuitry — to recreate a smaller robot with all the same functionalities.
“The wonderful part about this exercise is that we did not have to change anything about the previous design,” said Jayaram. “We proved that this process can be applied to basically any device at a variety of sizes.”

HAMR-JR comes in at 2.25 centimeters in body length and weighs about 0.3 grams — a fraction of the weight of an actual penny. It can run about 14 body lengths per second, making it not only one of the smallest but also one of the fastest microrobots.
Scaling down does change some of the principles governing things like stride length and joint stiffness, so the researchers also developed a model that can predict locomotion metrics like running speeds, foot forces, and payload based on a target size. The model can then be used to design a system with the required specifications.
“This new robot demonstrates that we have a good grasp on the theoretical and practical aspects of scaling down complex robots using our folding-based assembly approach,” said co-author Robert Wood, Ph.D., Charles River Professor of Engineering and Applied Sciences in SEAS and Core Faculty Member of the Wyss Institute.
This research was co-authored by Jennifer Shum, Samantha Castellanos and E. Farrell Helbling, Ph.D. This research was supported by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) and the Wyss Institute.
- WYSS TECHNOLOGY: HAMR: Versatile Crawling Microrobot
- PUBLICATION – IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation 2020: Scaling down an insect-size microrobot, HAMR-VI into HAMR-Jr





