
Robohub.org
Pangolin the inspiration for medical robot

Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems in Stuttgart have developed a magnetically controlled soft medical robot with a unique, flexible structure inspired by the body of a pangolin. The robot is freely movable despite built-in hard metal components. Thus, depending on the magnetic field, it can adapt its shape to be able to move and can emit heat when needed, allowing for functionalities such as selective cargo transportation and release as well as mitigation of bleeding.
Pangolins are fascinating creatures. This animal looks like a walking pine cone, as it is the only mammal completely covered with hard scales. The scales are made of keratin, just like our hair and nails. The scales overlap and are directly connected to the underlying soft skin layer. This special arrangement allows the animals to curl up into a ball in case of danger.
While pangolins have many other unique features, researchers from the Physical Intelligence Department at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems in Stuttgart, which is led by Prof. Dr. Metin Sitti, were particularly fascinated by how pangolins can curl up their scale-covered bodies in a flash. They took the animal as a model and developed a flexible robot made of soft and hard components that, just like the animal, become a sphere in the blink of an eye – with the additional feature that the robot can emit heat when needed.
In a research paper published in Nature Communications, first author Ren Hao Soon and his colleagues present a robot design that is no more than two centimeters long and consists of two layers: a soft layer made of a polymer studded with small magnetic particles and a hard component made of metal elements arranged in overlapping layers. Thus, although the robot is made of solid metal components, it is still soft and flexible for use inside the human body.
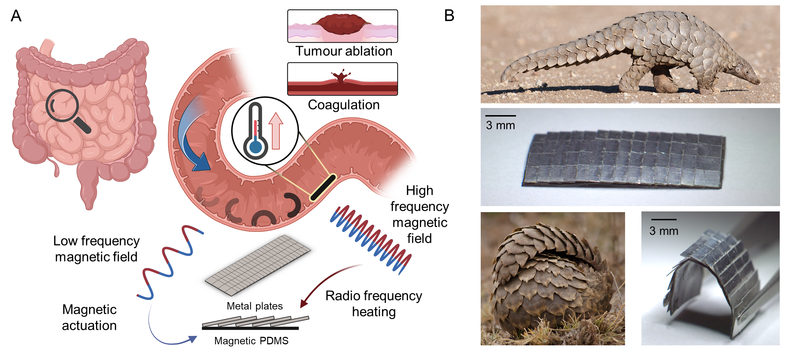
Fig. 1 shows the pangolin-inspired untethered magnetic robot. A Conceptual illustration of the pangolin-inspired robot operating in the small intestine. Robot is actuated with a low-frequency magnetic field and heated remotely with a high-frequency magnetic field. The pangolin’s body consist of individual overlapping hard keratin scales. The robot inspired by this overlapping design is shown on the right. Images of pangolins used under Standard licence from Shutterstock.
When the robot is exposed to a low-frequency magnetic field, the researchers can roll up the robot and move it back and forth as they wish. The metal elements stick out like the animal’s scales, without hurting any surrounding tissue. Once it is rolled up, the robot can transport particles such as medicines. The vision is that such a small machine will one day travel through our digestive system, for example.
Double useful: freely movable and hot
When the robot is exposed to a high-frequency magnetic field, it heats up to over 70oC thanks to the built-in metal. Thermal energy is used in several medical procedures, such as treating thrombosis, stopping bleeding and removing tumor tissue. Untethered robots that can move freely, even though they are made of hard elements such as metal and can also emit heat, are rare. The pangolin robot is therefore considered promising for modern medicine. It could one day reach even the narrowest and most sensitive regions in the body in a minimally invasive and gentle way and emit heat as needed. That is a vision of the future. Already today, in a video, the researchers are showing how they can flexibly steer the robot through animal tissue and artificial organs.




