
Robohub.org
Robot fish makes splash with motion breakthrough
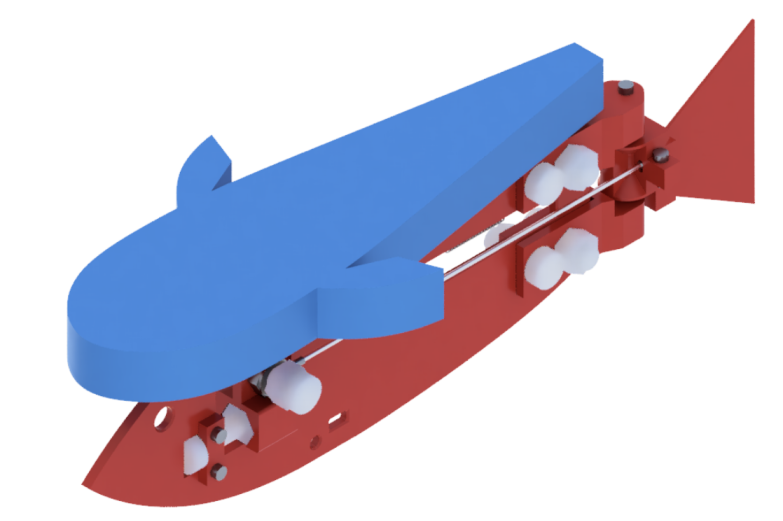
Robot fish. Image credit: Tsam Lung You
The robot fish was fitted with a twisted and coiled polymer (TCP) to drive it forward, a light-weight low cost device that relies on temperature change to generate movement, which also limits its speed.
A TCP works by contracting like muscles when heated, converting the energy into mechanical motion. The TCP used in this work is warmed by Joule heating – the pass of current through an electrical conductor produces thermal energy and heats up the conductor. By minimising the distance between the TCP on one side of the robot fish and the spring on the other, this activates the fin at the rear, enabling the robot fish to reach new speeds. The undulating flapping of its rear fin was measured at a frequency of 2Hz, two waves per second. The frequency of the electric current is the same as the frequency of tail flap.
The findings, published at the 6th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft 2023), provide a new route to raising the actuation – the action of causing a machine or device to operate – frequency of TCPs through thermomechanical design and shows the possibility of using TCPs at high frequency in aqueous environments.
Lead author Tsam Lung You from Bristol’s Department of Engineering Mathematics said: “Twisted and coiled polymer (TCP) actuator is a promising novel actuator, exhibiting attractive properties of light weight, low-cost high energy density and simple fabrication process.
“They can be made from very easily assessable materials such as a fishing line and they contract and provide linear actuation when heated up. However, because of the time needed for heat dissipation during the relaxation phase, this makes them slow.”
By optimising the structural design of the TCP-spring antagonistic muscle pair and bringing their anchor points closer together, it allowed the posterior fin to swing at a larger angle for the same amount of TCP actuation.
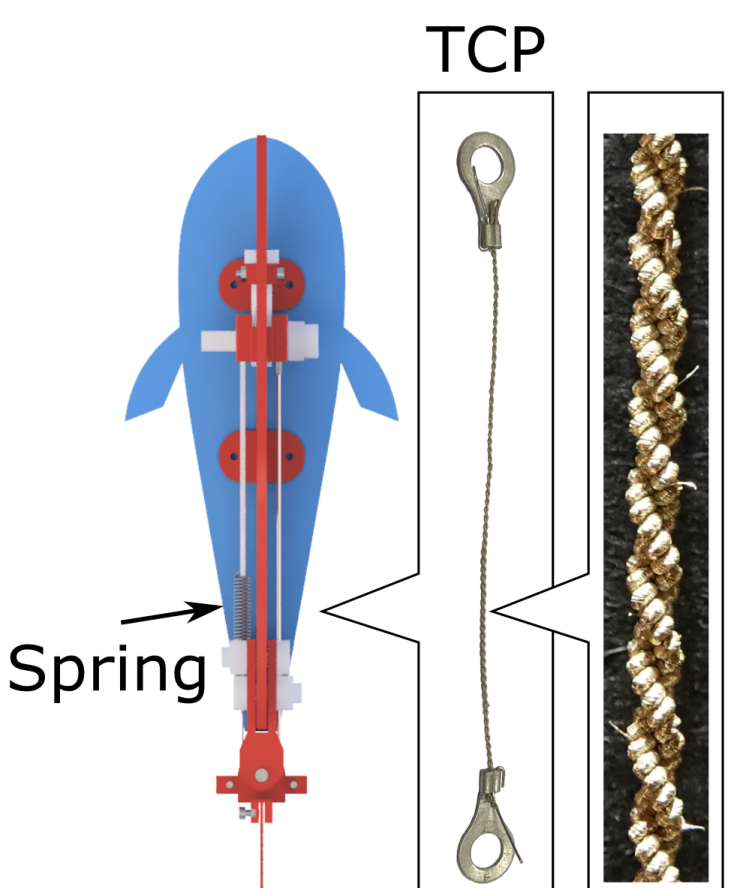
Antagonistic muscles. Image credit: Tsam Lung You
Although this requires greater force, TCP is a strong actuator with high work energy density, and is still able to drive the fin.
Until now, TCPs have been mostly used for applications such as wearable devices and robotic hands. This work opens up more areas of application where TCP can be used, such as marine robots for underwater exploration and monitoring.
Tsam Lung You added: “Our robotic fish swam at the fastest actuation frequency found in a real TCP application and also the highest locomotion speed of a TCP application so far.
“This is really exciting as it opens up more opportunities of TCP application in different areas.”
The team now plan to expand the scale and develop a knifefish-inspired TCP-driven ribbon fin robot that can swim agilely in water.





