
Robohub.org
The Year of CoCoRo Video #30/52: Combined scenario number one
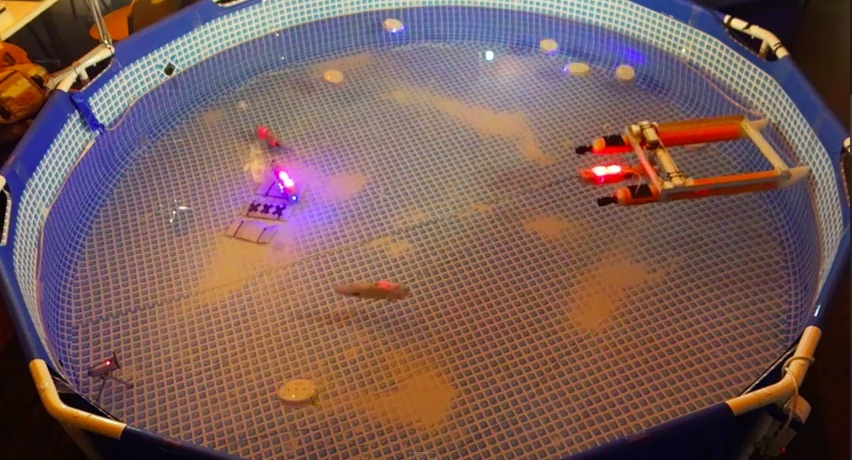 The EU-funded Collective Cognitive Robotics (CoCoRo) project has built a swarm of 41 autonomous underwater vehicles (AVs) that show collective cognition. Throughout 2015 – The Year of CoCoRo – we’ll be uploading a new weekly video detailing the latest stage in its development. This week there are two videos. The first shows a computer animation of our “combined scenario #1.” The second shows how this scenario was performed by real robots in the water.
The EU-funded Collective Cognitive Robotics (CoCoRo) project has built a swarm of 41 autonomous underwater vehicles (AVs) that show collective cognition. Throughout 2015 – The Year of CoCoRo – we’ll be uploading a new weekly video detailing the latest stage in its development. This week there are two videos. The first shows a computer animation of our “combined scenario #1.” The second shows how this scenario was performed by real robots in the water.
In CoCoRo, the search for a sunken metallic object on the waterbed was dealt with in several scenarios. The first video is a computer animation illustrating the phases of the most complex, “scenario #1:”
- The base station at the water surface moves into the habitat, with docked Jeff robots and a swarm of Lily robots confined to it.
- The Jeff robots are released. They sink to the ground and search the habitat.
- As soon as the first Jeff robot has found the target, it recruits other Jeff robots to the location via blue-light LED signals, leading to a positive feedback loop that attracts more and more Jeff robots to the area.
- Meanwhile, the Lily robots build a chain that connects the surface station to the aggregated Jeff robots on the ground.
- Through this “relay chain,” information (blink signals or other data) can be sent from the ground swarm to the surface station (and human operators) and vice versa.
Scenario #1 combines many of the individual algorithms and functionalities shown in previous videos in “The Year of CoCoRo.”
The second video shows how this scenario was performed by real robots in the water. It is noteworthy that all the phases in the scenario were executed in one single run and not split into different experiments. It was important for us to demonstrate that, using the modular algorithmic design of CoCoRo, it is possible to build up complex behavioral programs to solve composite tasks.
To date, in bio-inspired and swarm robotics, there have either been simple algorithms to enable robots to perform basic tasks or complex scenarios achieved by very complicated and specifically written software. To our knowledge, this is the first time in swarm robotics that several very simple signal exchange patterns and behavioral responses, triggered by simple signals within the environment, are combined with an elementary piece of code that allows the robot swarm to perform a very sophisticated behavioral program. There is no recourse to global knowledge, mapping, ego-positioning, image tracking or computer vision within this autonomous swarm. There are only: a few blue-light blinks, photoreceptors to receive these, random-walk programs, communication-free shoaling-behavior for the relay chain, radio-frequency pulsing and a simple internal-robot compass. This is how swarm robotics should be: simple, robust, flexible, scalable and – most importantly – it works!
tags: AUV, c-Research-Innovation, CoCoRo, EU, EU robotics industry news, Swarming, UAV, underwater video




