Robohub.org
Using 3D snapshots to control a small helicopter
 In the latest article in the Autonomous Robots journal, researchers from the Australian Defense Force Academy present a new control strategy for small flying robots that uses only vision and inertial sensors.
In the latest article in the Autonomous Robots journal, researchers from the Australian Defense Force Academy present a new control strategy for small flying robots that uses only vision and inertial sensors.
To control a flying robot, you usually need to know the attitude of the robot (roll, pitch, yaw), where it is in the horizontal plane (x,y), and how high it is from the ground (z). While attitude measurements are provided by inertial sensors on board the robot, most flying robots rely on GPS and additional range sensors such as ultra-sound sensors, lasers or radars to determine their position and altitude. GPS signal however is not always available in cluttered environments and can be jammed. Additional sensors increase the weight that needs to be carried by the robot. Instead Garratt et al. propose to replace position sensors with a single small, low cost camera.
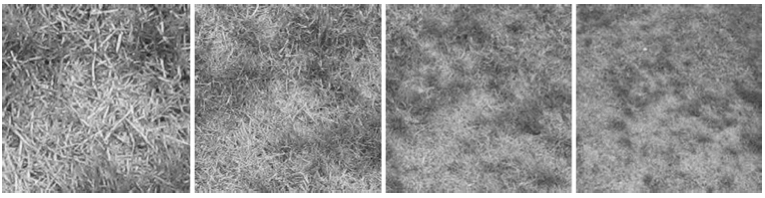
By comparing a snapshot taken from a downward pointing camera and a reference snapshot taken at an earlier time, the robot is able to calculate its displacement in the horizontal plane. The loom of the image is used to calculate the change in altitude. Image loom corresponds to image expansion or contraction as can be seen in the images below. By reacting to these image displacements, the robot is able to control its position.
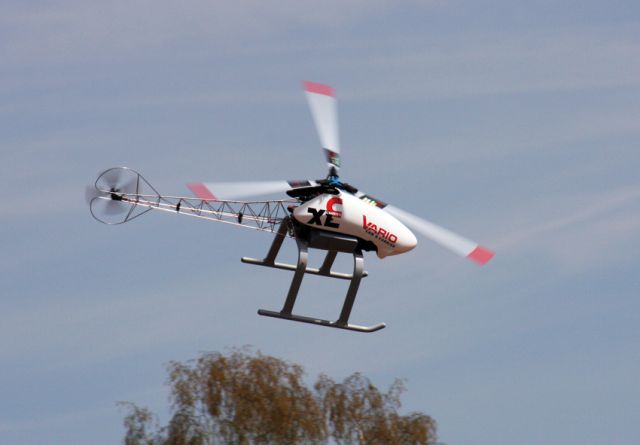
Using this strategy, the researchers were able to show in simulation that a helicopter could perform take-off, hover and the transition from low speed forward flight to hover. The ability to track horizontal and vertical displacements using 3D snapshots from a single camera was then confirmed in reality using a Vario XLC gas-turbine helicopter.
In the future, the authors intend to further test the 3D snapshot control strategy in flight using their Vario XLC helicopter before moving to smaller platforms such as an Asctec Pelican quadrotor. Additional challenges include taking into account the shadow of the robot, which might change position from snapshot to snapshot.