
Robohub.org
Using geometry to help robots map their environment
This post is part of our ongoing efforts to make the latest papers in robotics accessible to a general audience.
To get around unknown environments, most robots will need to build maps. To help them do so, robots can use the fact that human environments are often made of geometric shapes like circles, rectangles and lines. The latest paper in Autonomous Robots presents a flexible framework for geometrical robotic mapping in structured environments.
Most human designed environments, such as buildings, present regular geometrical properties that can be preserved in the maps that robots build and use. If some information about the general layout of the environment is available, it can be used to build more meaningful models and significantly improve the accuracy of the resulting maps. Human cognition exploits domain knowledge to a large extent, usually employing prior assumptions for the interpretation of situations and environments. When we see a wall, for example, we assume that it’s straight. We’ll probably also assume that it’s connected to another orthogonal wall.
This research presents a novel framework for the inference and incorporation of knowledge about the structure of the environment into the robotic mapping process. A hierarchical representation of geometrical elements (features) and relations between them (constraints) provides enhanced flexibility, also making it possible to correct wrong hypotheses. Various features and constraints are available, and it is very easy to add even more.
A variety of experiments with both synthetic and real data were conducted. The map below was generated from data measured by a robot navigating Killian Court at MIT using a laser scanner, and allows the geometrical properties of the environment to be well respected. You can easily tell that features are parallel, orthogonal and straight where needed.
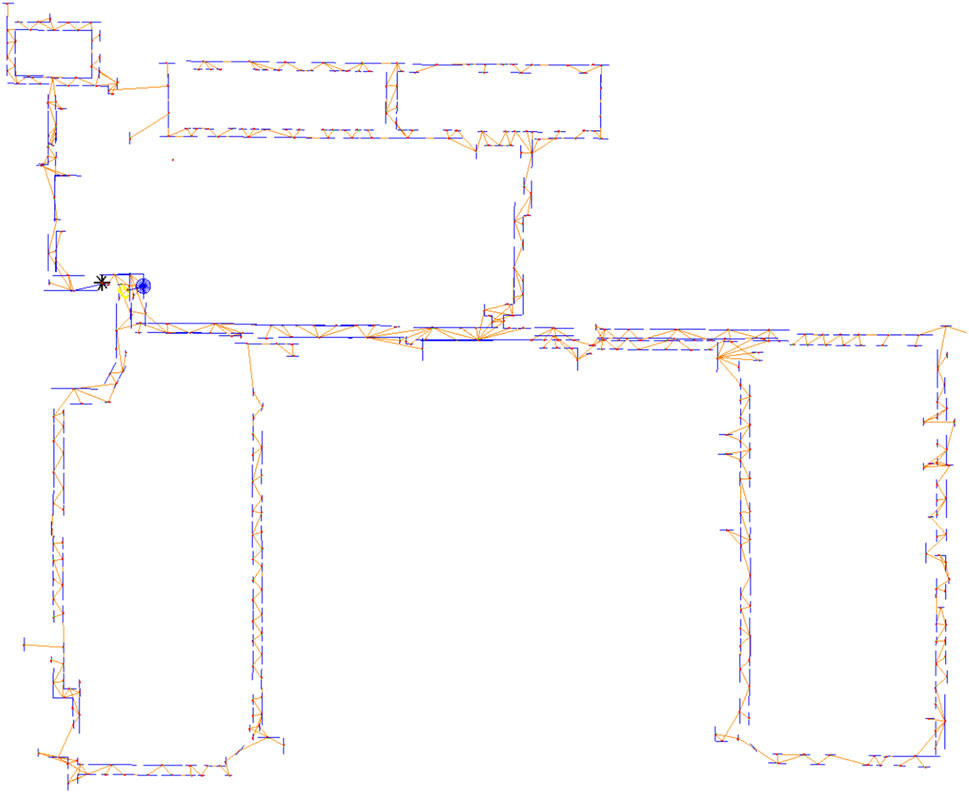
For more information, you can read the paper Feature based graph-SLAM in structured environments ( P. de la Puente and D. Rodriguez-Losada , Autonomous Robots – Springer US, Feb 2014) or ask questions below!
tags: c-Research-Innovation, Mapping-Surveillance




