
Robohub.org
Why it’s difficult to trust robots

Robots raise all kinds of concerns. They could steal our jobs, as some experts think. And if artificial intelligence grows, it might even be tempted to enslave us, or to annihilate the whole of humanity. Robots are strange creatures, and not only for these frequently invoked reasons. We have good cause to be a little worried about these machines.
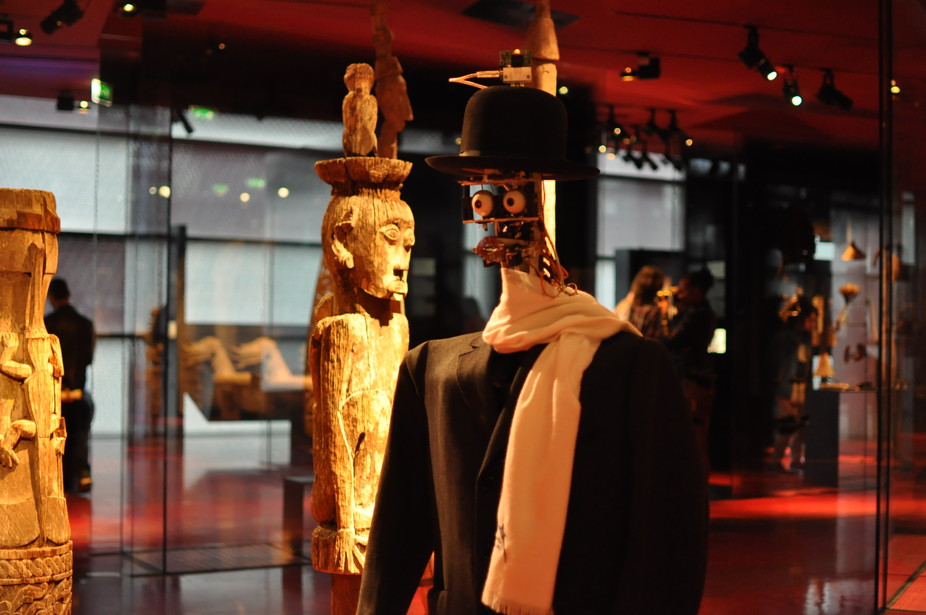
Imagine that you are visiting the Quai Branly-Jacques Chirac, a museum in Paris dedicated to anthropology and ethnology. As you walk through the collection, your curiosity leads you to a certain piece. After a while, you begin to sense a familiar presence heading towards the same objet d’art that has caught your attention.
You move slowly, and as you turn your head a strange feeling seizes you because what you seem to distinguish, still blurry in your peripheral vision, is a not-quite-human figure. Anxiety takes over.
As your head turns, and your vision become sharper, this feeling gets stronger. You realise that this is a humanoid machine, a robot called Berenson. Named after the American art critic Bernard Berenson and designed by the roboticist Philippe Gaussier (Image and Signal processing Lab) and the anthropologist Denis Vidal (Institut de recherche sur le développement), Berenson is part of an experiment underway at the Quai Branly museum since 2012.
The strangeness of the encounter with Berenson leaves you suddenly frightened, and you step back, away from the machine.
The uncanny valley
This feeling has been explored in robotics since the 1970s, when Japanese researcher Professor Masahiro Mori proposed his “uncanny valley” theory. If a robot resembles us, he suggested, we are inclined to consider its presence in the same way as we would that of a human being.
But when the machine reveals its robot nature to us, we will feel discomfort. Enter what Mori dubbed “the uncanny valley”. The robot will then be regarded as something of a zombie.
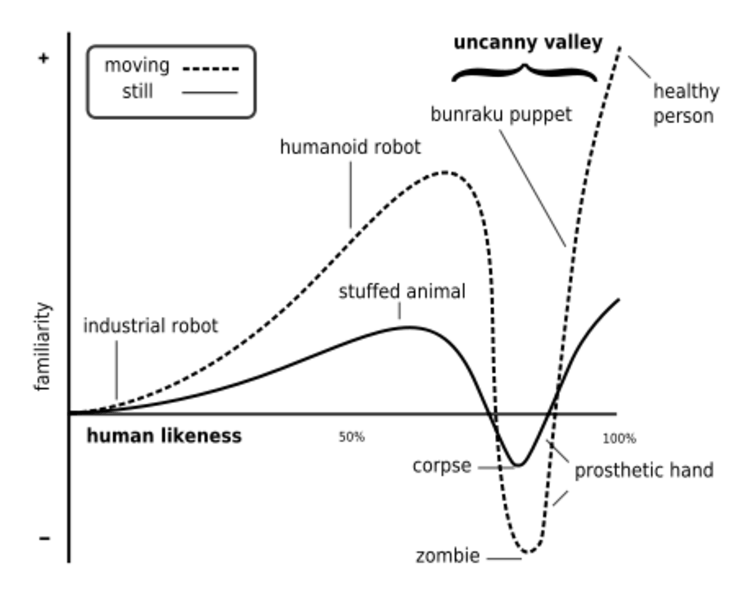
Mori’s theory cannot be systematically verified. But the feelings we experience when we meet an autonomous machine are certainly tinged with both incomprehension and curiosity.
The experiment conducted with Berenson at the Quai Branly, for example, shows that the robot’s presence can elicit paradoxical behaviour in museum goers. It underlines the deep ambiguity that characterises the relationship one can have with a robot, particularly the many communication problems they pose for humans.
If we are wary of such machines, it is mainly because it is not clear to us whether they have intentions. And, if so, what they are and how to establish a basis for the minimal understanding that is essential in any interaction. Thus, it is common to see visitors of the Quai Branly adopting social behaviour with Berenson, such as talking to it, or facing it, to find out how it perceives its environment.
In one way or another, visitors mainly try to establish contact. It appears that there is something strategic in considering the robot, even temporarily, as a person. And these social behaviours are not only observed when humans interact with machines that resembles us: it seems we make anthropomorphic projections whenever humans and robots meet.
Social interactions
An interdisciplinary team has recently been set up to explore the many dimensions revealed during these interactions. In particular, they are looking at the moments when, in our minds, we are ready to endow robots with intentions and intelligence.
This is how the PsyPhINe project was born. Based on interactions between humans and a robotic lamp, this project seeks to better understand people’s tendency to anthropomorphise machines.
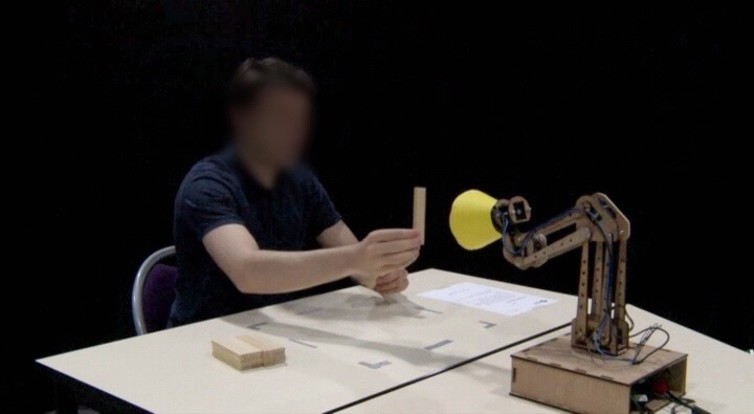

Trying to communicate with a robotic lamp, 2016
After they get accustomed to the strangeness of the situation, it is not uncommon to observe that people are socially engaging with the lamp. During a game in which people are invited to play with this robot, they can be seen reacting to its movements and sometimes speaking to it, commenting on what it is doing or on the situation itself.
Mistrust often characterises the first moments of our relations with machines. Beyond their appearance, most people don’t know exactly what robots are made of, what their functions are and what their intentions might be. The robot world seems way too far from ours.
But this feeling quickly disappears. Assuming they have not already run away from the machine, people usually seek to define and maintain a frame for communication. Typically, they rely on existing communication habits, such as those used when talking to pets, for example, or with any living being whose world is to some degree different from theirs.
Ultimately, it seems, we humans are as suspicious of our technologies as we are fascinated by the possibilities they open up.
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.
tags: c-Politics-Law-Society, Culture and Philosophy, cx-Education-DIY, human-robot interaction, humanoid, Social aspect, Uncanny Valley





