Robohub.org
Flying Ring robot can fly on its side
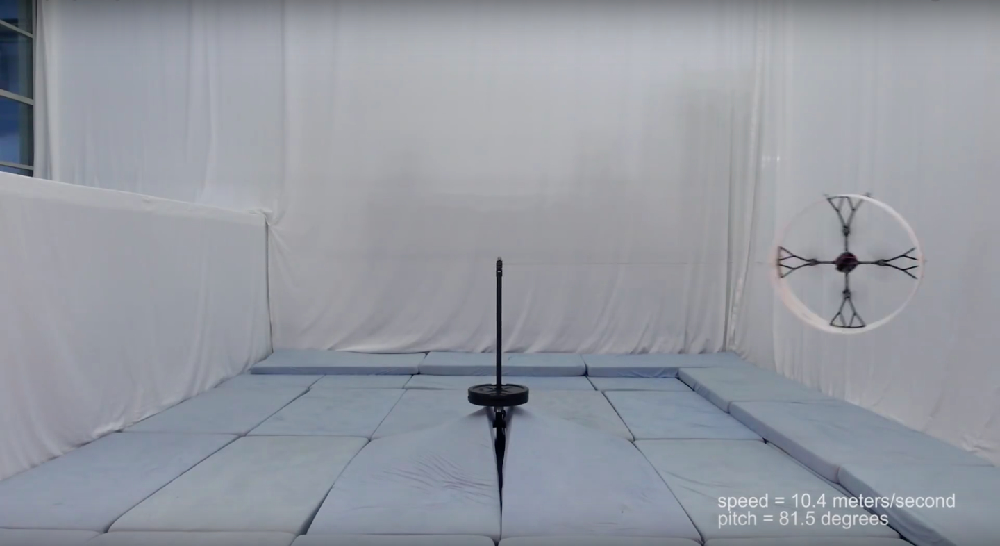
The Flying Ring is a new flying vehicle being developed at the Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control, ETH Zurich. The goal of the project is to fully characterize all aerodynamic properties of the vehicle. While traditional quadcopters are agile and carry high payloads they are not efficient in forward flight, with traditional lift to drag ratios comparable to a fruit fly. The Flying Ring vehicle, however, can fly on its side, allowing the blades to propel it forward faster than a typical quadcopter.
The video depicts the first prototype flying tethered. The annular wing (or ring) has a flat airfoil shape, which also covers the propellers and enhances human safety. These autonomous controlled flights help extract aerodynamic properties of the vehicle. A lift to drag ratio (which is a metric for aerodynamic efficiency) of 12 is achieved for the ring only. The total vehicle lift to drag ratio is lower, but can be substantially improved upon with an optimized design. Further details will be submitted to a future conference or research journal.
Why is the Flying Ring tethered? Flying tethered is an important part of the test, as it is used to characterize the steady state operating conditions at various flight speeds in a tight space, namely:
- Thrust of the propeller in forward flight
- Analysing annular wing lift and drag
- Evaluating body drag
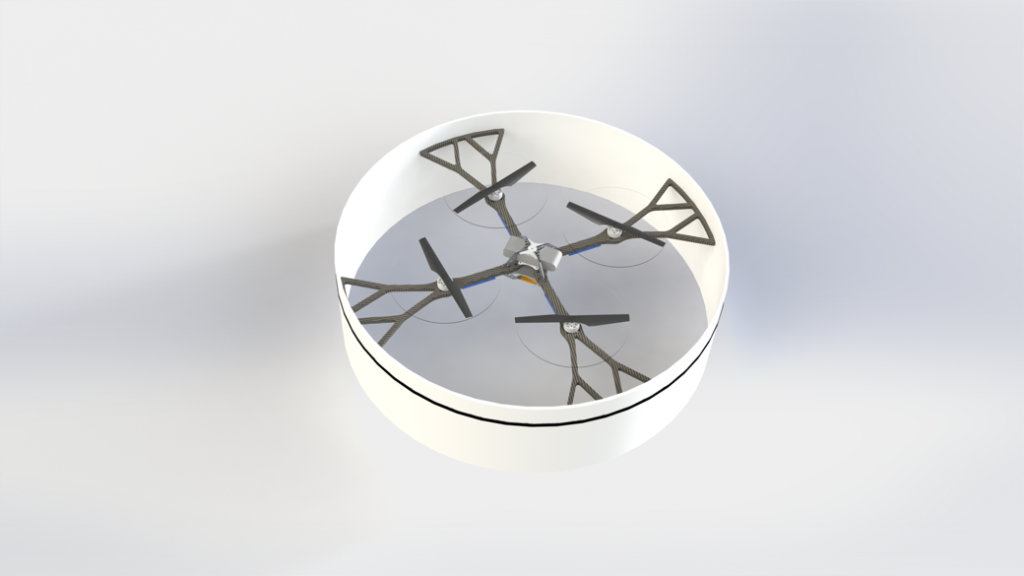
In terms of structure, the vehicle is a standard quadrotor configuration. It has depron foam sheet attached via zip ties to the four motor mount arms, with black carbon slab wrapped around the foam.
Links to other videos shown:
Quadrotor pole acrobatics
Cooperative quadrotor ball throwing and catching
Onboard quadrocopter failsafe: flight after actuator failure
Flying Robots, Builders of tomorrow
Researchers
Rajan Gill and Raffaello D’Andrea
Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control (IDSC), ETH Zurich, Switzerland
ETH Zurich, Flying Machine Arena
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by and builds upon prior contributions by numerous collaborators in the Flying Machine Arena project.
This research was funded in part by the National Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF).
If you enjoyed this article, you may also want to read:
- ‘IDSC Tailsitter’ flying robot performs vertical loops and easily transitions between hover and forward flight
- ‘Tailsitter’ flying robot hovers and recovers easily thanks to new algorithm
- Multiple tethered quadrotors whip around a pole together at high speeds
- Quadrocopter failsafe algorithm: Recovery after propeller loss
- Three new quadrotor videos demonstrate agile control and the power of machine learning
- Video: Quadrocopter learns from its mistakes, perfects slalom air racing
See all the latest robotics news on Robohub, or sign up for our weekly newsletter.
tags: c-Aerial, ETH Zurich, Raffaello D'Andrea