
Robohub.org
Using soft robots for artificial muscles
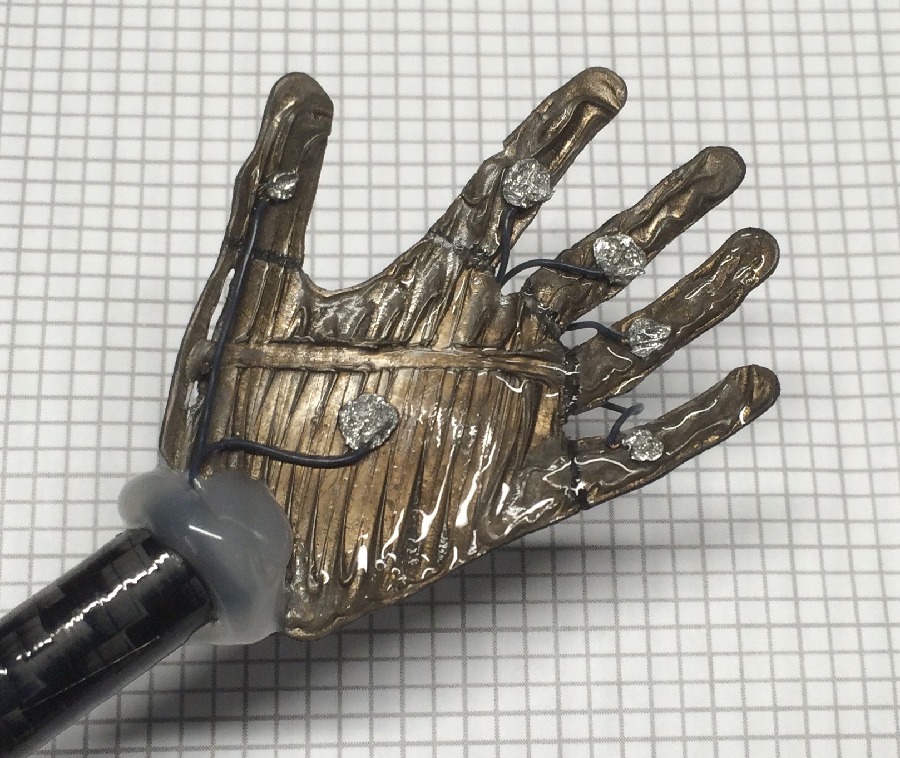
A small 3-D printed ionic polymer-metal composite soft robotic hand. National Science Foundation researchers are working to transform this material into artificial muscles. Credit: Kam K. Leang. University of Utah
Forget steel and aluminum. The robots of tomorrow may be able to squish, stretch and squeeze.
Novel robotic devices, part of the emerging field of soft robotics, offer many advances over conventional robots. Soft robots can more easily maneuver in tough spaces. They can better interact with humans, making them excellent assistants for elderly people. And one day they may lead to high-tech artificial muscles: a life-changing innovation for millions of disabled people around the globe.
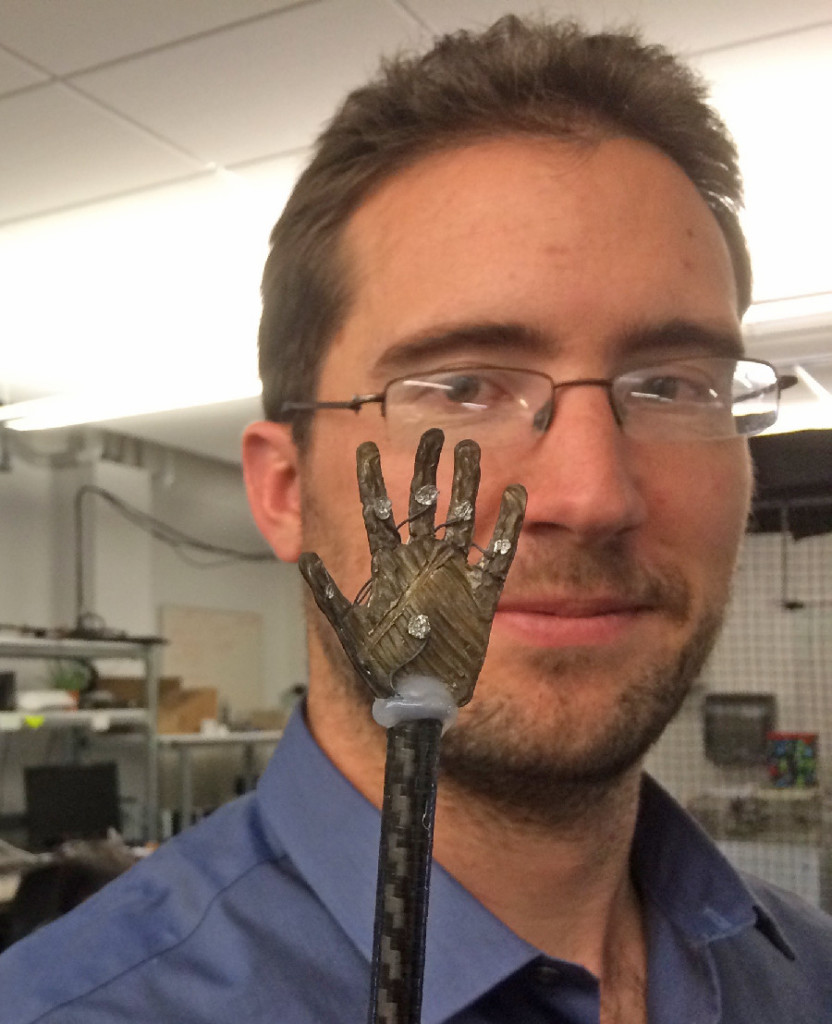

James Carrico, a Ph.D. graduate student at the University of Utah, displaying a small 3-D printed ionic polymer-metal composite soft robotic hand. Credit: Kam K. Leang
Creating artificial muscles requires not only developing a powerful, flexible material, but figuring out how to precisely control and cleverly manufacture it. That’s the mission of Kwang Kim of the University of Nevada, Las Vegas and his National Science Foundation (NSF)-funded team.
Kim is lead investigator on a NSF award pairing a diverse group of researchers — at four U.S. universities plus research institutions in Japan and South Korea — to transform a novel polymer-based material into artificial muscles. The research is supported through NSF’s Partnerships for International Research and Education (PIRE) program, which supports innovative, global research collaborations across all fields of science and engineering.
PIRE leverages U.S. funding and expertise to tackle global challenges. Kim’s U.S. team is working with researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and Japan’s National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, both known for strong expertise in robotics. (KAIST, for example, won the recent Robotics Challenge, hosted by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency.)
One of the big challenges in soft robotics is finding the right material. “It has to be soft, but it also has to produce enough power to do lots of different things,” Kim said. His team is using a type of synthetic material called Ionic Polymer-Metal Composites, which is a kind of electroactive polymer — meaning running electricity through the material makes it change shape.

The PIRE award will work to transform electroactive polymers, a type of material that changes shape when electricity runs through it, into artificial muscles. Credit: Kwang J. Kim, University of Nevada, Las Vegas; Kam K. Leang, University of Utah (both formerly of University of Nevada, Reno)
“In robotics you’ve got to be able to move and you’ve got to be able to sense,” said Kam Leang, an associate professor at the University of Utah Robotics Center and a co-investigator on this project. Traditional robots use electric motors to do the former. “In this PIRE, we are using the electroactive polymer itself.”
Electroactive polymers can also be used to sense motion, making them a great candidate for soft robotics. Leang and his colleagues have also devised a way to 3-D print the material. His component of the PIRE research is focused on how to scale up the manufacturing, as well as devising ways to better control the motion of the polymer. Others are working to better understand — and improve — the polymer material to make it more responsive, strong and affordable.
The project, which received NSF funding last fall, is still in its early stages. Kim, who has been working in electroactive polymers for nearly two decades, said soft robotics itself is still a relatively new field.
“I’m learning every day.”
Investigators: Paul Oh, Kam Leang, Kwang Kim, Chulsung Bae, Maurizio Porfiri
Related Institutions/Organizations: New York University, The University of Utah, University of Nevada Las Vegas, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
If you liked this article, you may also be interested in:
See all the latest robotics news on Robohub, or sign up for our weekly newsletter.
tags: c-Research-Innovation, NSF, robohub focus on soft robotics, soft robotics





