
Robohub.org
3D-printed houses and cars on the horizon as manufacturing goes large
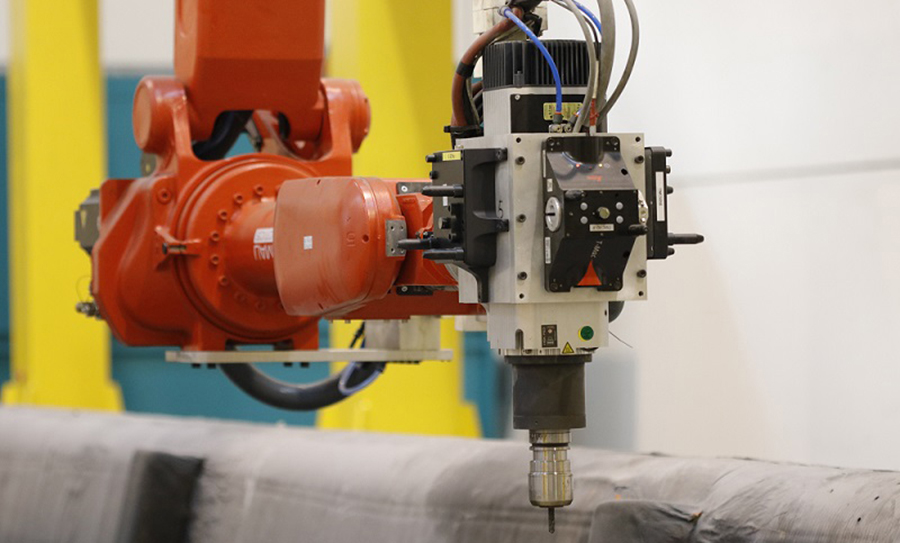
Housebuilders and makers of car parts in a few decades time may need nothing more than a large robotic arm, some raw ingredients and a programmable design, thanks to the next-generation of 3D printing machines which are opening up the technique to large-scale industry.
There are currently two types of manufacturing: additive, also known as 3D printing, where an item is built by adding material layer by layer; and subtractive, which starts with a piece of material and takes pieces away through processes such as milling and polishing until you’re left with the final product.
Now, researchers are building hybrid machines that are able to perform both types of manufacturing at once, and on a scale that brings 3D-printed houses and cars within reach.
‘We want to use the best of both technologies,’ said Jose Antonio Dieste, from Spanish technology centre AITIIP. ‘Additive manufacturing has some problems, one is the accuracy for large parts, another is the quality of the finishing. We are trying to complement this additive with subtractive in order to improve the performance.’
He runs the EU-funded KRAKEN project, which is designing a ceiling-mounted robotic arm that lays down a thin layer of a material, such as aluminium, then finishes that layer by taking away any unnecessary material, before repeating this process until the product is built.
The idea is to accurately construct large components such as side panels for cars, while saving on materials by only using exactly what is required, thus lessening the environmental footprint of industry.
Large components
‘We are going to work on medium and large components,’ he said. ‘[Now] additive machines are working on quite small parts, half a metre maximum. We are going to be able to build 24-metre-long parts.’
New innovations in the nozzles and in the ingredients should also speed up this type of manufacturing, by increasing the deposit rates of the materials, says Dr Dieste.
‘Additive 3D printing machines are very slow. In order to build a half-metre part, some of the machines need one to two days. We need to go faster. For example, a five-metre-long (car) should take two or three days maximum.’
A prototype of the KRAKEN machine, which will be modelled on a robotic arm developed in a previous project called MEGAROB, should be ready by 2019.
It will specifically be designed to build components from metal, particularly aluminium, and resins known as thermosets. However, other researchers are creating hybrid manufacturing machines that can work with other types of materials.
If you liked this article, you may also want to read these other articles on 3D printing:
- Sticky business: Five adhesives tested for 3D printing
- Foundry tool: Multi-material designing for 3-D printing
- 3-D printing hydraulically-powered robots, no assembly required
- AI, deep learning and 3D printing produce ‘The Next Rembrandt’
- Rising Media acquires RoboUniverse and Inside 3D Printing shows
See all the latest robotics news on Robohub, or sign up for our weekly newsletter.
tags: 3D printing, c-Industrial-Automation, cx-Research-Innovation, Industrial Other, Robotics technology





