Robohub.org
A drone that flies (almost) like a bird
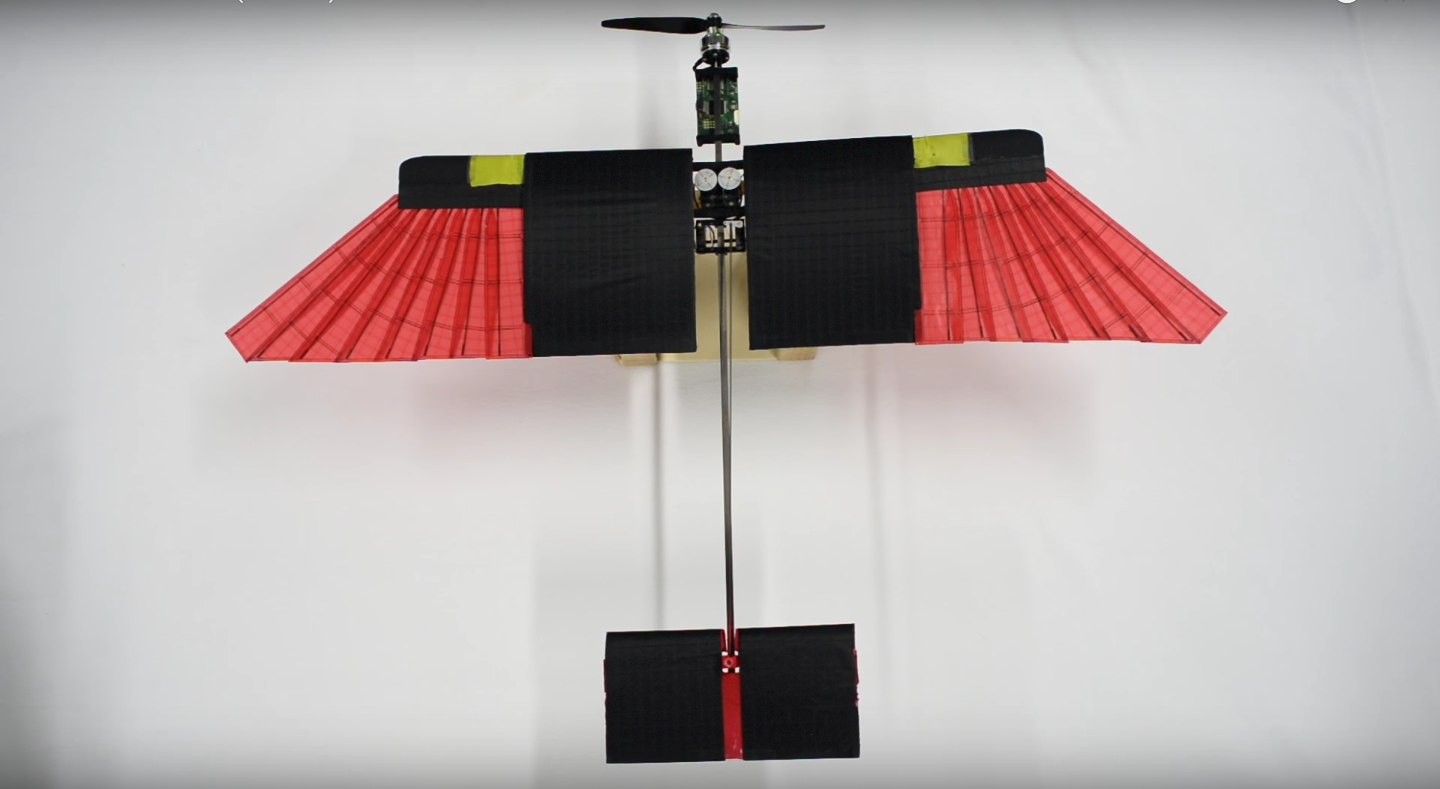
Bioinspired robots that take their designs from biology has been a big research area in recent years, but a team from NCCR Robotics, Floreano Lab have just gone one step further and designed a feathered drone to fully replicate the agile flight of birds.
Small winged drones can experience sudden and extreme variations in aerodynamic conditions, for example from winds or air disturbances coming from passing obstacles or other moving objects. Birds adapt to these changing environmental conditions by changing the shape of their wings. Their feathered wings can quickly change shape mid-flight, for example, folding the outer layer of feathers, a bird significantly reduces the surface area of its wing and the aerodynamic drag allowing high-speed flight.
It is this folding and simple reduction of wing span that the team wished to exploit. By having a wing that can easily change size and shape, a drone can adapt to nippy manoeuvres (larger wing span required), or can reduce its drag at high speeds to fly in strong headwinds (short wing span required).

Birds can dramatically alter the shape and size of their wings because they are composed of an articulated skeleton controlled by muscles and covered with feathers that can overlap. Similarly, the presented drone has a wing equipped with artificial feathers that can be folded to actively change the surface. The wing contains two artificial tendons that can either rotate or straighten the front edge of the wing, thus splaying or storing the feathers. By enabling the drone to reduce its wingspan, the surface area is decreased by 41%, thus significantly reducing drag giving the possibility to fly against strong headwinds. On the other hand, when the wing is fully deployed, the drone can perform turns that are 40% sharper. Since the two foldable wings act independently of each other, the mechanism can also be used to control roll eliminating the need of additional ailerons with advantages in terms of reduced weight and mechanical complexity.
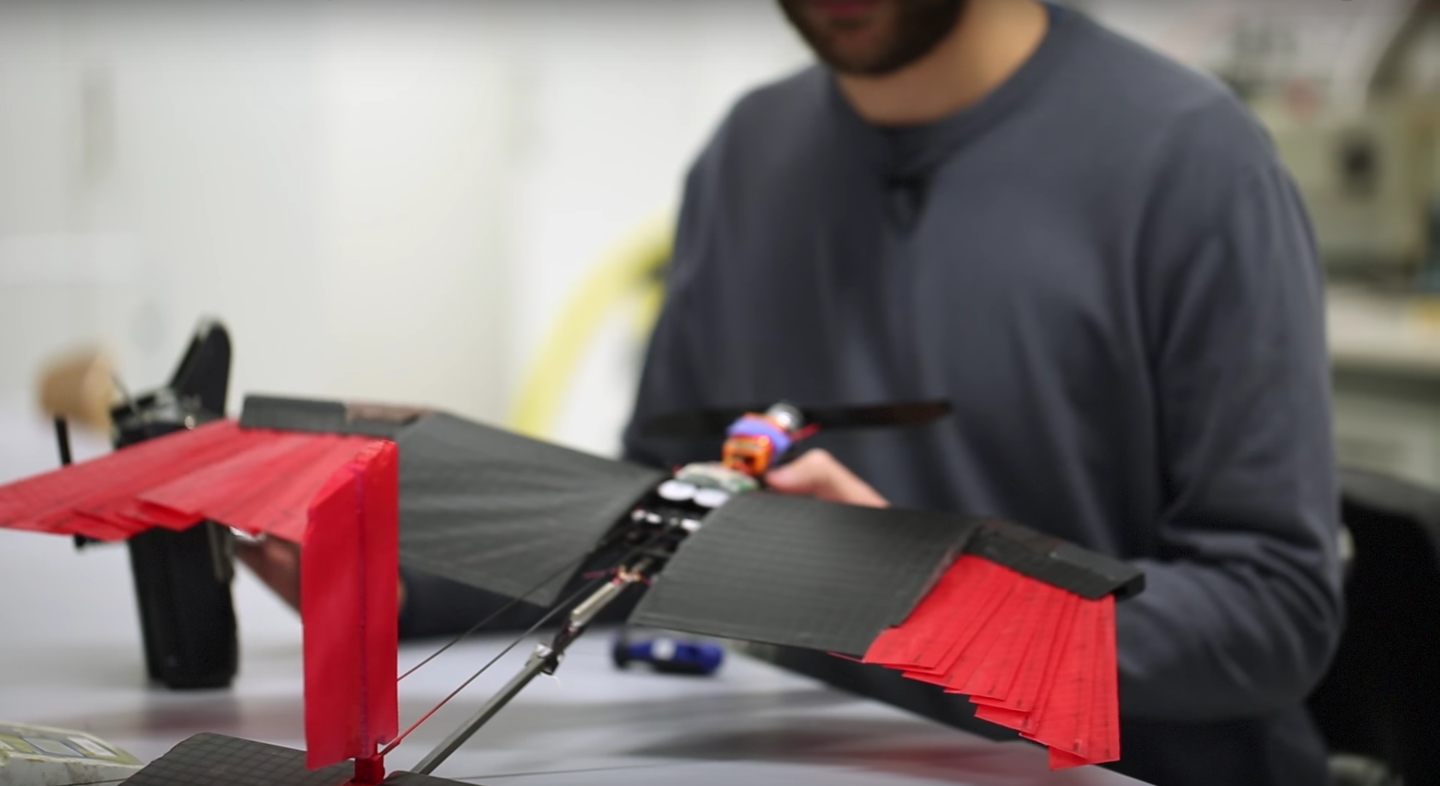

This new advent means that the drones of the future may not only manoeuvre like birds, but may also look like them too!
Reference:
M. Di Luca, S. Mintchev, G. Heitz, F. Noca, and D. Floreano, Bio-inspired morphing wings for extended flight envelope and roll control of small drones, Journal of the Royal Society, Interface Focus, 16 December 2016. DOI – http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rsfs.2016.0092
tags: c-Aerial, drones, EPFL, NCCR Robotics