
Robohub.org
A new versatile gripper with electroadhesion
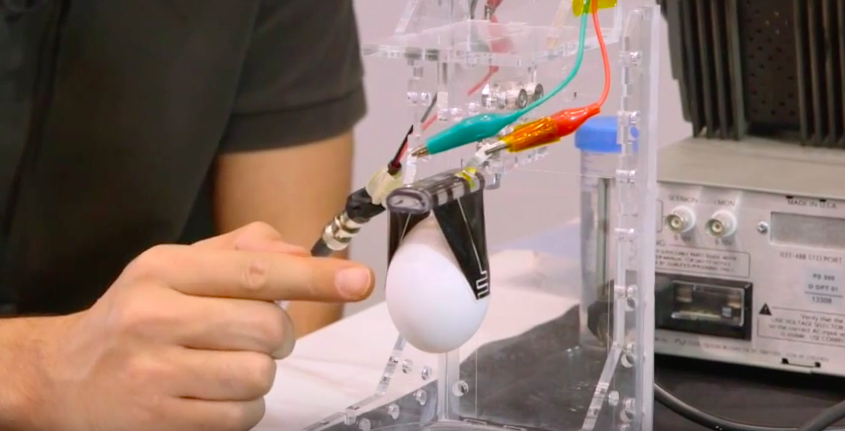

From early childhood, when a person picks up an object using their hands they use haptic feedback to automatically adjust the force of their grip according to the object they are lifting. A completely different grip is required when holding a soft piece of fruit or a glass ornament – both very delicate in their own ways. Your body will automatically adjust to the appropriate grip by sensing small shear movements and exploiting the natural compliance of the soft, fleshy pads of your finger tips to do so. Equipping robotic grippers with this level of compliance and versatility has long been a problem, but in a paper published in Advanced Materials, a team from LMTS and LIS, EPFL and NCCR Robotics proposes a solution with a simple control input that has been used to pick up diverse objects including a raw chicken egg, a water balloon and a flat piece of paper.
While most robotic grippers are designed for the type of object they will pick up, the versatility of this two-fingered version comes from its ability to maximise electroadhesion and electrostatic actuation while allowing self-sensing through newly designed bending dielectric elastomer actuators (DEAs). Electroadhesion force alternates holding force to pick up heavier objects, and minimises required mechanical grasping force generated from electrostatic actuation, allowing the gripper to handle very fragile and deformable objects and a wide variety of shapes.
 The key novelty that allows this new gripper to behave differently is the arrangement of electrodes within the DEA. Traditionally, DEAs function through a thin elastomer membrane sandwiched between two highly compliant, uniform parallel electrodes. When a voltage is applied across the membrane the opposing charges on the electrodes generate electrostatic pressure, which in turn leads to thickness reduction and area expansion, resulting in bending actuation.
The key novelty that allows this new gripper to behave differently is the arrangement of electrodes within the DEA. Traditionally, DEAs function through a thin elastomer membrane sandwiched between two highly compliant, uniform parallel electrodes. When a voltage is applied across the membrane the opposing charges on the electrodes generate electrostatic pressure, which in turn leads to thickness reduction and area expansion, resulting in bending actuation.
For DEA actuation, electric fields inside the membrane normal to the surface are usually the only ones considered, but not the only ones produced: Fringe electrical fields are created at the electrode edge, which can bring about electroadhesion in nearby objects.
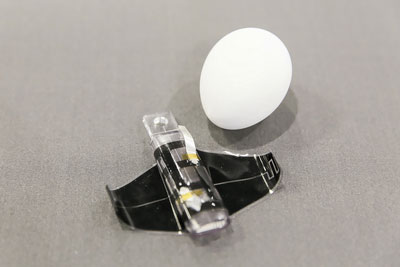 In order to exploit the electroadhesion and the electrostatic actuation of the DEA, four compliant electrodes are interwoven in a way that causes adjacent electrode segments on the same planar surface to orientate with the opposite polarity nearest. Thus, when a voltage is applied, the fringe electric fields are experienced across the whole DEA, rather than just at the edges, leading to electroactuation forces being increased tenfold.
In order to exploit the electroadhesion and the electrostatic actuation of the DEA, four compliant electrodes are interwoven in a way that causes adjacent electrode segments on the same planar surface to orientate with the opposite polarity nearest. Thus, when a voltage is applied, the fringe electric fields are experienced across the whole DEA, rather than just at the edges, leading to electroactuation forces being increased tenfold.
The simple structure of the gripper means that it is lightweight (approx. 1.5g), fast functioning (approx. 100ms to close the fingers), and has a design flexibility for potential applications such as small transportation drones, the food industry and medical robotics.
References
J. Shintake, S. Rosset, B. Schubert, D. Floreano and H. Shea, “Versatile soft grippers with intrinsic electroadhesion based on multifunctional polymer actuators,” Advanced Materials, 2015. doi:10.1002/adma.201504264
All photographs courtesy of Alain Herzog and NCCR Robotics.
tags: c-Research-Innovation, gripper, NCCR




