
Robohub.org
Book Review: ‘Peer Reviews in Software, A Practical Guide,’ by Karl Wiegers

Code review of a C++ program with an error found.
I have been part of many software teams where we desired to do code reviews. In most of those cases the code reviews did not take place, or were pointless and a waste of time. So the question is: how do you effectively conduct peer reviews in order to improve the quality of your systems?
I found this book, Peer Reviews in Software: A Practical Guide by Karl E. Wiegers. This book was recommended to me, and having “practical guide” in the title caught my attention — I have reviewed other books that claimed practical, but were not. Hopefully this book will help provide me (and you) with tools for conducting valuable code reviews.

Peer Reviews in Software: A Practical Guide. Photo: Amazon
As a human, I will make mistakes when programming; finding my mistakes is often difficult since I am very close to my work. How many times have you spent hours trying to find a bug in your code only to realize you had a bad semi-colon or parentheses? Another person who has not worked on the code for hours might have been able to spot the problem right away. When I first started programming it could be embarrassing to have somebody review my code and point out the problems. However now that I am more senior, I do not view it as an embarrassment, but as a learning opportunity since everybody has a different set of experiences that influences their code. I would encourage other developers to view it as a learning experience and not be bashful about reviews. Remember the person is critiquing the work, not you; this is how to become a better developer.
According to Wiegers, there are many types of peer reviews including: inspections, team reviews, walkthroughs, pair programming, peer desk check passaround, and finally ad hoc review.
This book is divided into three sections:
- Cultural & social aspects
- Different types of reviews (with a strong focus on inspection)
- How to implement review process within your projects
Cultural & Social Aspects
In this first section of the book, the author makes the argument that quality work is not free and that “paying” the extra cost of peer reviews is a good investment in the future. By having peer review you can reduce failures before the product is released out into the world and any applicable reworks. Shifting the defect detection to the early stages of a product has huge potential payoff, due to high costs of fixing defects found late in the release cycle, or after release. The space shuttle program found the relative cost for fixing a defect is: $1, if found during initial inspection; $13, if found during a system test; and $92, to fix after delivery! In the book, the author documents various companies who saved substantial amounts of time and money all by having code inspection programs.
One thing I like is the reference to IEEE 1999, which talks about other items that are good to review. People don’t think about it but other things, such as marketing brochures, requirement specifications, user guides, test plans and many other things, are good candidates for peer review.
I have seen many project teams try to do error tracking and/or code reviews but fail, due to team culture. I saw one case where peer review actually worked: when a dedicated person’s only job was to manage reliability in the project. He was great at hounding people to track bugs and review code. This book discussed how team culture must be developed to value “quality”. If you are the type of person that does not want to waste time reviewing another’s code, you must remember you will want the other person to “waste” time looking at your code. In this manner, we must all learn to scratch each other’s back. There are also two traps to watch out for:
- Becoming lazy and submitting bad code for review since somebody else will find/fix it, or
- Trying to perfect your code before sharing it, in order to protect your ego from getting bruised, and to only show your best work.
We also cannot forget managers. Managers need to value quality and provide time and resources for employees to develop good practices. Managers need to understand the point of these exercises are to find flaws and people should not be punished based on those flaws. I have often seen managers not putting time in the schedule for good code reviews.
Types of reviews
Before discussing the types of reviews there is a good discussion on the guiding principles for reviews. Some of the principles are:
- Check your egos at the door
- Keep the review team small
- Find problems during review, but don’t try to fix them at the review. Give up to 1 minute for discussion of fixes.
- Limit review meeting to 2 hours max
- Require advanced preparation
There are several types of peer reviews discussed in this book. This list starts with the least formal approach and develops until the most formal approach (the book uses the opposite order which I found non intuitive).
- Ad Hoc – These are the spur of the moment meetings where you call a coworker to your desk to help with a small problem. Usually, this just solves an immediate problem. (This is super useful when trying to work out various coordinate transforms)
- Peer passaround/deskcheck, – In this approach a copy of the work is sent to multiple reviewers, after which you can then collate all of the reviews. This allows multiple people to look at the code/item and also lets you get something if one person does not respond. In the peer deskcheck version, only one person looks at it instead of passing it around for multiple reviews.
- Pair Programming – This is the idea that two people program together. So while there is no official review two sets of eyes see each line of code being typed. This has an added bonus that now two people will understand the code. The downside is that often one of the coders can “doze-off” and not be effective at watching for flaws. Also, many coders might not like this.
- Walkthrough – This is where the author of the code walks through the code to a group of reviewers. This is often unstructured and heavily dependent on how good of a job the author prepared. In my experience this is good for helping people understand the code and finding large logic flaws, but not so much for finding smalls flaws/bugs.
- Team Review – This is similar to the walkthrough however reviewers are provided with documentation/code in advance to review and their results are collated.
- Inspection – Finally, we have the most formal approach which the author appears to favor. In this approach the author of the code does not lead the review, rather, a moderator, often with the help of checklists, will lead the meeting and read out the various sections. After the moderator reads a section, the reviewers discuss it. The author of the code can answer questions and learn how to improve various sections. Often the author might identify other instances of the same problem that the reviewers did not point out. An issue log should be maintained as a formal way of providing feedback and a list to verify fixes against.
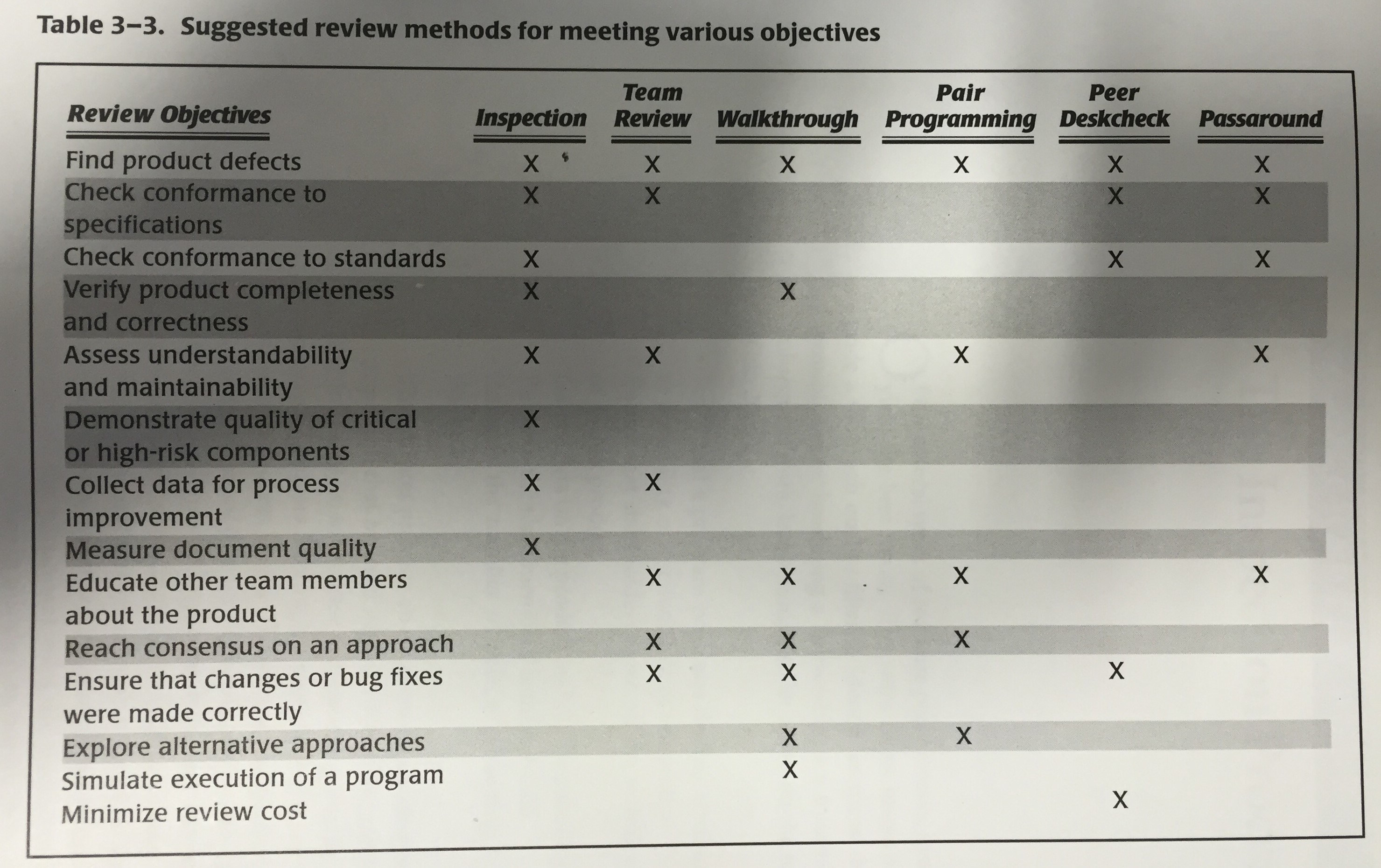
Suggested review methods from “Peer Reviews in Software”
The book then spends the next few chapters detailing the inspection method of peer review. Here are just a few notes. As always, read the book to find out more.
- In most situation 3-7 is a good size group for the inspection. The number of people can be based on the item being reviewed.
- The review needs to be planned in advance and have time to prepare content to distribute to reviewers.
- After the meeting the author should address each item in the issue log that was created and submit it to the moderator (or other such person) to verify that the solutions are good.
- Perform an inspection when that module is ready to pass to the next development stage. Waiting too long can leave a person with a lot of bad code that is now too hard to fix.
- You can (sort of) measure the ROI by looking at the bugs found and how long they took to find. There are many other metrics detailed in the book.
- Keep spelling and grammar mistakes on a separate paper and not on the main issue list.
How to implement review processes within your projects
Getting a software team and management to change can be difficult. The last part of this book is dedicated to how you can get reviews started, and how to let them naturally grow within the company. One significant thing identified is to have a key senior person act as a coordinator for building a culture of peer review and to provide training to developers. There is a nice long table in the book of the various pitfalls that an organization may encounter and how to deal with them.
This book also discusses special challenges and how it can affect your review process. Some of the situations addressed are:
- Large work products
- Geographic or time separation
- Distributed reviewers
- Asynchronous review
- Generated and non-procedural code
- To many participants
- No qualified reviewers available
At the end of this book, there is a link to supplemental material online. I was excited to see this. However when I went to the site, I saw it was all for sale and not free (most things were around $5). That kind of burst my bubble of excitement for the supplemental material. There is a second website for the book that is referenced but does not seem to be valid anymore.
Throughout the book the idea is getting proper training for people on how to conduct inspection reviews. Towards the end of the book, the idea of hiring the book’s author as a trainer to help with this training is suggested.
Overall, I think this is a good book. It introduces people on how to do software reviews. The use of graphics and tables in the book are pretty good. It is practical and easy to read. I also like how this book addresses management and makes the business case for peer reviews. I give this book 4.5 out of 5 stars. The missing 0.5 stars is due to the supplemental material not being free and for not providing those forms with the book.
Disclaimer: I do not know the book author. I purchased this book myself from Amazon.
tags: Book, c-Education-DIY, review, software





