
Robohub.org
New soft ‘antagonistic’ actuator enables robots to fold
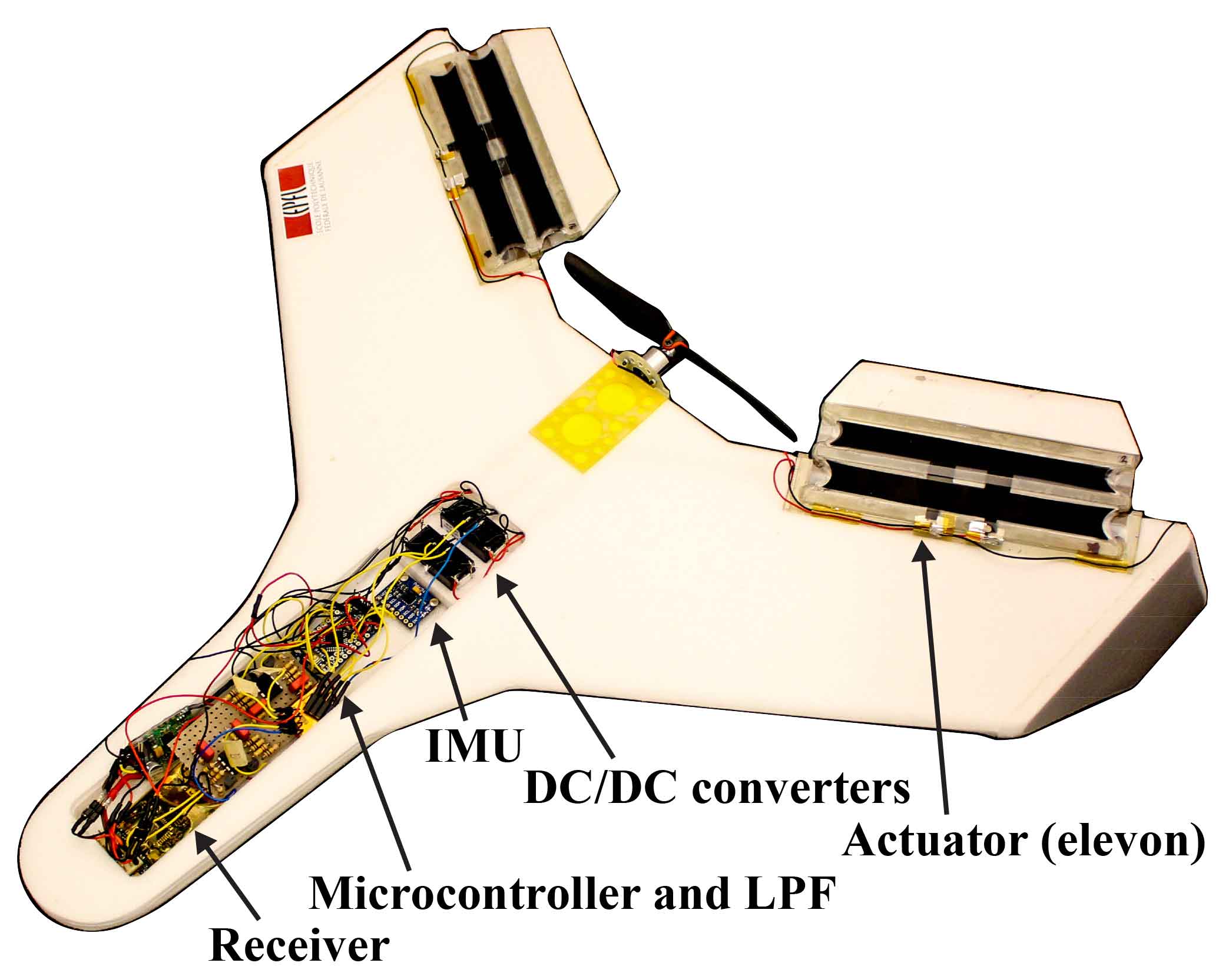
A new foldable actuator has been successfully used to fly a MAV.
Traditionally, many key robot components (including sensors and actuators) are rigid, and this makes it difficult for researchers and industry to make them truly compliant with their surroundings. It’s with this problem in mind that a team from NCCR Robotics in the Laboratory of Intelligent Systems and the Microsystems for Space Technologies Laboratory both at EPFL in Switzerland have developed a new soft actuator that enables robots to fold.
To use hard actuators requires a complex design and can make the final structure fragile – and this is a problem when developing robots for use in cluttered environments such as search and rescue or surveying. Recent solutions have used shape memory alloys (SMAs), pneumatic actuators and electroactive polymers – each with their own advantages but also with disadvantages.
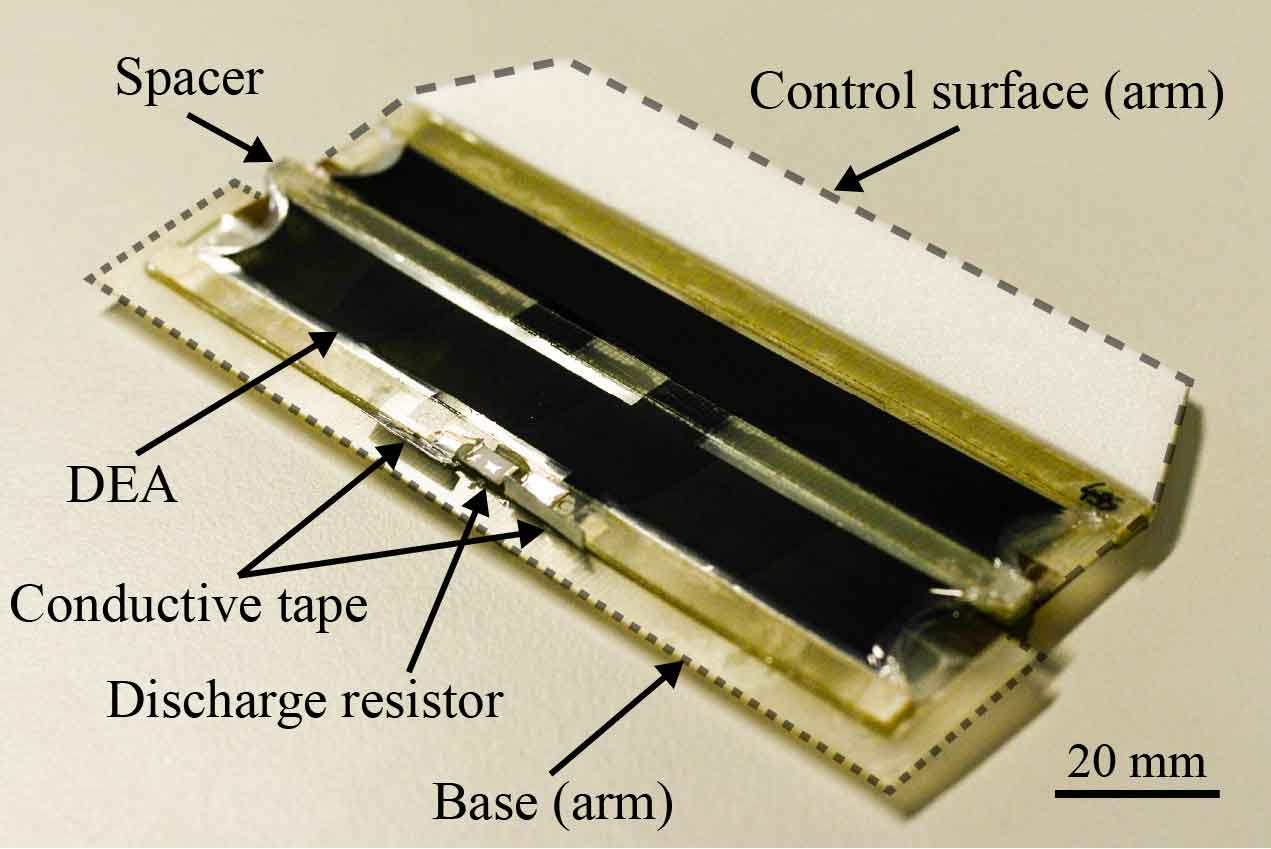
The actuator uses two DEAs
To get around these issues, the NCCR team placed two stacked or single dielectric elastomer actuators (DEAs) on top of each other in an antagonistic configuration in order to create an actuator that allows bidirectional actuation and passive folding. Each DEA consists of a thin elastomer membrane between two compliant electrodes – the opposing charges on each electrode generate an electrostatic force (Maxwell stress), which squeezes the membrane causing thinning and expansion in the direction of free boundary conditions and therefore results in actuation stretch.
The actuator itself consists of two rigid arms connected via elastic hinges, and two sets of DEAs in an antagonistic configuration. When an electric current is applied to one of the DEAs it creates a biased stress between the two DEAs, thus bending the actuator. What is particularly exciting is that this actuator can be literally bent in half without being damaged in any way .
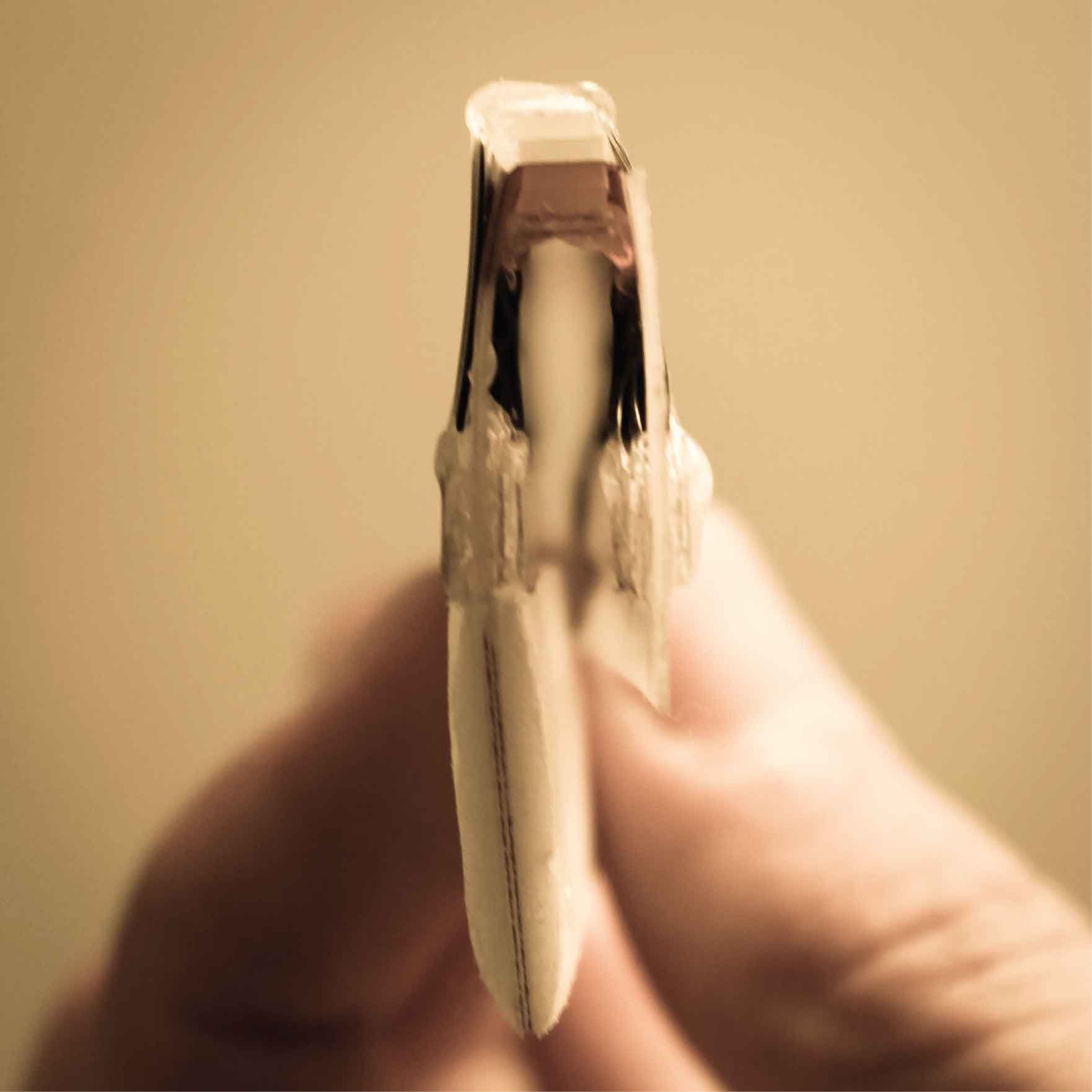

The actuator can be folded completely in half without being damaged
As a result of this robustness, the team behind the actuator have tested it as an elevon (surface used to control pitch and roll) on a remotely controlled, fixed-wing MAV. The elevons were used successfully for numerous flights, with a hand launch and a ground landing (landing is a particularly dangerous time for hardware). The elevon must sustain an angle during flight, meaning that the aerodynamic force acts on its surface, another a common reason for failure in flying robots. A good correlation found between the control signal and movement of the robot illustrates the high performance of the actuator.
What is particularly striking about this actuator is how simply it can be designed and made. By using this structure without additional mechanical parts, transmission loss is prevented. Further, by using a silicon type elastomer, a fast response speed and good positioning control can be achieved.
Fully foldable machines
The possibilities for this kind of compliant actuator are endless – from handling fragile goods in manufacturing to safe human-robot interactions. Future uses may also enable robots to self-deploy without the need for further actuation, leading to a generation of robots capable of programmable shape change and reconfiguration.
The full paper by Shintake, J., Rosset, S., Schubert, B. E., Floreano, D. and Shea, H.R. will be published in an upcoming edition of IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics and can be downloaded ahead of printing here.
tags: c-Research-Innovation, EPFL, NCCR, robohub focus on soft robotics




