
Robohub.org
Cooperative payload transportation with UAVs
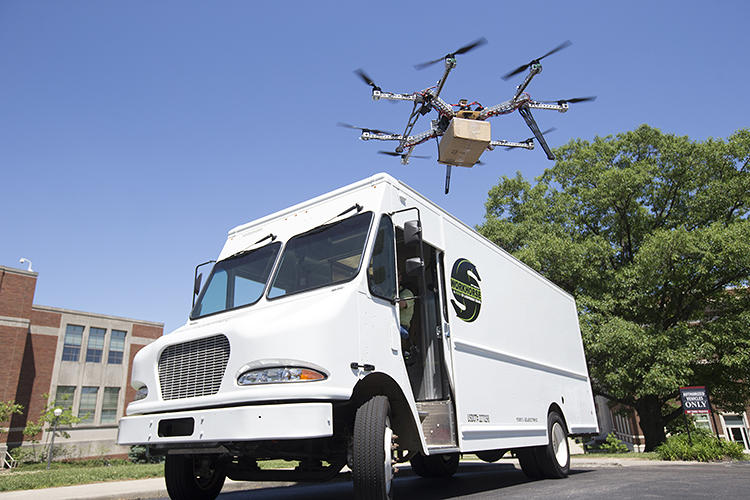

Delivery robots are touted as gaining widespread popularity in the near future. Wheeled models could be suitable for urban areas, while UAVs have great potential in accessing difficult areas and carrying a variety of payloads. But first we have to overcome technical barriers, safety issues and more than a few legal aspects.
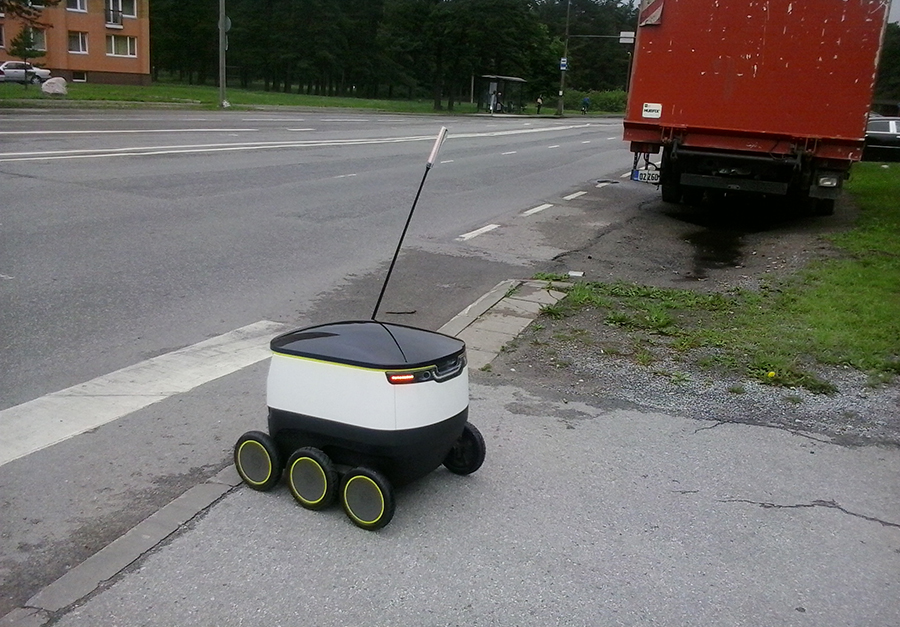

We are use to thinking that a single UAV will only transport a single small box. However a mass delivery service should also focus on the possibility of charging big solids in the pursuit of service viability and success. In this scenario, UAV cooperative teams could play a key role in the industry. This idea has proven to be feasible, as ETH shows:
UAV swarms could be useful in cases where payloads are too heavy to be charged by a single multirotor, its shape is large, or even with deformable solids (such as wires or ropes). Two or more drones can form a swarm.
In the case of deformable linear solids, the payload could be the solid itself (for instance, high tension lines and tethered multirotors), or we could make use of the ropes to transport a payload attached to them. In fact, this type of transportation solution is not only needed for commercial delivery purposes, but also might be useful for cable manipulation in catastrophic indoor scenarios or maintenance operations in narrow spaces. A wire linking some drones restricts their behaviour differently from solid bars links or no links at all.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Cb6DBu8pHO0
Cooperative transportation systems require a specific control and path planning strategy compared to single robots. Deformable solids act as passive loads that affect robot dynamics, and a proper coordination among robots is essential for an efficient energy usage. Imagine a drone running out of battery faster than the rest of the swarm. Equi-load distribution of all the team members, and keeping the payload clamped to the gravity centre of the UAV, are some of the basic assumptions to be made in this kind of systems. An additional requisite is that particularly in paths with obstacles, the displaced distance of each drone also is very important. About engineering control, different options may vary depending on the centralised or decentralised control of the drones, and deterministic type of control (such as PID or LQR) are showing good results.
Deformable solid linking among flying vehicles is not a new phenomenon: aerial refuelling already exists, but with manned vehicles. Unmanned vehicles present new challenges, and researchers have advanced this field in the last decade, although hundreds of real tests under wind conditions and variable payloads are necessary to achieve a fully operative and robust system.
References:
Estevez, J., Graña, M., & Lopez-Guede, J. M. (2016). “Online fuzzy modulated adaptive PD control for cooperative aerial transportation of deformable linear objects”. Integrated Computer-Aided Engineering, 24(1), pp. 41-55.
Maza, I., Kondak, K., Bernard, M., & Ollero, A. (2010). “Multi-UAV cooperation and control for load transportation and deployment”. Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems, 57(1-4), 417.
Michael, N., Fink, J., & Kumar, V. (2011). “Cooperative manipulation and transportation with aerial robots”. Autonomous Robots, 30(1), 73-86.
Palunko, R. Fierro, and P. Cruz (2012). “Trajectory generation for swing-free maneuvers of a quadrotor with suspended payload: A dynamic programming approach”. In Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2012 IEEE International Conference on, pages 2691–2697.
tags: c-Aerial, cx-Industrial-Automation, Flying, opinion, Swarming, UAV





