Robohub.org
Localization uncertainty-aware exploration planning
Autonomous exploration and reliable mapping of unknown environments corresponds to a major challenge for mobile robotic systems. For many important application domains, such as industrial inspection or search and rescue, this task is further challenged from the fact that such operations often have to take place in GPS-denied environments and possibly visually-degraded conditions.
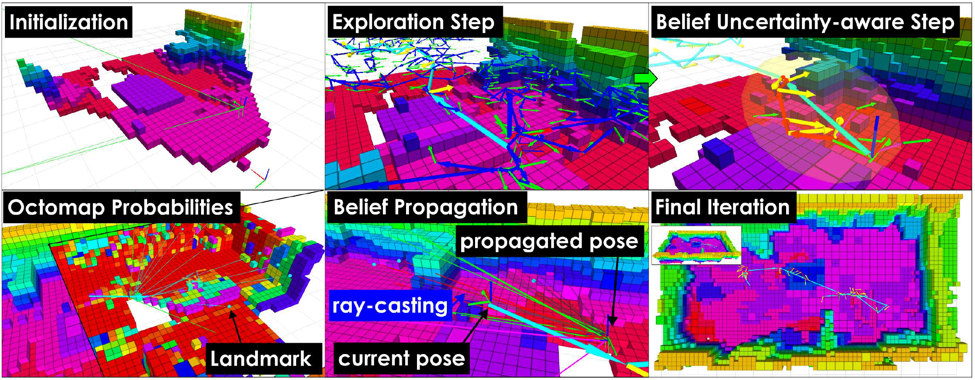
In this work, we move away from deterministic approaches on autonomous exploration and we propose a localization uncertainty-aware autonomous receding horizon exploration and mapping planner verified using aerial robots. This planner follows a two-step optimization paradigm. At first, in an online computed random tree the algorithm finds a finite-horizon branch that optimizes the amount of space expected to be explored. The first viewpoint configuration of this branch is selected, but the path towards it is decided through a second planning step. Within that, a new tree is sampled, admissible branches arriving at the reference viewpoint are found and the robot belief about its state and the tracked landmarks of the environment is propagated. The branch that minimizes the expected localization uncertainty is selected, the corresponding path is executed by the robot and the whole process is iteratively repeated.
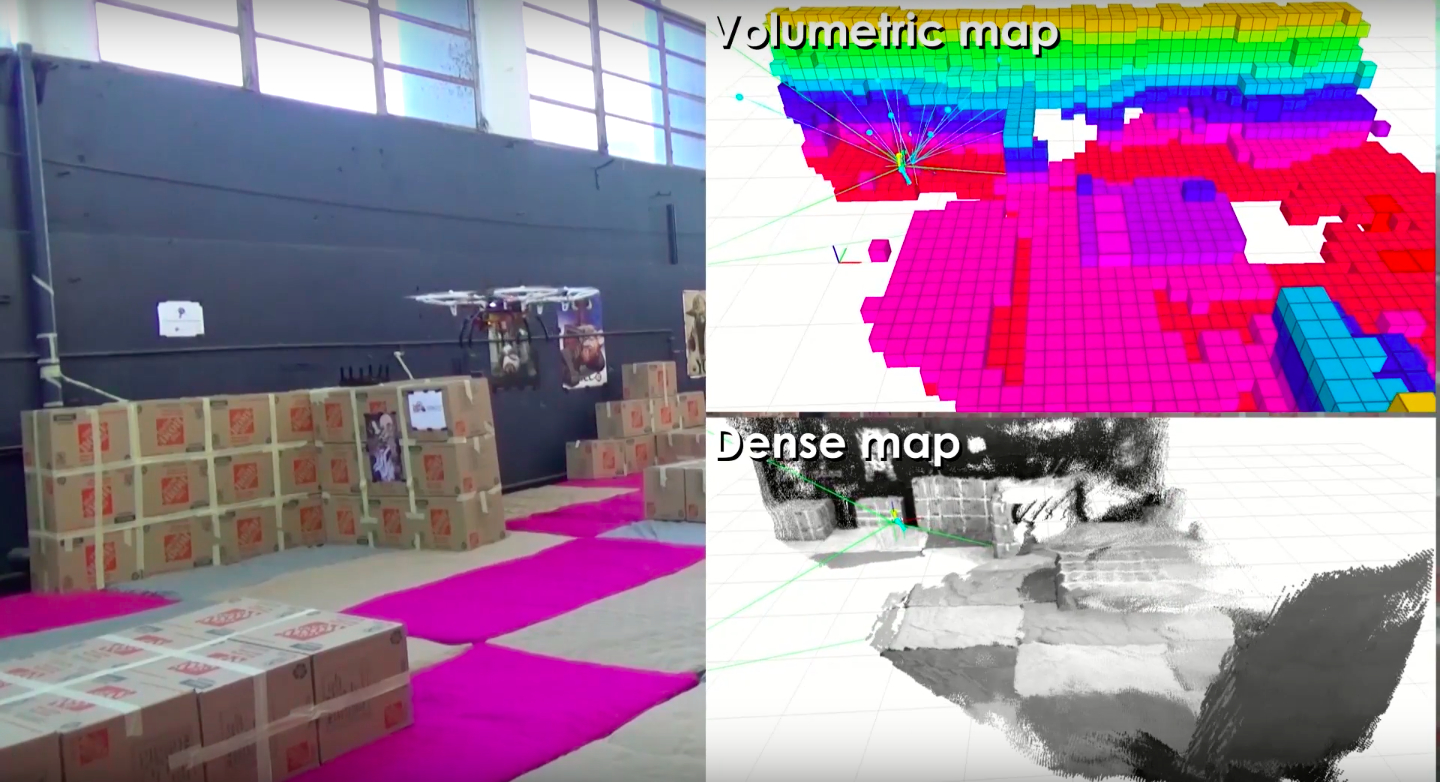
The algorithm has been experimentally verified with aerial robotic platforms equipped with a stereo visual-inertial system operating in both well-lit and dark conditions, as shown in our videos:
To enable further developments, research collaboration and consistent comparison, we have released an open source version of our localization uncertainty-aware exploration and mapping planner, experimental datasets and interfaces. To get the code, please visit: https://github.com/unr-arl/rhem_planner
This research was conducted at the Autonomous Robots Lab of the University of Nevada, Reno.
Reference:
tags: c-Research-Innovation, UAVs