Robohub.org
Tackling the European refugee crisis with solar-powered UAVs: A fully autonomous 26 hour search-and-rescue flight
One year after having demonstrated the 81-hour continuous solar-powered flight that is still the current world record in flight endurance for all aircrafts < 50kg total mass, the AtlantikSolar UAV has completed its next milestone by demonstrating the first-ever fully autonomous (from launch to landing) solar-powered perpetual flight with significant payload (Color + Thermal Camera) in a 26-hour Search-and-Rescue (SaR) mission.
While the 81-hour and 28-hour endurance record flights were important milestones that demonstrated the perpetual endurance capability of AtlantikSolar, they required manual pilot control for launch and landing and did not carry any aerial imaging payload. However, the missions that our team really cares about – Search-and-Rescue missions relying on long-endurance aerial sensing to support authorities e.g. in the European refugee crisis currently unfolding over the Mediterranean Sea – require both of these elements, i.e. ease-of-use through full launch-to-land aircraft autonomy as well as significant payloads to help the rescue teams with the detection of victims on land and sea.
The 26-hour solar-powered Search-and-Rescue flight performed by AtlantikSolar AS-3 from July 19th – 20th 2016 demonstrated exactly that, and is, therefore the first-ever flight worldwide to combine:
- Perpetual flight: 26-hours of solar-powered day/night- and thus energetically-perpetual flight.
- Full aircraft autonomy: No pilot stick moved within 26-hours of flight.
- SaR payload: The aircraft carried a 10 Watt 300g payload (1 Color camera, 1 Thermal Camera, 1 ODROID onboard computer with WLAN) and performed victim detection from the air during day and night.
- Environment-aware: The aircraft performed automatic thermal updraft tracking for increased energetic efficiency and to speed up the battery recharge.
Flight summary
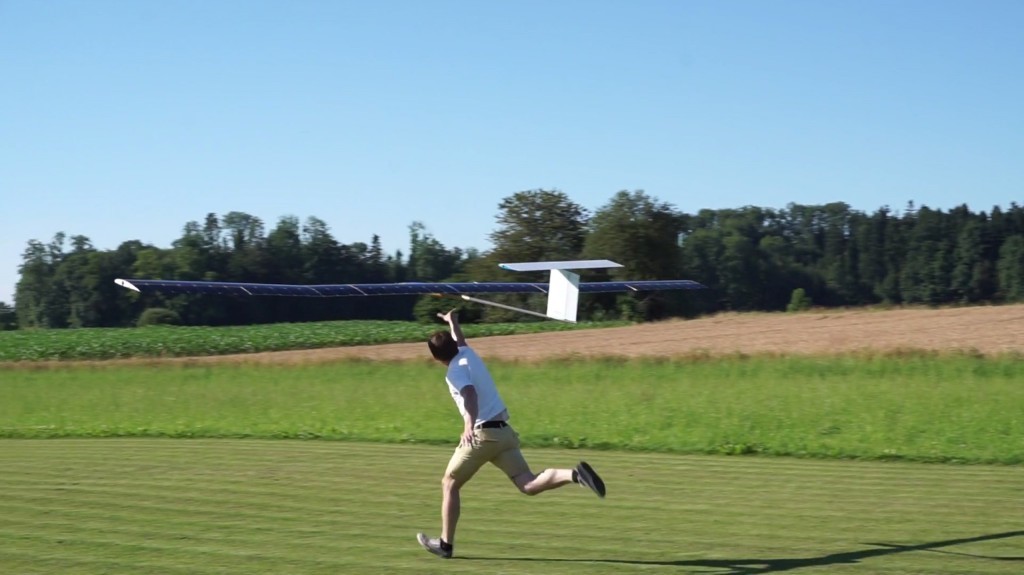
The 26-hour flight started on July 19th at 18:02 local time in Hinwil, CH with full batteries. The launch was performed fully autonomously: After all system checks were complete, the aircraft was tossed in the air via a hand-launch and then continued automatically and without pilot interaction towards its first loitering waypoint.
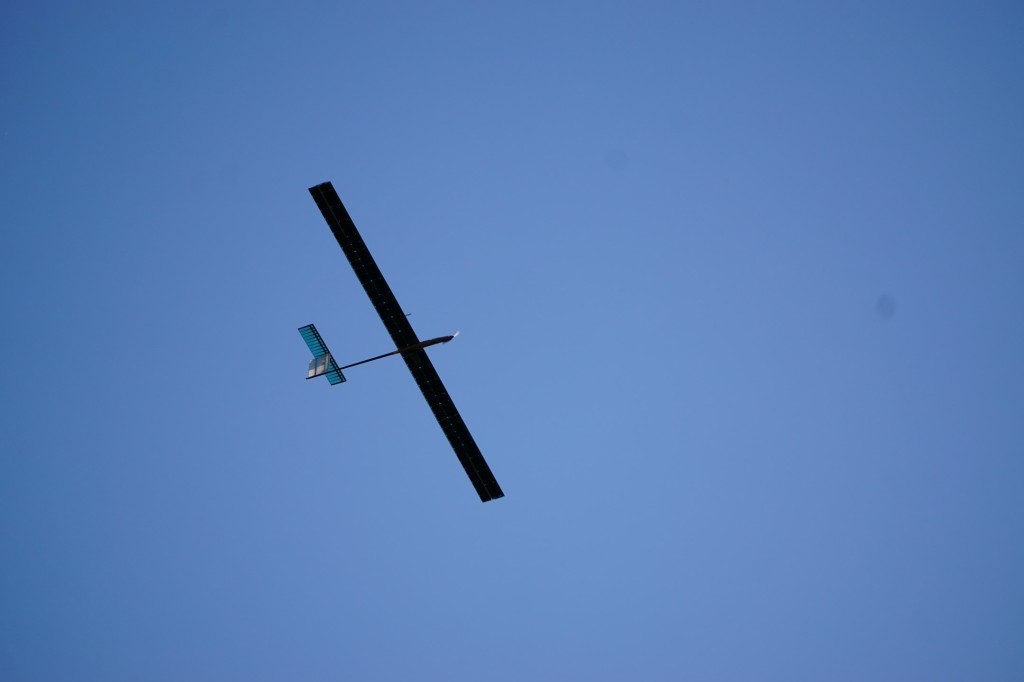
The respective flight control technology is based on an ETHZ/3DR Pixhawk autopilot with a custom flight controller designed at the Autonomous Systems Lab. Equipped with a color camera, thermal camera, an onboard computer and wireless LAN, the aircraft began live-streaming the respective images. The full payload was operated until around 21 o’clock, after which the color camera was switched off because of the insufficient lighting conditions. The batteries were at 95% state of charge at that time, having started their discharge shortly before 20 o’clock. Note that operating a fully-fledged SaR payload consuming 10W is a significant challenge for perpetual flight on a small-scale solar-powered UAV such as AtlantikSolar, and the overall power consumption of ~60W was thus closely tracked during the first hours of the evening flight.

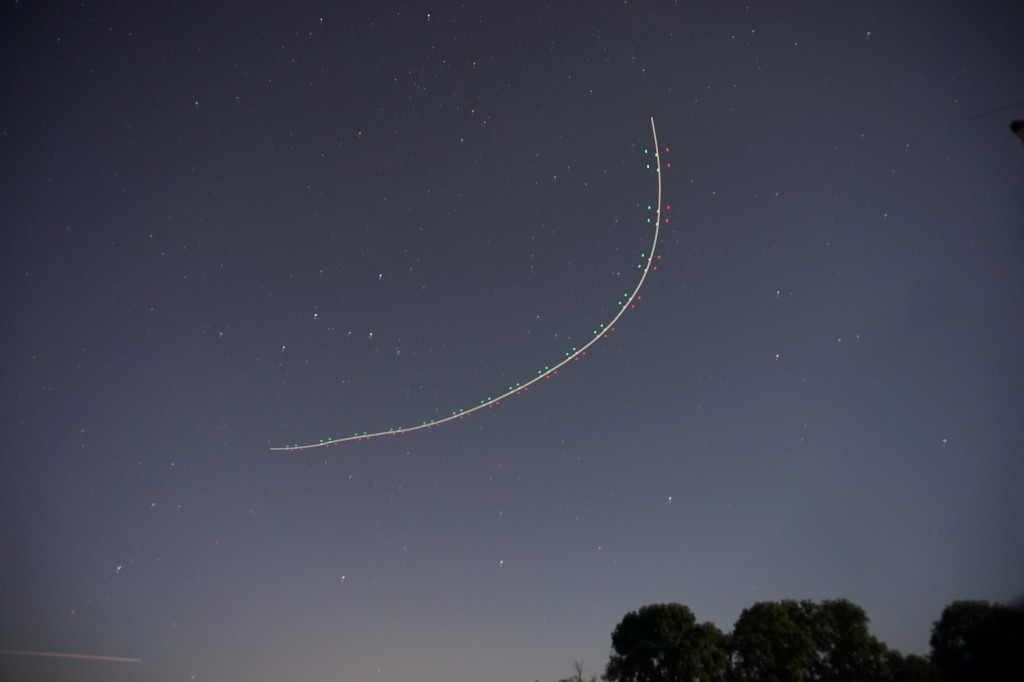
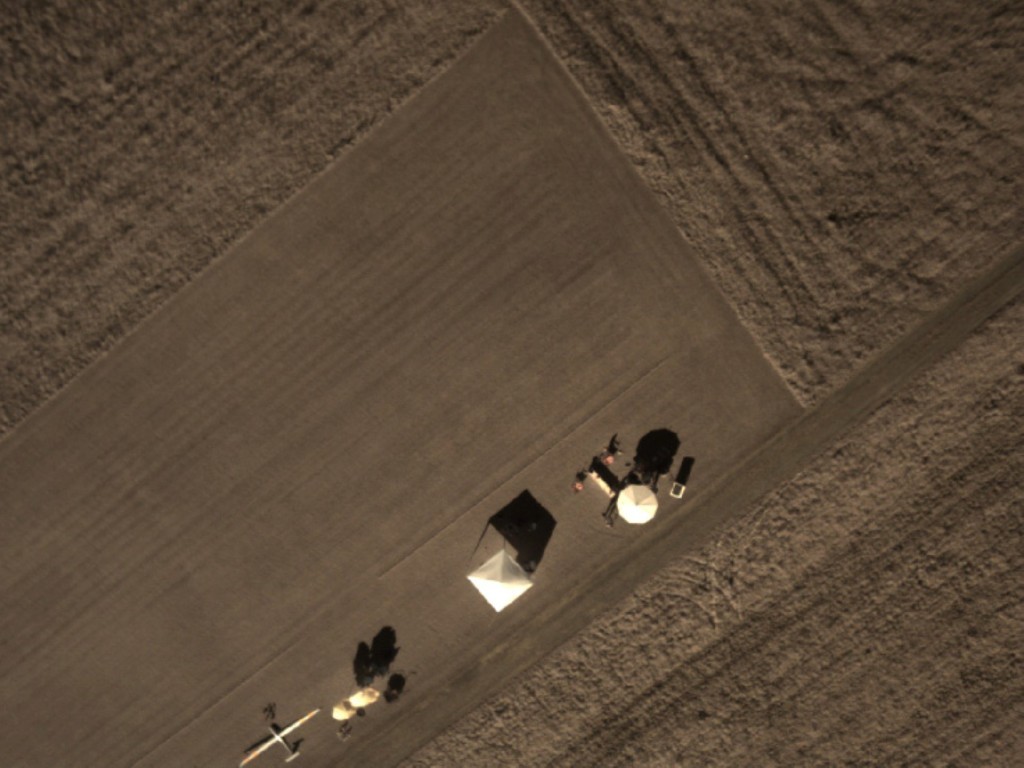
T=5h. The airplane is seen loitering in the top left, performing the SolAIR Search-and-Rescue mission.
The actual testing of the Search-and-Rescue capabilities started just before 23:00. With the aircraft now flying in total darkness, the infrared camera served as the only source of aerial imaging information. As visible in the video, the payload system clearly manages to find the victim lying in low grass (and surrounding houses, tents, cars, the streets and especially the warm electric generator) at 23:05. The victim detection was performed manually by the ground station operator based on the live-streamed images this time. However, the next AtlantikSolar test flight will have automatic on-board victim detection (as already tested in the ICARUS search and rescue project) implemented. These demonstrated capabilities are integral elements for perpetual flight and aerial victim detection missions. We are convinced they can be of great help in solving pressing issues, such as the European refugee crisis of 2015 and 2016 above the Mediterranean Sea.
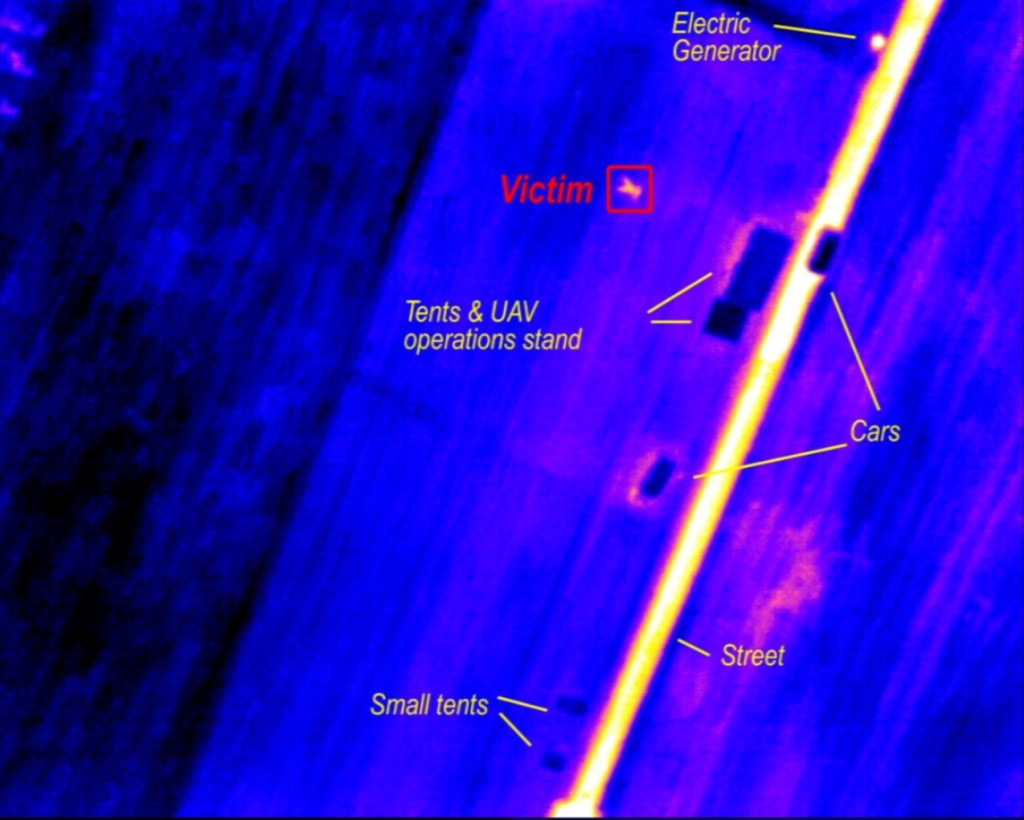

T=5h. Live-streamed thermal camera images with annotation. Note the victim that can easily be detected.
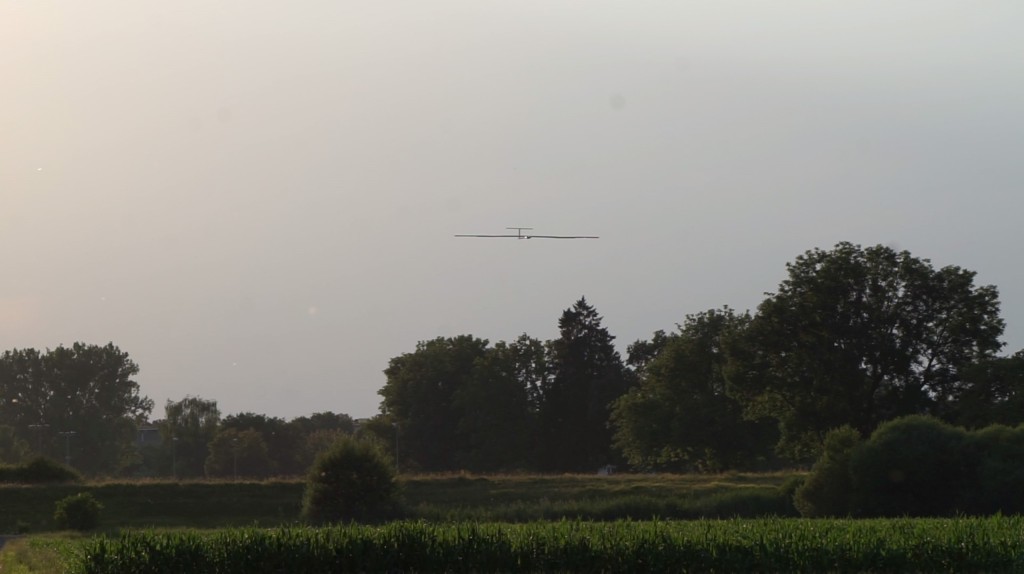
Despite heavy winds of up to 8m/s, the Search-and-Rescue support activities with the infrared camera payload were continued throughout the rest of the night. The sun hit at 06:20 local time on July 20th and the minimum battery state of charge was reached with 26% battery energy remaining at 08:04. Considering the additional payload power consumption (and mass) of 10W , this energetic margin – achieved on July 20th, and thus about one month after the solar solstice on June 21st – is a success and even exceeds the margin of 23% predicted by our simulations. To accelerate the battery recharging process, the aircraft also implemented autonomous thermal updraft tracking that was enabled during the late morning once thermal updrafts were encountered (see video). Multiple “free” altitude gains of >100m were achieved this way – again without any pilot interaction. The batteries were fully re-charged at 15:30.
As a final step, and after 26-hours of solar powered flight, the aircraft performed a fully autonomous landing at the Hinwil, CH airfield. Using its lightweight LIDAR (Light Detection And Ranging) sensor to measure its distance to the ground, AtlantikSolar – a hard to fly aircraft that can usually only be steered and landed by extremely experienced pilots – could safely perform the automatic landing. We consider the demonstrated full flight autonomy a vital step to allow search-and-rescue support teams, which usually do not possess extensive UAV flight training, to benefit from the significant advantages of solar-powered and in general high-performance UAVs.
Further information
Detailed design and technical information on the UAV platform can be found in “Oettershagen P, Melzer A, Mantel T, Rudin K, Lotz R, Siebenmann D, Leutenegger S, Alexis K, Siegwart R (2015), A Solar-Powered Hand-Launchable UAV for Low-Altitude Multi-Day Continuous Flight. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)” [Download] .
An additional up-to-date publication, including the research for this flight, is planned.
Some more impressions from the flight were broadcasted live through our twitter account.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded through the research project SolAIR – Solar-powered Automated Aerial Imaging and Reconnaissance Using Infrared Cameras. SolAIR is a project funded under Armasuisse contract #043-12. The AtlantikSolar project is in addition funded with ETH Zurich’s internal resources, private supporters, and the European Union FP7 Search-And-Rescue research projects ICARUS and SHERPA .
Multiple project partners and collaborators have contributed towards making this important milestone possible, and we’d like to thank all of them for their various and ongoing support. Finally, we are grateful towards the Hinwil and Rafz model aeroplane clubs for providing the airfield!
Pilots: Rainer Lotz, Adrian Eggenberger. Development and Operations Team (Autonomous Systems Lab): Philipp Oettershagen, Rainer Lotz, Amir Melzer, Thomas Mantel, Bartosz Wawrzacz, Konrad Rudin, Thomas Stastny, Timo Hinzmann, Dieter Siebenmann, Dr. Gregory Hitz, Prof. Dr. Roland Siegwart.
The AtlantikSolar project was developed at the Autonomous Systems Lab at ETH Zurich.
If you liked this article, you may want to read:
- Solar-powered flight for 81 hours: A new endurance world record
- Solar powered day/night autonomous flight achieved: Airborne for 28 hours without fuel!
- Flying Ring robot can fly on its side
- IDSC Tailsitter’ flying robot performs vertical loops and easily transitions between hover and forward flight
- ‘Tailsitter’ flying robot hovers and recovers easily thanks to new algorithm
See all the latest robotics news on Robohub, or sign up for our weekly newsletter.
tags: ASL, AtlantikSolar, c-Aerial, drones, ETH Zurich