
Robohub.org
Can a brain-computer interface convert your thoughts to text?

By Srividya Sundaresan, Frontiers Science Writer
Ever wonder what it would be like if a device could decode your thoughts into actual speech or written words? While this might enhance the capabilities of already existing speech interfaces with devices, it could be a potential game-changer for those with speech pathologies, and even more so for “locked-in” patients who lack any speech or motor function.
“So instead of saying ‘Siri, what is the weather like today’ or ‘Ok Google, where can I go for lunch?’ I just imagine saying these things,” explains Christian Herff, author of a review recently published in the journal Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
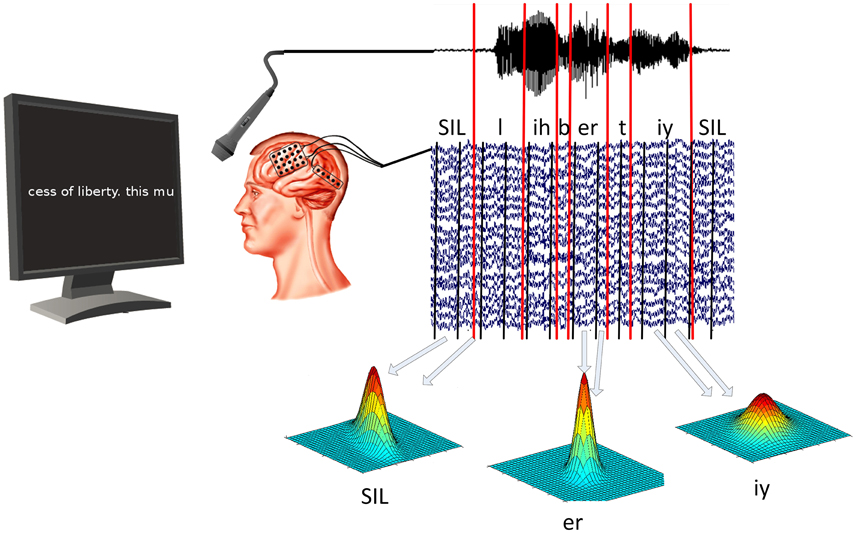
ECoG and audio data are recorded at the same time. Speech decoding software is then used to determine timing of vowels and consonants in acoustic data. ECoG models are then trained for each phone individually by calculating the mean and covariance of all segments associated with that particular phone. Courtesy of Christian Herff
While reading one’s thoughts might still belong to the realms of science fiction, scientists are already decoding speech from signals generated in our brains when we speak or listen to speech.
In their review, Herff and co-author, Dr. Tanja Schultz, compare the pros and cons of using various brain imaging techniques to capture neural signals from the brain and then decode them to text.
The technologies include functional MRI and near infrared imaging that can detect neural signals based on metabolic activity of neurons, to methods such as EEG and magnetoencephalography (MEG) that can detect electromagnetic activity of neurons responding to speech. One method in particular, called electrocorticography or ECoG, showed promise in Herff’s study.
This study presents the Brain-to-text system in which epilepsy patients who already had electrode grids implanted for treatment of their condition participated. They read out texts presented on a screen in front of them while their brain activity was recorded. This formed the basis of a database of patterns of neural signals that could now be matched to speech elements or “phones”.
When the researchers also included language and dictionary models in their algorithms, they were able to decode neural signals to text with a high degree of accuracy. “For the first time, we could show that brain activity can be decoded specifically enough to use ASR technology on brain signals,” says Herff. “However, the current need for implanted electrodes renders it far from usable in day-to-day life.”
So, where does the field go from here to a functioning thought detection device? “A first milestone would be to actually decode imagined phrases from brain activity, but a lot of technical issues need to be solved for that,” concedes Herff.
Their study results, while exciting, are still only a preliminary step towards this type of brain-computer interface.
If you liked this article, you may also like reading:
- Robot co-workers in the operating room
- Video of human controlling a quadrotor via non-invasive brain/computer interface
- Robots can successfully imitate human motions in the operating room
- Putting humanoid robots in contact with their environment
- Living with a prosthesis that learns: A case-study in translational medicine
See all the latest robotics news on Robohub, or sign up for our weekly newsletter.
tags: brain-computer interface, c-Research-Innovation





