
Robohub.org
3’600-strong underwater robot sensor network returns 1’000’000th measurement, has scientists craving for more
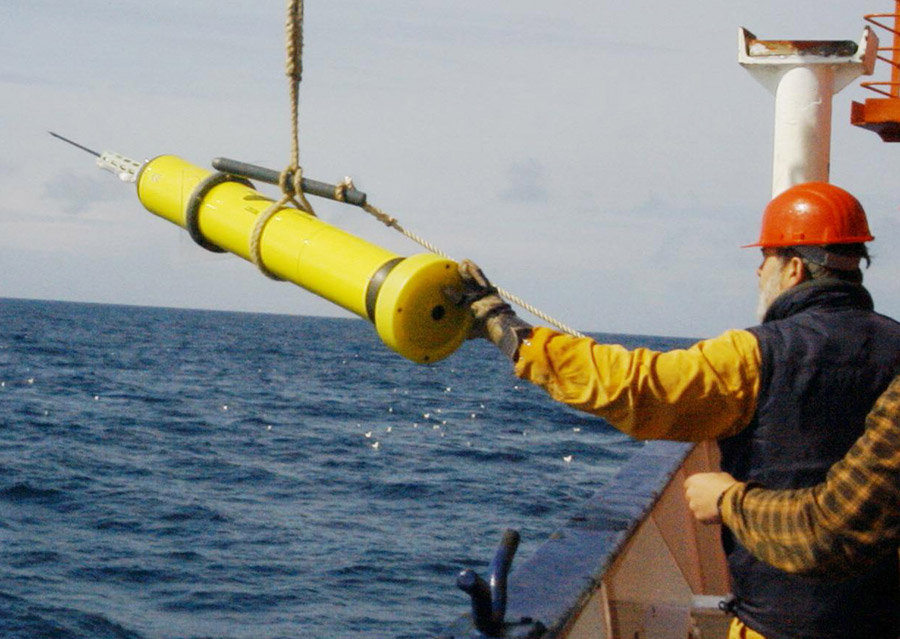

The Argo project, which has deployed a network of more than 3’600 robots covering all of the world’s oceans, has returned it’s 1’000’000th measurement.
The yellow underwater robots with their characteristic cylindrical body topped by an antenna have now been successfully used for more than 10 years for precise, long-term measurements of ocean temperatures and salt content. The robots stay submerged for up to 10 days at a time, drifting with ocean currents at a specified depth, or rising and falling in pre-defined paths down to depths of 2000 meters. Upon surfacing, they send their recorded data and current position home via satellite link. The recorded data are then made freely available online in near real-time.
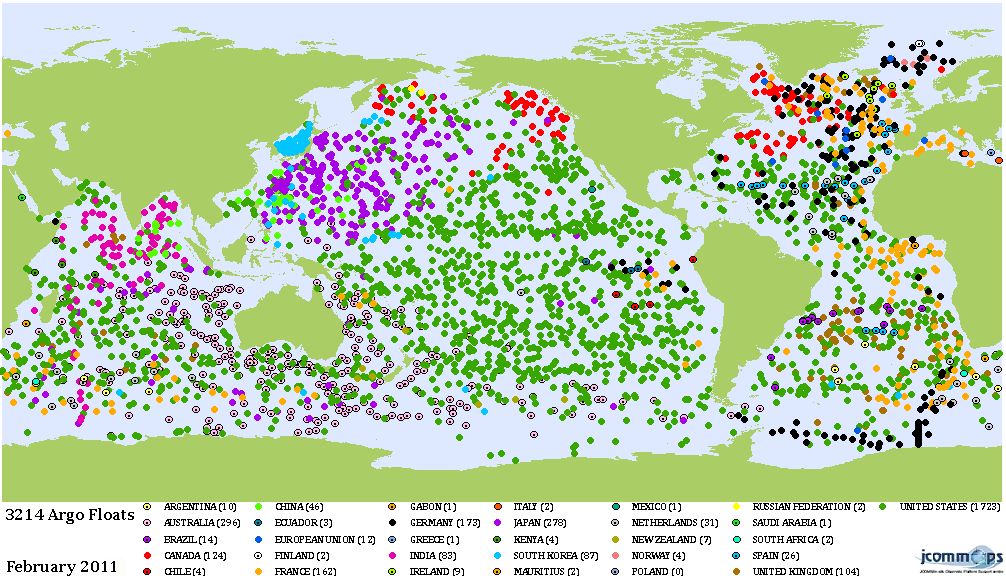
The gigantic network of robot sensors has resulted in a wealth of data, with more than 100 scientific papers published a year. However, it seems scientists on the project agree that Argo’s 10 year data set is not yet long enough to draw reliable conclusions for global change signals such as a global rise in ocean temperatures.
Here are some photos that explain the process:
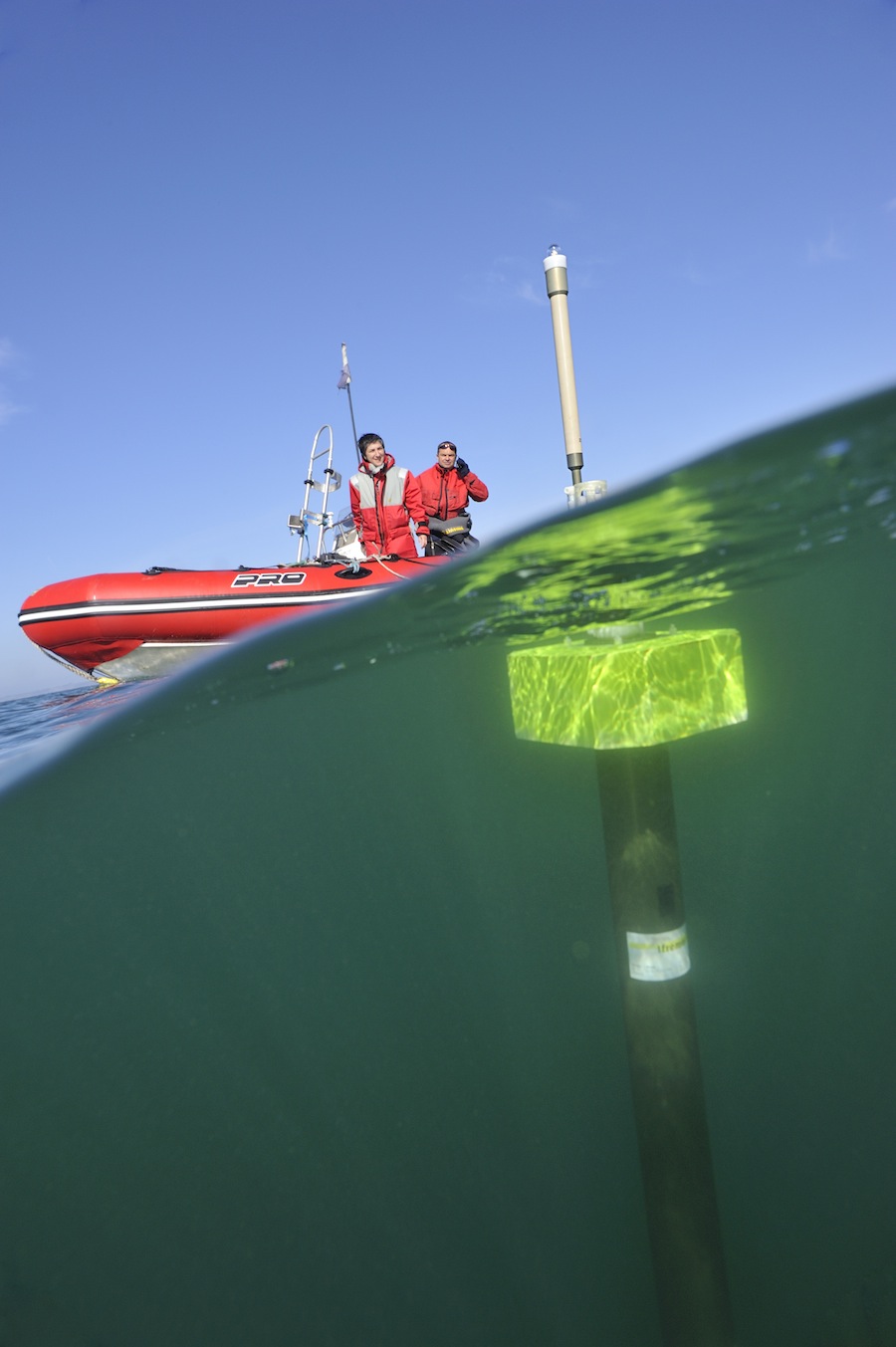

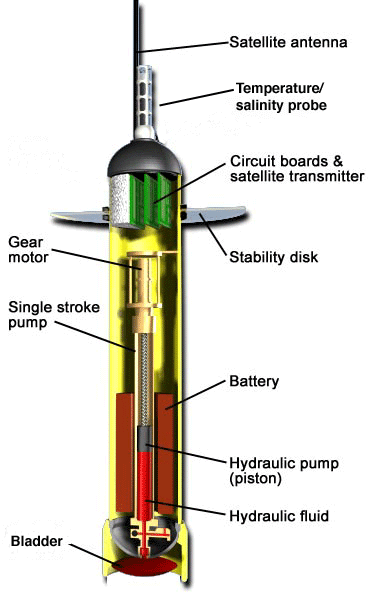
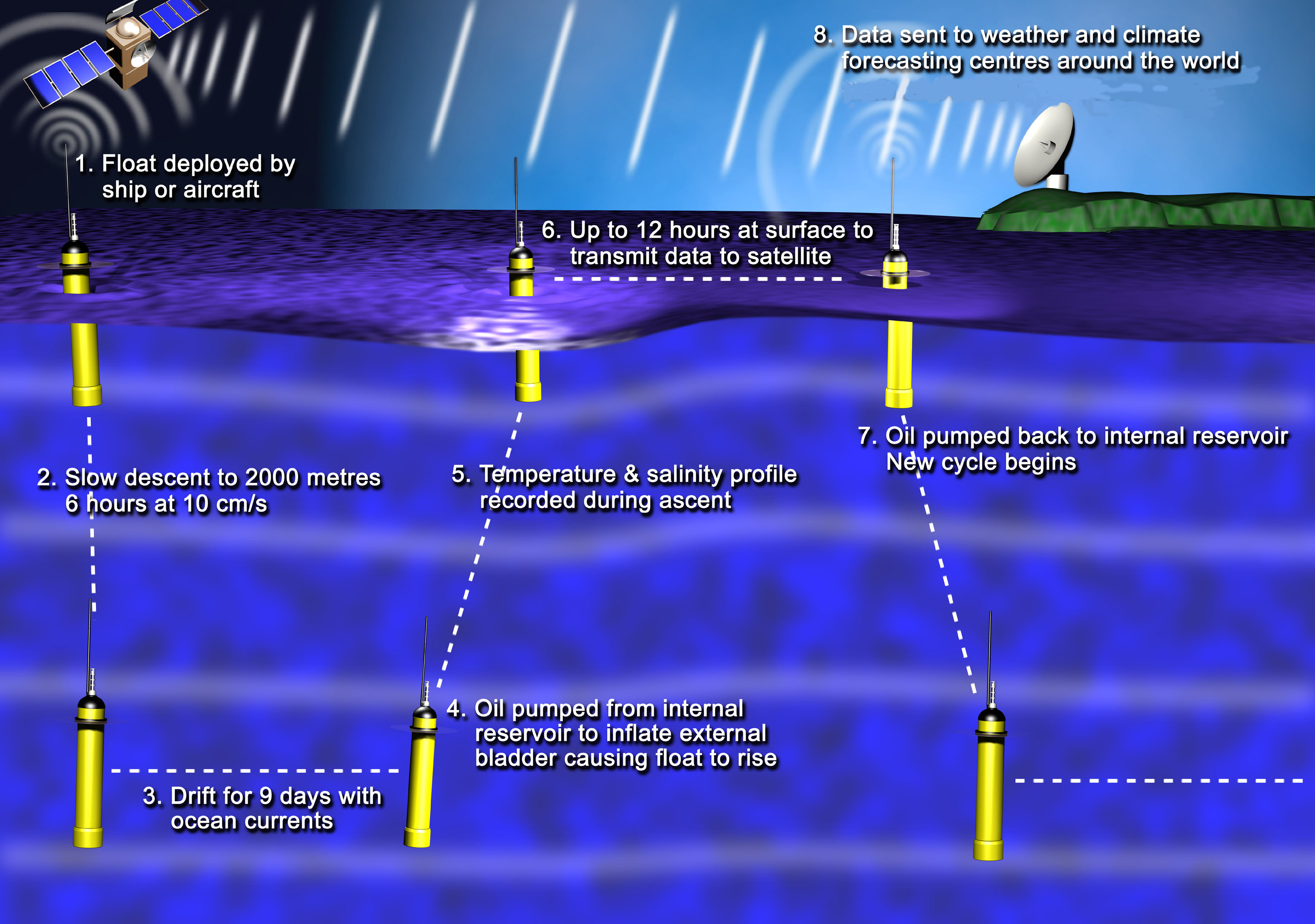
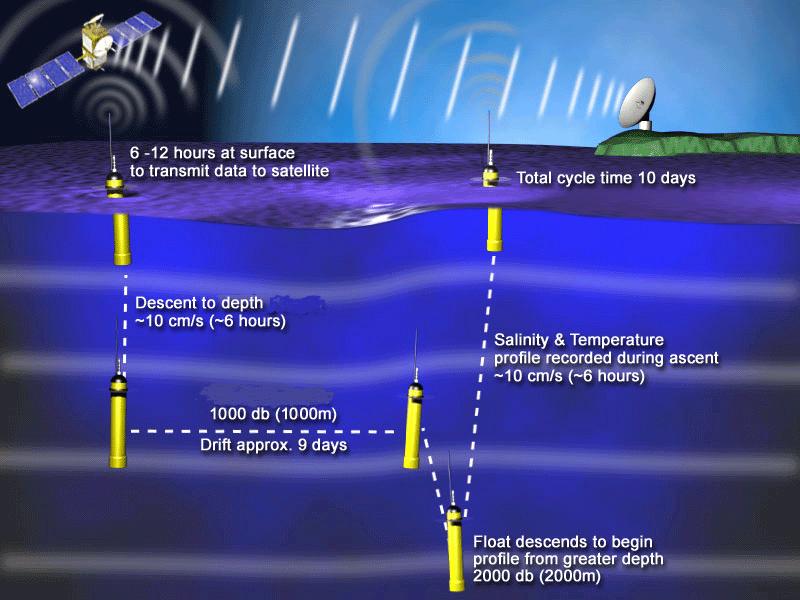
Photos: Argo project
tags: Business, c-Industrial-Automation, cx-Research-Innovation, review, robot, Sensing, Service Professional Field Robotics Other, UUV





