Robohub.org
Bipedal robot uses high-speed vision to run
We have developed a visually controlled bipedal running robot named ACHIRES: Actively Coordinated High-speed Image-processing Running Experiment System. This robot has a leg length of 14cm and 6 degrees of freedom, and can run in the sagittal plane at 4.2 km/h . Its key technologies are high-speed vision for recognizing the posture of the robot at 600 fps, and high-speed actuation for realizing high speed motion. The combination of these technologies plays an important role in the robot’s ability to run stably at high speeds.
In our laboratory we develop various types of high-speed vision hardware and algorithms that can implement high-speed image processing with a sampling time from 10ms up to 1ms. High-speed vision can provide control data at the same sampling rate as that of the servo controller used for the robot actuators. This means that vision can control actuators just like other sensors e.g. an encoder. Although at present the camera is located off board the robot, it will be attached to the body in future iterations.
In addition, we developed a light-weight, high-power actuator for high-speed motion. Its torque per weight ratio is 3.5 times higher than that of previous products of same actuators.
Those technologies are used in various demonstrations of our robots such as:
- Janken (Rock Paper Scissors)
- batting
- raw egg catching
- regrasping
- dribbling
- picking up with tweezers
- flexible material handling
- book flipping scanning
- 1ms pan/tilt
- micro visual feedback
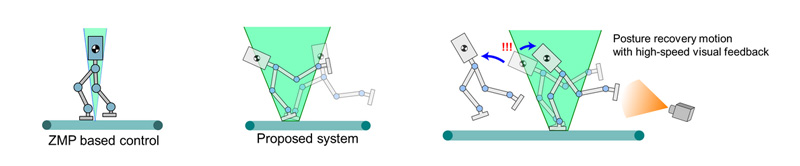
The running algorithm used in the ACHIRES robot is different from those typically used in other running robots. While most running robots use a method based on ZMP-criteria for maintaining stable and balanced posture, we introduced a very simple algorithm using high-speed performance of a sensory-motor system without ZMP criteria. The aerial posture is recovered to compensate for the deviation from the stable trajectory using high-speed visual feedback.
It took four years to develop ACHIRES, in part because analyzing robot dynamics that are faster than video capture rates requires high speed video analysis. You can see how the abilities of the robot have evolved since the project was first started in 2009:
Although ACHIRES is a research platform with no direct application at the present moment, the combination of high-speed vision and actuation could be applied to various types of high-speed intelligent systems, including high-speed robots, manufacturing systems, aircraft, microscope image control for bio/medical applications, and human-machine interfaces. We believe it will open new era of visual feed back systems.
More info:
Project Website
YouTube channel
Reference: T. Tamada, W. Ikarashi, D. Yoneyama, K. Tanaka, Y. Yamakawa, T. Senoo, M. Ishikawa: High Speed Bipedal Robot Running Using High Speed Visual Feedback, The Robotics Society of Japan The 32nd Annual Conference (RSJ2014) (Fukuoka, 2014)/1B2-03.
tags: Algorithm Controls, bipedal robot, c-Research-Innovation, Japan, machine vision, University of Tokyo