
Robohub.org
Bristol scientists develop insect-sized flying robots with flapping wings
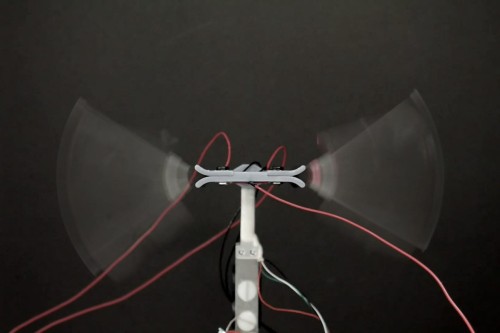
Front view of the flying robot. Image credit: Dr Tim Helps
This new advance, published in the journal Science Robotics, could pave the way for smaller, lighter and more effective micro flying robots for environmental monitoring, search and rescue, and deployment in hazardous environments.
Until now, typical micro flying robots have used motors, gears and other complex transmission systems to achieve the up-and-down motion of the wings. This has added complexity, weight and undesired dynamic effects.
Taking inspiration from bees and other flying insects, researchers from Bristol’s Faculty of Engineering, led by Professor of Robotics Jonathan Rossiter, have successfully demonstrated a direct-drive artificial muscle system, called the Liquid-amplified Zipping Actuator (LAZA), that achieves wing motion using no rotating parts or gears.
The LAZA system greatly simplifies the flapping mechanism, enabling future miniaturization of flapping robots down to the size of insects.
In the paper, the team show how a pair of LAZA-powered flapping wings can provide more power compared with insect muscle of the same weight, enough to fly a robot across a room at 18 body lengths per second.
They also demonstrated how the LAZA can deliver consistent flapping over more than one million cycles, important for making flapping robots that can undertake long-haul flights.
The team expect the LAZA to be adopted as a fundamental building block for a range of autonomous insect-like flying robots.
Dr Tim Helps, lead author and developer of the LAZA system said: “With the LAZA, we apply electrostatic forces directly on the wing, rather than through a complex, inefficient transmission system. This leads to better performance, simpler design, and will unlock a new class of low-cost, lightweight flapping micro-air vehicles for future applications, like autonomous inspection of off-shore wind turbines.”
Professor Rossiter added: “Making smaller and better performing flapping wing micro robots is a huge challenge. LAZA is an important step toward autonomous flying robots that could be as small as insects and perform environmentally critical tasks such as plant pollination and exciting emerging roles such as finding people in collapsed buildings.”
tags: bio-inspired, c-Research-Innovation, Flying, Micro




