
Robohub.org
Eliminating cords with wireless ‘millimeter wave’ virtual reality headsets
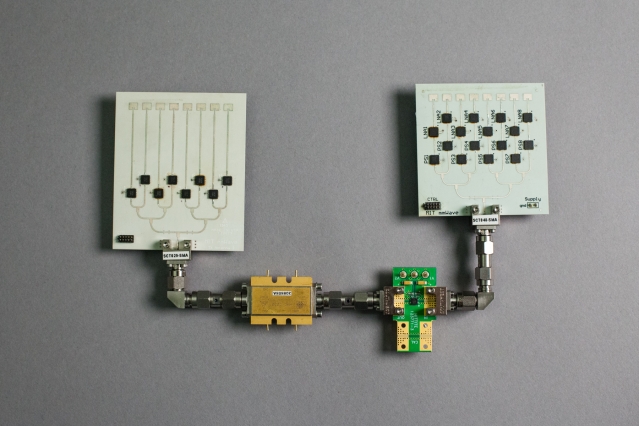
A new cordless virtual reality device consists of two directional “phased-array” antennas, each less than half the size of a credit card. Future versions could be small enough for users to have several in a single room, enabling multi-player gameplay. Photo: MIT CSAIL
One of the limits of today’s virtual reality (VR) headsets is that they have to be tethered to computers in order to process data well enough to deliver high-resolution visuals. But wearing an HDMI cable reduces mobility and can even lead to users tripping over cords.
Fortunately, researchers from MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) have recently unveiled a prototype system called “MoVR” that allows gamers to use any VR headset wirelessly.
In tests, the team showed that MoVR can enable untethered communication at a rate of multiple Gbps, or billions of bits per second. The system uses special high-frequency radio signals called “millimeter waves” (mmWaves) that many experts think could someday help deliver blazingly-fast 5G smartphones.
“It’s very exciting to get a step closer to being able to deliver a high-resolution, wireless-VR experience,” says MIT professor Dina Katabi, whose research group has developed the technology. “The ability to use a cordless headset really deepens the immersive experience of virtual reality and opens up a range of other applications.”
Researchers tested the system on an HTC Vive but say that it can work with any headset. Katabi co-wrote a paper on the topic with PhD candidate Omid Abari, postdoc Dinesh Bharadia, and master’s student Austin Duffield. The team presented their findings last week at the ACM Workshop on Hot Topics in Networks (HotNets 2016) in Atlanta.
How it works
One issue with existing wireless technologies like WiFi is that they can’t support advanced data-processing.
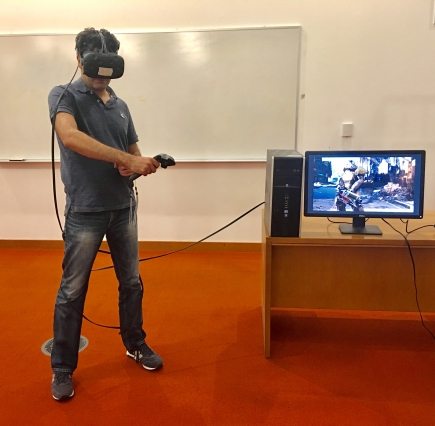

The “MoVR” system allows for cable-free virtual-reality gaming, eliminating the possibility of users tripping over cords. Photo: MIT CSAIL
“Replacing the HDMI cable with a wireless link is very challenging since we need to stream high-resolution multi-view video in real-time,” says Haitham Hassanieh, an assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Illinois at Urbana Champaigna who was not involved in the research. “This requires sustaining data rates of more than 6 Gbps while the user is moving and turning, which cannot be achieved by any of today’s systems.”
Since VR platforms have to work in real-time, systems also can’t use compression to accommodate lower data rates. This has led companies to make some pretty awkward attempts at untethered VR, like stuffing the equivalent of a full PC in your backpack.
The CSAIL team instead turned to mmWaves, which have promising applications for everything from high-speed Internet to cancer diagnosis. These high-frequency waves have one major downside, which is that they don’t work well with obstacles or reflections. If you want mmWaves to deliver constant connectivity for your VR game, you would need to always have a line of sight between transmitter and receiver. (The signal can be blocked even by just briefly moving your hand in front of the headset.)
To overcome this challenge, the team developed MoVR to act as a programmable mirror that detects the direction of the incoming mmWave signal and reconfigures itself to reflect it toward the receiver on the headset. MoVR can learn the correct signal direction to within two degrees, allowing it to correctly configure its angles.
“With a traditional mirror, light reflects off the mirror at the same angle as it arrives,” says Abari. “But with MoVR, angles can be specifically programmed so that the mirror receives the signal from the mmWave transmitter and reflects it towards the headset, regardless of its actual direction.”
Each MoVR device consists of two directional antennas that are each less than half the size of a credit card. The antennas use what are called “phased arrays” in order to focus signals into narrow beams that can be electronically steered at a timescale of microseconds.
Abari says that future versions of MoVR’s hardware could be as small as a smartphone, allowing for users to put several devices in a single room. This would enable multiple people to play a game at the same time without blocking each others’ signals.
tags: c-Research-Innovation, Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL), Computer science and technology, Electrical Engineering & Computer Science (eecs), gaming, Research, School of Engineering, wireless




