
Robohub.org
Insect-inspired mechanical resilience for multicopters

Over recent years the explosion in popularity of drones, both professionally and for amateur use, has inspired researchers to consider how to make flying robots as safe and robust as possible. Previous design methods have included producing bulky protective cages or making them as unlikely to crash as possible. Recently, researchers from Floreano Lab, NCCR Robotics and EPFL have presented a new approach to making crash resilient quadcopters – making them soft, so it doesn’t matter if they come into contact with their surrounding environment.
Improving on a previous iteration of a folding quadcopter, Stefano Mintchev, the lead researcher on the project, developed a quadcopter utilising the dual stiffness properties seen in insect wings. Insect wings are composed of sections made of cuticle, a stiff material that takes the load bearing portion of the wing, connected with flexible joints made of the protein resilin that have evolved to be shock absorbent and compliant. These two factors together allow insect wings to be both strong and load-bearing, and compliant and durable.
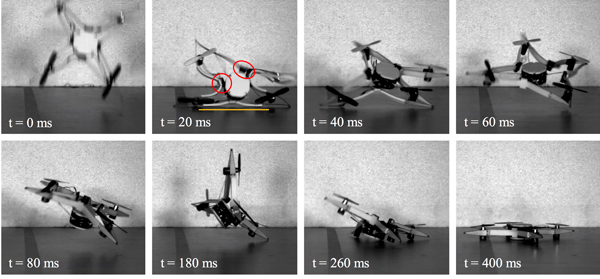
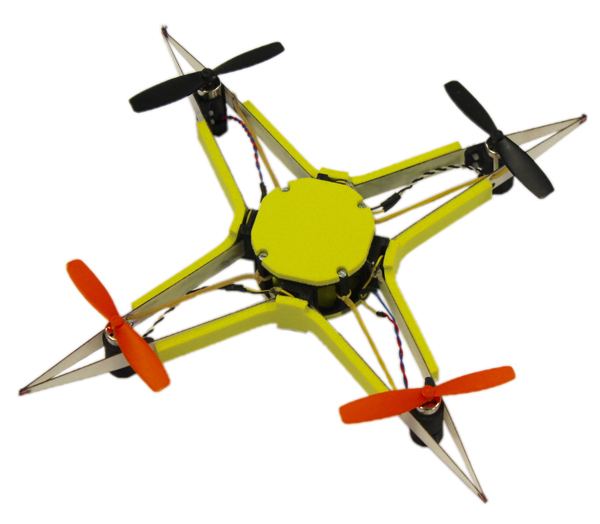
The presented drone is made of a central case and a thin fibreglass external frame with four arms held together by four magnetic joints. As this fibreglass frame is only 0.3mm thick, it is soft and flexible, making it able to withstand collisions without permanent deformation. The four magnetic joints connect the frame to the central case (modelled after hard insect exoskeletons, just to complete the inspiration from nature) and rigidly hold the frame in place during flight. Where these magnets come into their own, is that during a collision they break, meaning that the drone transition to a soft state where the frame becomes disengaged and can safely deform without damaging itself or the inner core. Soft elastic bands ensure that the frame is held close enough in place that the magnets snap back after the collision, allowing the frame to realign and thus ensuring that the drone is once again ready to fly.
The collision resistant drone was tested by dropping it from a height of 2m whereby it completely disengaged the magnetic joints and automatically restored to its pre-crash configuration. In fact, the drone was dropped over 50 times with no permanent damage. On top of that, the design means that the drones can have as many rotators as desired and is not limited to a quadcopter configuration.
Reference
S. Mintchev, S.D. De Rivas and D. Floreano. Insect-Inspired Mechanical Resilience for Multicopters, In IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2017.
tags: c-Aerial, EPFL, ETH Zurich, NCCR Robotics, quadcopters




