Robohub.org
Liability concerns for drone co’s imposing technical measures to enforce no fly zones
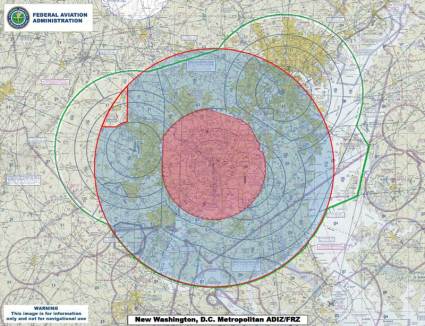
Shortly after a Phantom crash-landed on the grounds of the White House, its maker, DJI, announced that it would release a mandatory firmware update that would restrict flights within 15.5 miles of downtown Washington, D.C.
On Friday, Senator Schumer’s office released a statement urging the FAA to mandate that manufacturers impose technical controls to prevent drones from flying in high risk areas including near airports, other aircraft and the White House.
Whether drone manufacturers enforce “No Fly Zones” on their initiative as DJI has announced it will do, or whether they will be required to do so by the FAA at a later date, there are legal liability issues that should be considered.
If a manufacturer has not imposed technical measures to enforce No Fly Zones, and an operator enters a restricted area, liability is fairly straightforward. Assuming there is no design or manufacturing defect that causes the drone to fly into the restricted area, it is unlikely that the manufacturer would be held liable for any physical injury or property damage that may occur if the operator enters a No Fly Zone.
However, if a manufacturer implements technical measures to restrict drones from entering No Fly Zones, and such measures fail, they may be opening themselves up to legal liability if an operator flies into a restricted area and causes physical injury or property damage. Although it is unclear how liability may be allocated between an operator and a manufacturer in such a case, unless manufacturers are granted immunity from such lawsuits, they may be opening themselves up to liability by attempting to enforce No Fly Zones.
tags: c-Aerial, cx-Politics-Law-Society, DJI, drones, UAVs, White House drone crash