
Robohub.org
Micro bio-bots powered by beating heart cells
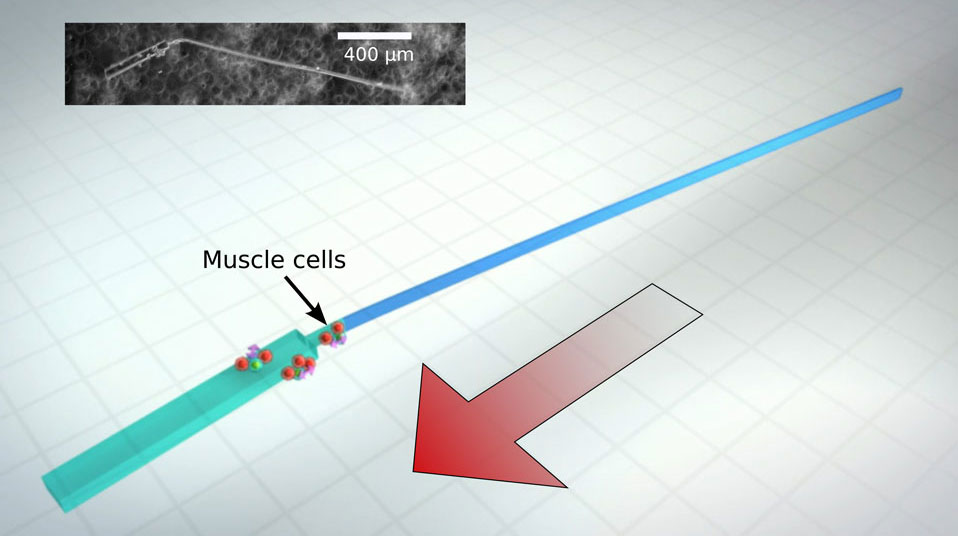
A paper in Nature Communications earlier this year reports on “bio-bots”. These tiny machines inspired by sperm, are a hybrid combination of live heart cells and a synthetic polymer body.
The new bots, developed by researchers from the University of Illinois and Arizona State University, are the first swimming micro-machines that mimic the flagellar movement of sperm to traverse the viscous fluids of biological environments. This means they can propel themselves onward, fired by the contractile power of heart cells. The bio-bots are just 2 millimeters long and basically consist of a head and a wire tail with the some live cells to make it functional. The small cluster of heart cells are grown at the intersection of the head and the tail. They are synchronized to beat together, creating a wave motion in the tail that can push the bot forward at a speed of up to 10 micrometers per second.
The bio-bot’s creators have also designed a similar micro-bot with two tails that can swim even faster; up to 81 micrometers per second. According to the team’s lead investigator, Taher Saif, this type of robotic phenomena is the first of its kind, and the team is not quite sure how the cells communicate to synchronize their movement. Saif explained that the additional tail allows the bio-bots to navigate. He predicts that future applications could include: chemical detection, light sensing or they could be programmed to reach a specific target for medical or environmental purposes.
While there is still much work to be done, this program marks the innovative first step towards a new realm of bio-hybrid machines. Saif teamed up with fellow University of Illinois researchers Brian J. Williams and Sandeep V. Anand, as well as Arizona State University’s Jagannathan Rajagopalan. Their work was completed as part of Emergent Behaviors in Integrated Cellular Systems (EBICS), a National Science Foundation-funded Science and Technology Center.
If you liked this article, you may also be interested in:
- Cell origami
- Micro-robotics and medicine: Interview with Toshio Fukuda
- Minimally-invasive eye surgery on the horizon as magnetically-guided microbots move toward clinical trials
- Crowdsourcing new strategies for cancer treatment: Towards swarming nanobots
- Medical robotic systems market to reach $13.6 billion by 2018
See all the latest robotics news on Robohub, or sign up for our weekly newsletter.
tags: Actuation, bio-inspired, c-Research-Innovation, cx-Health-Medicine, Swarming







