
Robohub.org
Robot-ants that communicate and work together
A team of EPFL researchers has developed tiny 10-gram robots that are inspired by ants: they can communicate with each other, assign roles among themselves and complete complex tasks together. These reconfigurable robots are simple in structure, yet they can jump and crawl to explore uneven surfaces. The researchers have just published their work in Nature.
Individually, ants have only so much strength and intelligence. However, as a colony, they can use complex strategies for achieving sophisticated tasks to survive their larger predators.
At EPFL, researchers in NCCR Robotics Professor Jamie Paik’s Laboratory have reproduced this phenomenon, developing tiny robots that display minimal physical intelligence on an individual level but that are able to communicate and act collectively. Despite being simple in design and weighing only 10 grams, each robot has multiple locomotion modes to navigate any type of surface. Collectively, they can quickly detect and overcome obstacles, pass them and move objects much larger and heavier than themselves. The related research has been published in Nature.
Robots modeled on trap-jaw ants
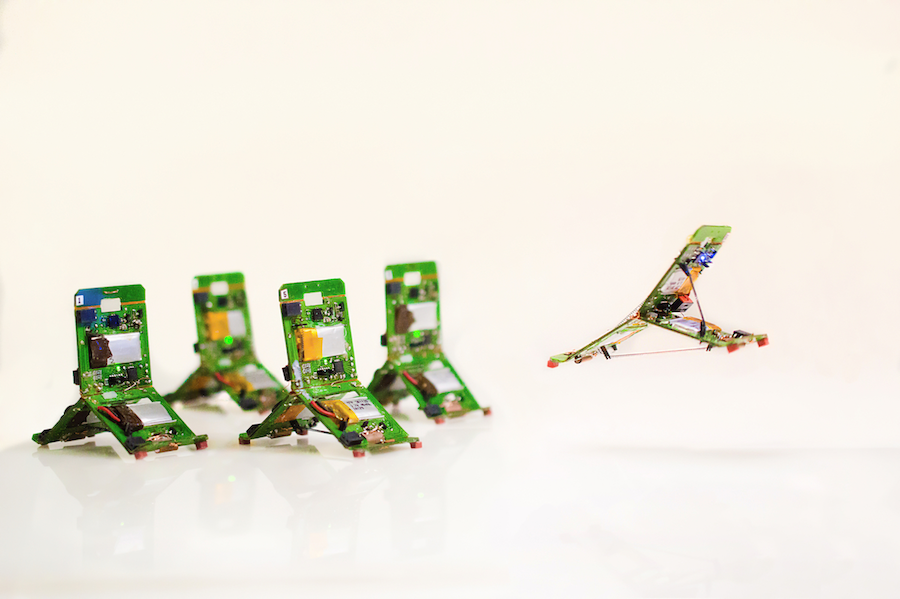
These three-legged, T-shaped origami robots are called Tribots. They can be assembled in only a few minutes by folding a stack of thin, multi-material sheets, making them suitable for mass production. Completely autonomous and untethered, Tribots are equipped with infrared and proximity sensors for detection and communication purposes. They could accommodate even more sensors depending on the application.
“Their movements are modeled on those of Odontomachus ants. These insects normally crawl, but to escape a predator, they snap their powerful jaws together to jump from leaf to leaf”, says Zhenishbek Zhakypov, the first author. The Tribots replicate this catapult mechanism through an elegant origami robot design that combines multiple shape-memory alloy actuators. As a result, a single robot can produce three distinctive locomotive motions – crawling, rolling and jumping both vertically and horizontally – just like these creatively resilient ants.
Roles: leader, worker and explorer
Despite having the same “anatomy”, each robot is assigned a specific role depending on the situation. ‘Explorers’ detect physical obstacles in their path, such as objects, valleys and mountains. After detecting an obstacle, they inform the rest of the group. Then, the “leader” gives the instructions. The ‘workers’, meanwhile, pool their strength to move objects. “Each Tribot, just like Odontomachus ants, can have different roles. However, they can also take on new roles instantaneously when faced with a new mission or an unknown environment, or even when other members get lost. This goes beyond what the real ants can do” says Paik.

Future applications
In practical situations, such as in an emergency search mission, Tribots could be deployed en masse. And thanks to their multi-locomotive and multi-agent communication capabilities, they could locate a target quickly over a large surface without relying on GPS or visual feedback. “Since they can be manufactured and deployed in large numbers, having some ‘casualties’ would not affect the success of the mission,” adds Paik. “With their unique collective intelligence, our tiny robots are better equipped to adapt to unknown environments. Therefore, for certain missions, they would outperform larger, more powerful robots.” The development of robots for search-and-rescue applications and the study of collective robotics are key research areas within the NCCR Robotics consortium, of which Jamie Paik’s lab is part.
In April, Jamie Paik has presented her reconfigurable robots at the TED2019 Conference in Vancouver. Her talk is available here.
Literature
Zhenishbek Zhakypov, Kazuaki Mori, Koh Hosoda and Jamie Paik, Designing minimal and scalable insect-inspired multi-locomotion millirobots, Nature
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1388-8
tags: herotagrc




