
Robohub.org
Soft robots for ocean exploration and offshore operations: A perspective
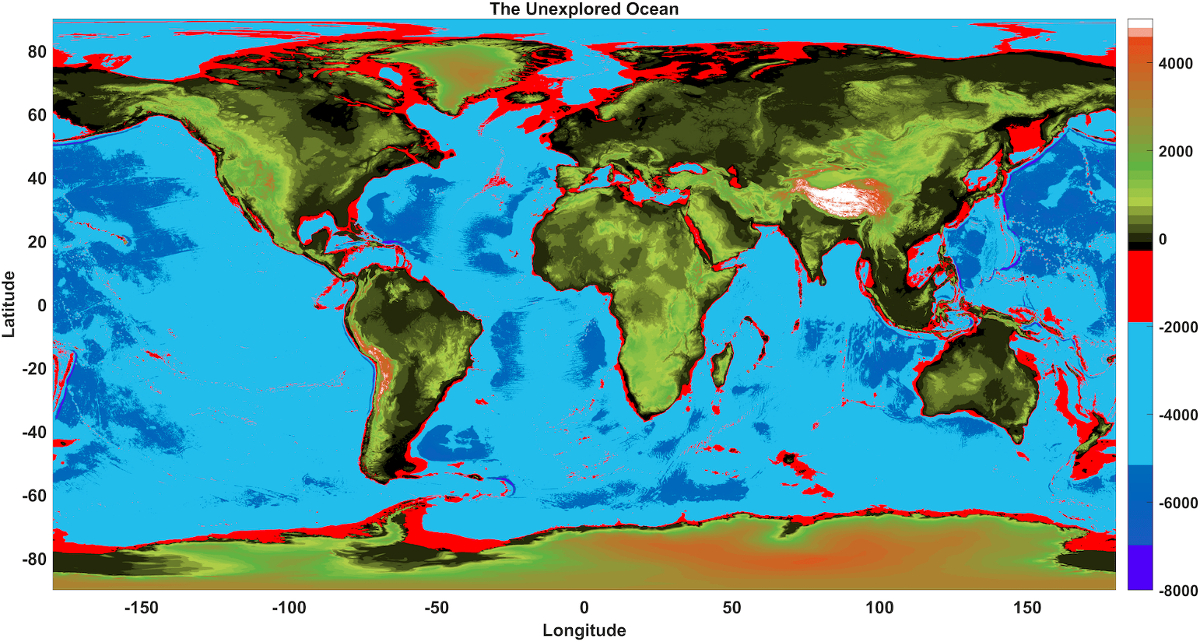
Most of the ocean is unknown. Yet we know that the most challenging environments on the planet reside in it. Understanding the ocean in its totality is a key component for the sustainable development of human activities and for the mitigation of climate change, as proclaimed by the United Nations. We are glad to share our perspective about the role of soft robots in ocean exploration and offshore operations at the outset of the ocean decade (2021-2030).
In this study of the Soft Systems Group (part of The School of Engineering at The University of Edinburgh), we focus on the two ends of the water column: the abyss and the surface. The former is mostly unexplored, containing unknown physical, biological and chemical properties; the latter is where industrial offshore activities take place, and where human operators face dangerous environmental conditions.
The analysis of recent developments in soft robotics brought to light their potential in solving some of the challenges that industry and scientists are facing at sea. The paper offers a discussion about how we can use the latest technological advances in soft robotics to overcome the limitations of existing technology. We synthesise the crucial characteristics that future marine robots should include.
Today we know that industrial growth needs to be supported by deep environmental and technological knowledge in order to develop human activities in a sustainable manner. Therefore, the remotest areas of the ocean constitute a common frontier for oceanography, robotics and offshore industry. The first challenge then is to create an interdisciplinary space where marine scientists, ocean engineers, roboticists and industry can communicate.
The offshore renewable energy sector is growing fast. By definition, wind and wave energy is better sourced from areas of the seas with a high energy content, which translates into wave dominated environments. In such conditions, operating in the vicinity of an offshore platform is dangerous for personnel and potentially destructive for traditional robots.
Recent development in soft robotics unveiled novel, bio-inspired maneuvering techniques, fluidic logic data logging capabilities and unprecedented dexterity. These characteristics would enable data collection, maintenance and repair interventions, unfeasible with rigid robots.
Traditional devices, often tethered, rigid and with limited activity range, cannot tackle the environmental conditions where ocean exploration is needed the most. The devices needed for ocean exploration require an innovative payload and delicate sampling capabilities. Soft sensors and soft gripping techniques are optimum candidates to push ocean exploration into fragile and unknown areas that require delicate sampling and gentle navigation. The inherent compliance of soft robots also protects the environment and the payload from damage. More importantly, recent studies have highlighted the potential for the manufacturing of soft robots to be entirely biocompatible and, hence, to minimise the impact on the natural environment in case of loss or mass deployment.
In a nutshell, soft robots for marine exploration and offshore deployment offer the advantage, over traditional devices, of novel navigation and manipulation techniques, unprecedented sensing and sampling capabilities, biocompatibility and novel memory and data logging methods. With this study we wish to invite a multidisciplinary approach in order to create novel sustainable soft systems.
tags: bio-inspired, c-Research-Innovation





