
Robohub.org
Teaching robots the physics of sliding and pushing objects
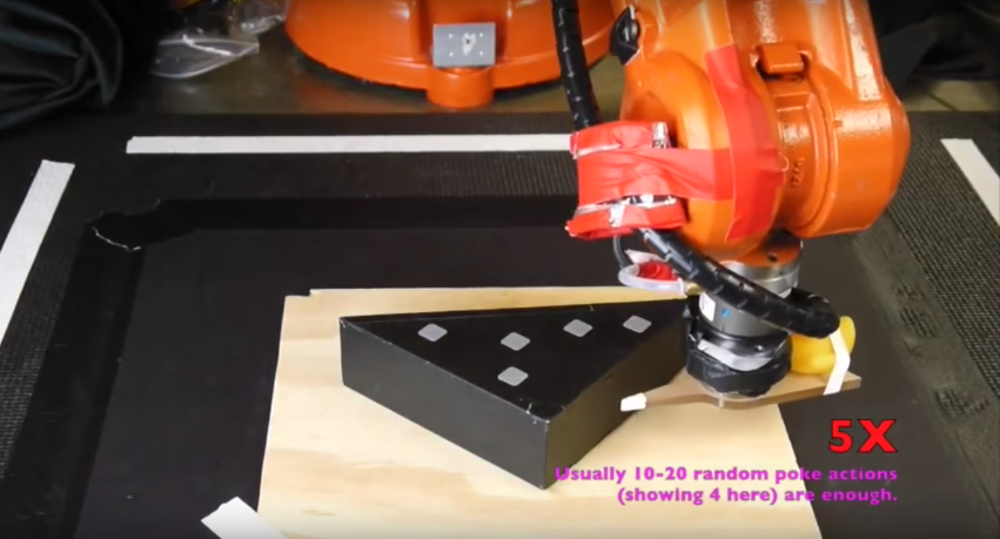
Robot learns to push object and identifies patch friction model. Source: YouTube
The Manipulation Lab at the CMU Robotics Institute proposes a computational model that relates an applied robot action to the resultant object motion. Their research won the Best Conference Paper Award at ICRA 2016.
Understanding the mechanics of manipulation is essential for robots to autonomously interact with the physical world. One of the common manipulation scenarios involves pushing objects in a plane subject to dry friction. We propose a planar friction (force-motion) model that relates an applied robot action to the resultant object motion.
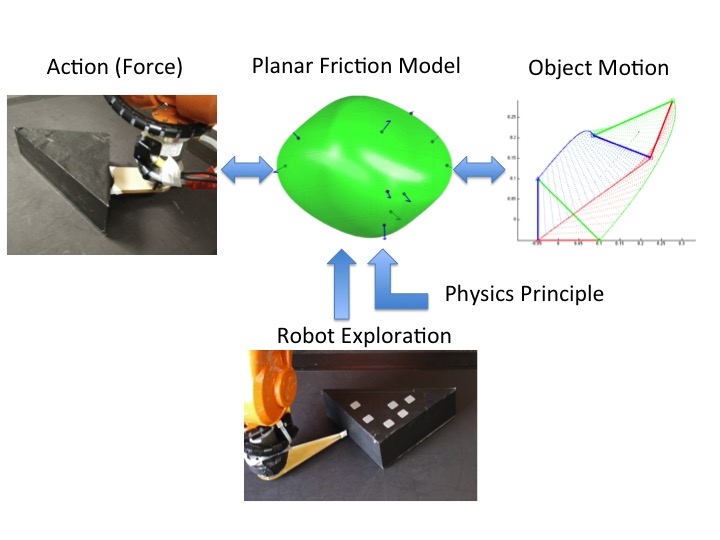
The robot randomly pokes the object of known shape with a point finger to collect force-motion data. We then optimize a convex polynomial friction representation with physics-based constraints. Based on the representation, we demonstrate applications of stable pushing and dynamic sliding simulation.
The difficulty lies in that the contact between the object and supporting surface is an area-to-area contact with unknown pressure distribution. We don’t know which part of the area is supporting how much weight nor do we know the coefficient of friction. This makes object motion hard to predict. The key observation is the space of generalized friction force forms a convex set based on the principle of maximum dissipation (a generalized Coulomb’s friction law) [1]. The boundary of such set is termed as limit surface [2]. The geometry of such surface, albeit convex, can be complicated. Fortunately, we have shown that level sets of sum of squares convex polynomials turn out to be good geometric approximations. Another advantage is the model is very data-efficient, i.e., model identification only requires few force and velocity data collected by the robot pushing the object with a point finger. There are some additional nice provable properties of the models, and with these properties, we are able to perform applications including stable pushing and free sliding dynamics simulation.
[1] J. J. Moreau, “Unilateral contact and dry friction in finite freedom dynamics,” in Nonsmooth Mechanics and Applications, pp. 1–82, Springer, 1988.
[2] S. Goyal, A. Ruina, and J. Papadopoulos, “Planar sliding with dry friction. Part 1. Limit surface and moment function,” Wear, vol. 143, pp. 307–330, 1991.
Paper: A Convex Polynomial Force-Motion Model for Planar Sliding: Identification and Application: Jiaji Zhou, Robert Paolini, James Bagnell, Matthew T. Mason
Read the award winning paper here.
tags: c-Research-Innovation, ICRA16





