Robohub.org
TERESA project adds a vital component to human-robot interaction: social intelligence
TERESA is a 3-year research project funded by the European Union and carried out by six institutions from four European countries. Its goal is to develop a new socially intelligent semi-autonomous telepresence system.
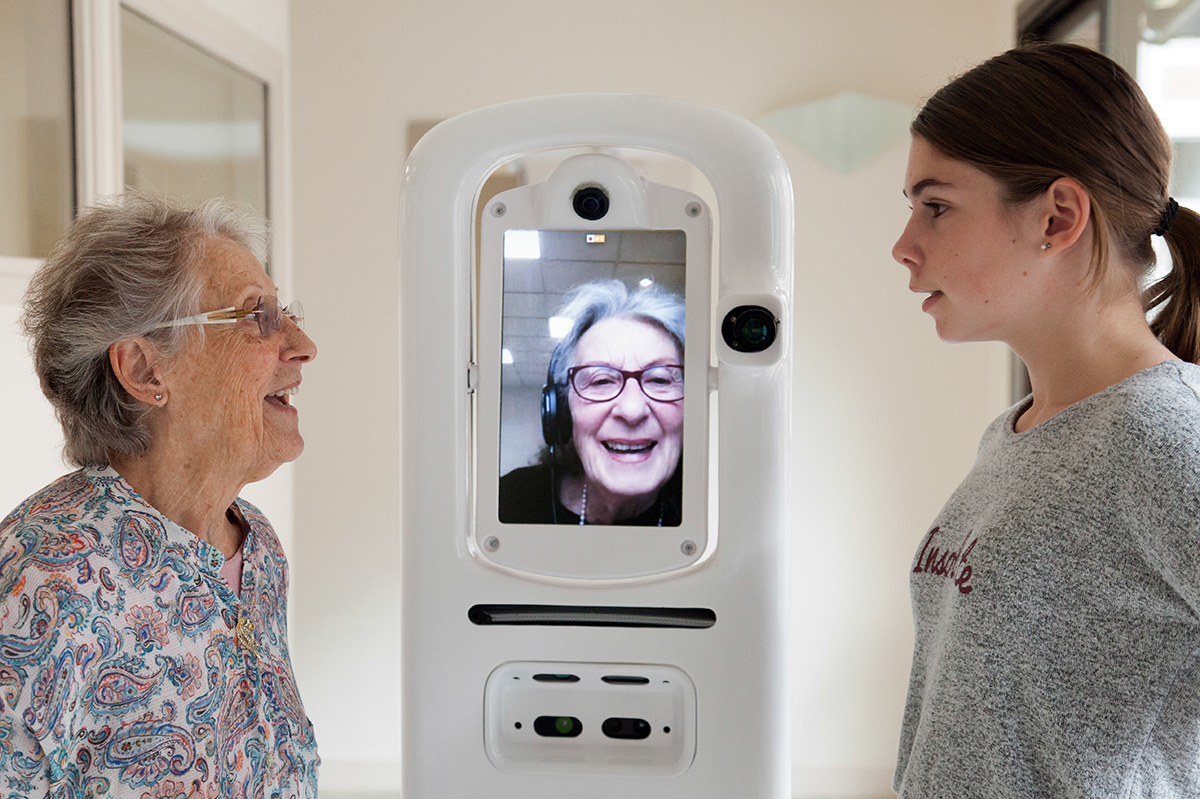
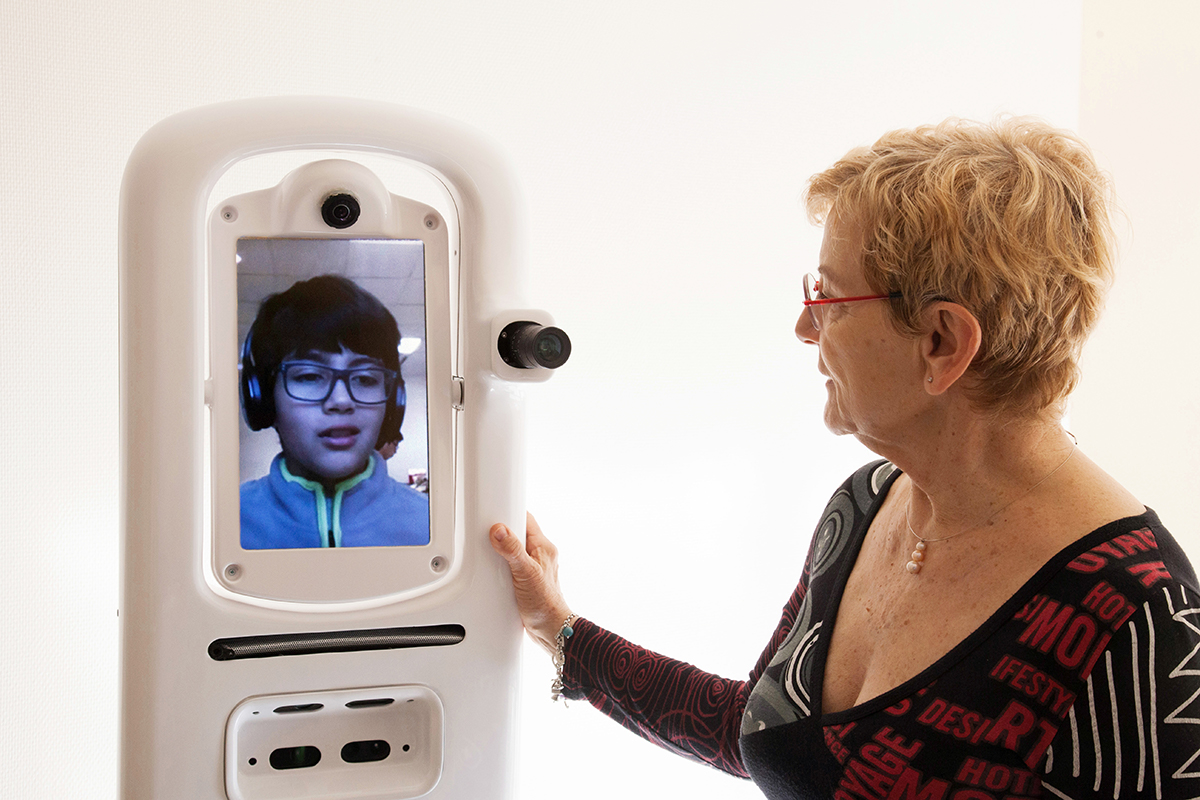
A telepresence system consists of an internet-connected mobile robot equipped with a video screen, speakers, and microphones. A remotely located pilot sitting at a computer can control the robot and use it to interact with people at the robot’s location.
Telepresence systems offer a number of advantages over traditional teleconferencing solutions such as Skype. The robot acts as an avatar for the pilot, allowing the pilot to appear much more present to people around the robot. In addition, because a telepresence robot is mobile, it enables spontaneous interaction, such as mingling at a cocktail party, that would not be possible with Skype.
However, existing telepresence systems suffer from a key limitation. They require the pilot to manually execute many behaviours that would happen automatically and effortlessly if the pilot was physically present. These include navigating through groups of people in a socially appropriate way, maintaining a socially appropriate distance and orientation to others, and maintaining socially appropriate eye contact.
The need to manually execute these low-level behaviours at the same time as selecting high-level behaviours, such as whom to talk to and what to say, can afflict the pilot with cognitive overload, which in turns leads to poor quality social interaction.
In the TERESA project, we have created a new semi-autonomous telepresence system that automates low-level decision making, thereby freeing the pilot to focus on the social interaction itself. TERESA can autonomously navigate through groups of people in a socially intelligent way and approach a specific person selected by the pilot. During conversation, TERESA can also maintain a socially appropriate distance from those around the robot and set the height, orientation, and tilt of its video screen so as to facilitate that conversation.
TERESA is not just intelligent but socially intelligent, thanks to advances in multi-modal perception, machine learning, and robotics developed in the project by an interdisciplinary team of computer scientists, engineers, sociologists, and experts in human-robot interaction.
Working with an elderly day centre in France, we have repeatedly validated TERESA with dozens of elderly subjects. Our results show that semi-autonomous telepresence systems can play a key role in improving the quality of remote interaction. Although TERESA is just a proof of concept, it illustrates the potential of social intelligence to transform telepresence systems and other robots as well.
If you enjoyed this article, you may want to read more about telepresence robotics:
- Telepresence robots help chronically ill kids maintain social, academic ties at school
- Telepresence has come a long way, where do we go from here?
- Personalizing telepresence in service robots
- ORIGIBOT: An affordable telepresence robotic test platform with arm and gripper
- Telepresence, or tele-existence? 4 devices seeking to break down barriers to remote presence
See all the latest robotics news on Robohub, or sign up for our weekly newsletter.
tags: c-Research-Innovation, human-robot interaction, robotics, robots, telepresence