
Robohub.org
EduExo: Robotic exoskeletons for everyone
For decades robotic exoskeletons were the subject of science fiction novels and movies. But in recent years, exoskeleton technology has made huge progress towards reality and exciting research projects and new companies have surfaced.
Typical applications of today’s exoskeletons are stroke therapy or support of users with a spinal cord injury, or industrial applications, such as back support for heavy lifting or power tool operation. And while the field is growing quickly, it is currently not easy to get involved. Learning materials or exoskeleton courses or classes are not widely available yet. This has made it difficult, as learning about exoskeletons is not possible by theory alone, but ideally, involves practical hands-on experience (feel it understand it). Unfortunately, the necessary exoskeleton hardware is expensive and not usually available to students or hobbyists wanting to explore the field.
This is the motivation behind the EduExo kit, a 3D-printable, Arduino-powered robotic exoskeleton now on Kickstarter. The goal of the project is to make exoskeleton technology available, affordable and understandable for anyone interested.
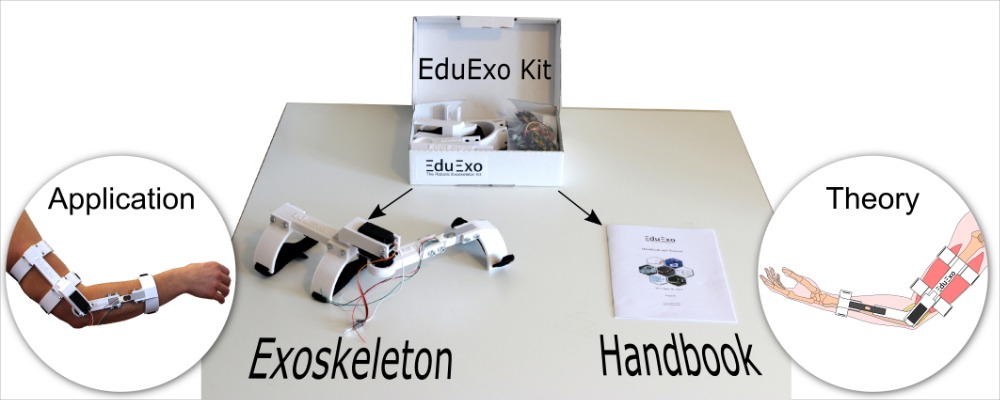
The EduExo is a robotic exoskeleton kit that you assemble and program yourself. The kit contains all the hardware you need to build an elbow exoskeleton. An accompanying handbook contains a tutorial that will guide you through the different assembly steps. In addition, the handbook provides background information on exoskeleton history, functionality and technology to offer a well-rounded introduction to the field.

The kit is being developed for the following users:
- High school and college students who want to learn about robotic exoskeleton technology to prepare themselves for a career in exoskeletons and wearable robotics.
- Makers and hobbyists who are looking for an interesting and entertaining project in a fascinating field.
- Teachers and professors who want to set up exoskeleton courses or labs. The EduExo classroom set provides additional teaching material to facilitate the preparation of a course.
The main challenge of the project was to design exoskeleton hardware that is both cheap enough to be affordable for a high school student, but still complex enough to be an appropriate learning platform that teaches relevant and state of the art exoskeleton technology.
To lower the price, mostly off-the-shelf components are used. The hardware is a simple one degree of freedom design for the elbow joint. The EduExo box comes fully equipped and contains the handbook, exoskeleton structure, preassembled cuffs, an Arduino Microcontroller to control the device, a force sensor (and amplifier) to measures the human-robot interaction, a servo motor for the actuation and all the small parts needed to assemble and wire the exoskeleton.
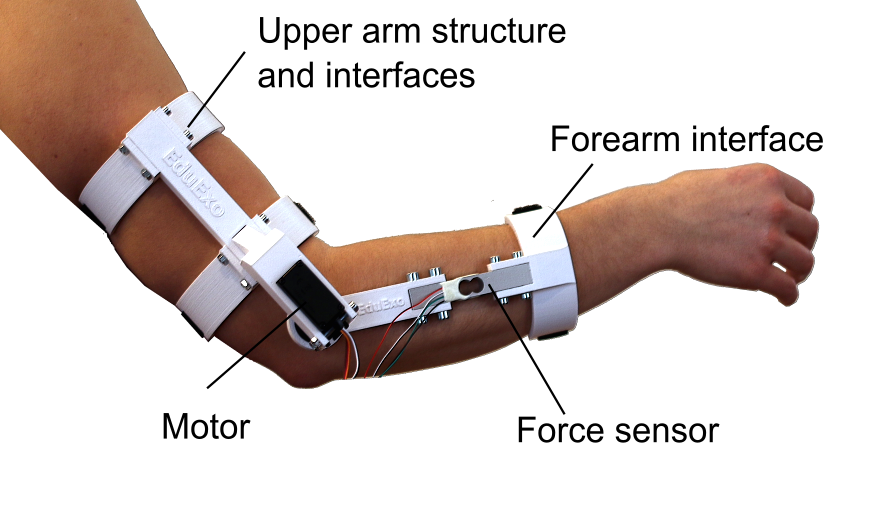
The exoskeleton’s structure is 3D printable and users with access to a 3D printer can produce the parts themselves. Therefore, a maker edition is available for people who prefer doing everything themselves.
The software required to program the exoskeleton and to create computer games can be downloaded for free (Arduino IDE to program the Microcontroller and the Unity 3D game engine).
Despite the comparatively simple design, the EduExo will teach its users many interesting aspects of exoskeleton technology. This includes how the mechanical design resembles the human anatomy, how to connect the sensors and the electronics board, and how to design and program an exoskeleton control system. Further, it explains how to connect the exoskeleton to a computer and learn how to use it as a haptic device in combination with a self-made virtual reality simulation or computer game.
A ‘muscle control’ extension is offered separately that explains how to measure the exoskeleton user’s muscle activity and use it to control the device.
The development of the kit is currently in its final phase and it is already possible to order it through the ongoing Kickstarter campaign. Shipping is scheduled for August 2017.
Additional information can be found on the EduExo website: www.eduexo.com
tags: c-Education-DIY, exoskeleton, Kickstarter, robot, robotics





