Robohub.org
Customer story: Deployable, autonomous vibration control of bridges using Husky UGV
Sriram Narasimhan’s research team are shaking things up in the Civil Engineering Structures Lab at the University of Waterloo. The research, which is led by Ph.D Candidate Kevin Goorts, is developing a new mobile damping system for suppressing unwanted vibrations in lightweight, flexible bridges. Whereas damping systems are often permanent fixtures built into the bridge, their system is designed to be adaptable, autonomous, and better suited for rapid, temporary deployment.
A SHIFT TOWARDS FLEXIBLE, LIGHT-WEIGHT STRUCTURES
Their work follows a recent industry shift towards using lightweight materials in the construction of civil engineering structures. Driven primarily by cost savings, as well as both the ease and speed of deployment, these lightweight structures could be a pedestrian bridge or a temporary bridge used in disaster relief scenarios, and are often more sensitive to external forces due to the reduced self-weight, and therefore require auxiliary damping devices.

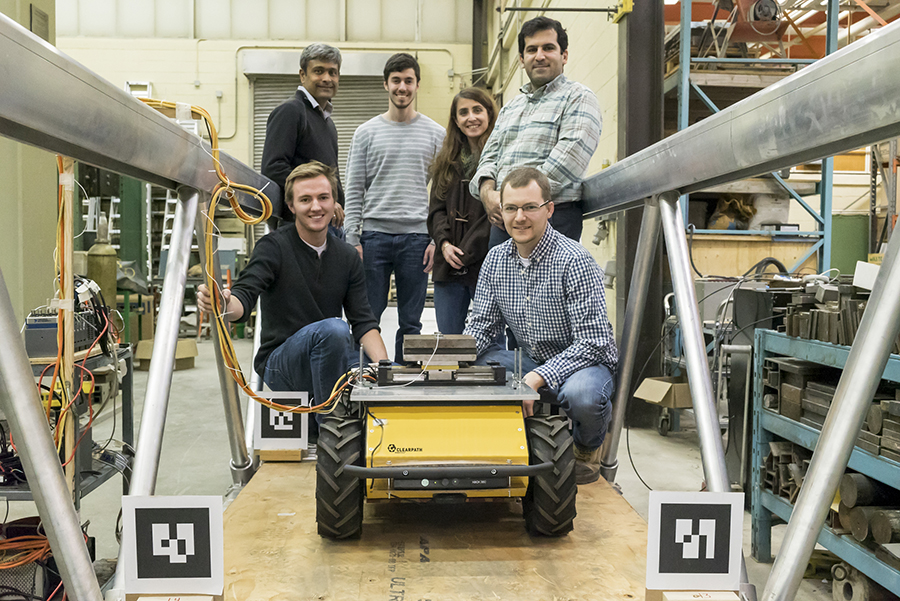
Husky-based mobile bridge damping system on a full-scale aluminum pedestrian bridge. Image: Clearpath
HUSKY UGV: THE IDEAL MOBILE ROBOTIC PLATFORM
At the center of the team’s mobile control system is a Husky unmanned ground vehicle (UGV). An electromechanical mass damper mounted on top of the Husky is used to generate inertial control forces which are magnified by the body dynamics of the Husky. When situated on a bridge, the system is able to respond to changes in the structural response by autonomously positioning itself at the appropriate location and applying the desired control force.
For Goorts’ research, Husky UGV was the ideal mobile base upon which to develop their system. “The Husky is a rugged vehicle suitable for outdoor applications with sufficient payload capacity for both the damper and associated computational equipment.” said Goorts. “The low-profile and large lug thread tires are well suited for providing the necessary static friction to prevent sliding and transfer control forces. Moreover, Husky’s readily available ROS (Robot Operating System) integration allowed us to use several sensor types and position control algorithms.”
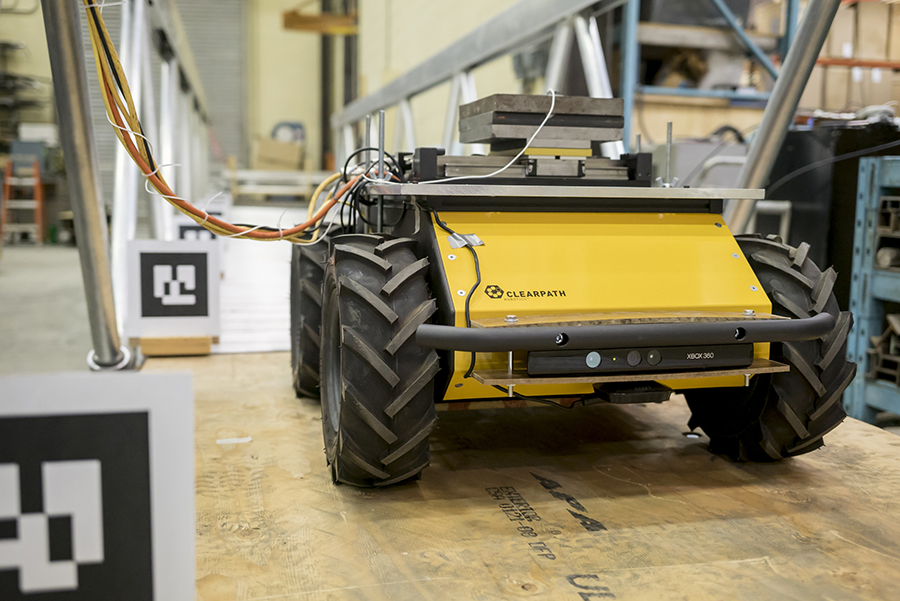

Linear motor and front-facing Kinect vision sensor mounted on Husky UGV mobile base. Image: Clearpath
The Husky is also equipped with a laptop running ROS and Kinect vision sensors on the front and back of the vehicle. Using wheel encoder data and measurements from the Kinect sensors, the system is able to perform SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) and autonomously navigate back and forth along the span of the bridge. One of the immediate challenges the team faced was getting the robot to accurately localize on a bridge with a repetitive structural design – everything looked the same to the robot from different positions. To overcome this, they placed unique AR (augmented reality) tags along the bridge between which the robot could navigate.
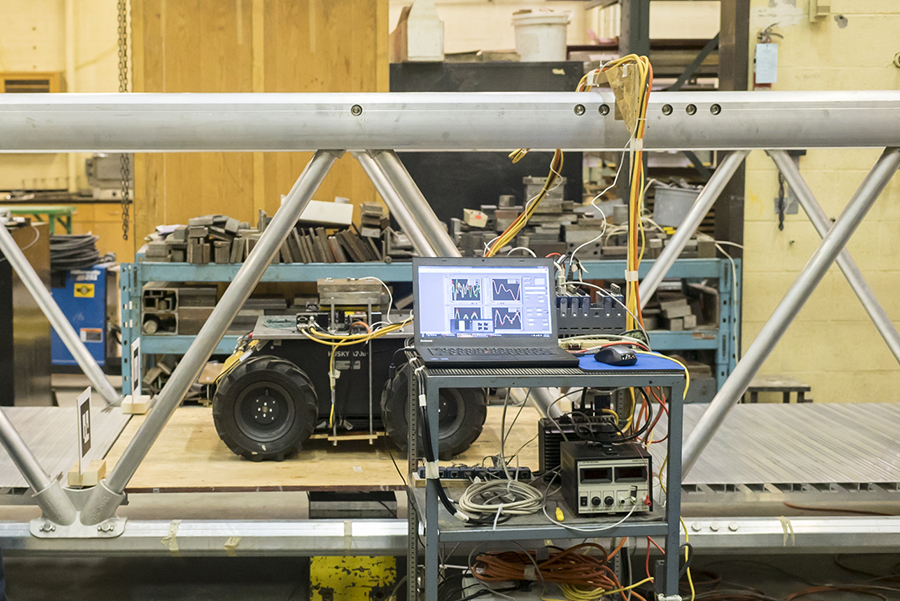
A National Instruments (NI) cRIO is being used for all data processing tasks and execution of the structural control loops, and a TCP data link communicates between the ROS laptop and cRIO. Image: Clearpath.
BRIDGE VIBRATIONS REDUCED BY 70%
The effectiveness of the control system is tested using real-time hybrid simulation (RTHS), a dynamic testing method that couples the physical control system with a numerical model of the structure. These tests were carried out on a full-scale aluminum pedestrian bridge with re-designed panels to measure the forces being applied by the system. Results from the simulations show the system can provide up to a 70% reduction in the lateral displacement of the bridge.
The current prototype is suitable for bridges with a mass up to 1-tonne and is scalable to accommodate larger structures, either with a larger vehicle or with multiple vehicles that work cooperatively. Looking forward, the team is exploring the idea of making the system vehicle agnostic, which could allow any vehicle to be turned into an autonomous bridge stabilizing machine.
The post Customer Story: Deployable, Autonomous Vibration Control of Bridges Using Husky UGV appeared first on Clearpath Robotics.
If you liked this article, you may also be interested in:
- Clearpath Robotics launches “Warthog UGV”, the amphibious robot
- Interview: International Ground Vehicle Ground Competition (IGVC) winner on “Bigfoot 2” Husky UGV
- 4 reasons why Industry 4.0 will leave AGVs behind
- 5 innovation challenges in materials transport
- Clearpath and Christie demo 3D video game with robots
See all the latest robotics news on Robohub, or sign up for our weekly newsletter.
tags: c-Research-Innovation, Clearpath Robotics, cx-Industrial-Automation, Husky, Prototype, Research, Robotics technology, Sensing, Service Professional Other, UGV






