Robohub.org
Natural scale caterpillar soft robot is powered and controlled with light
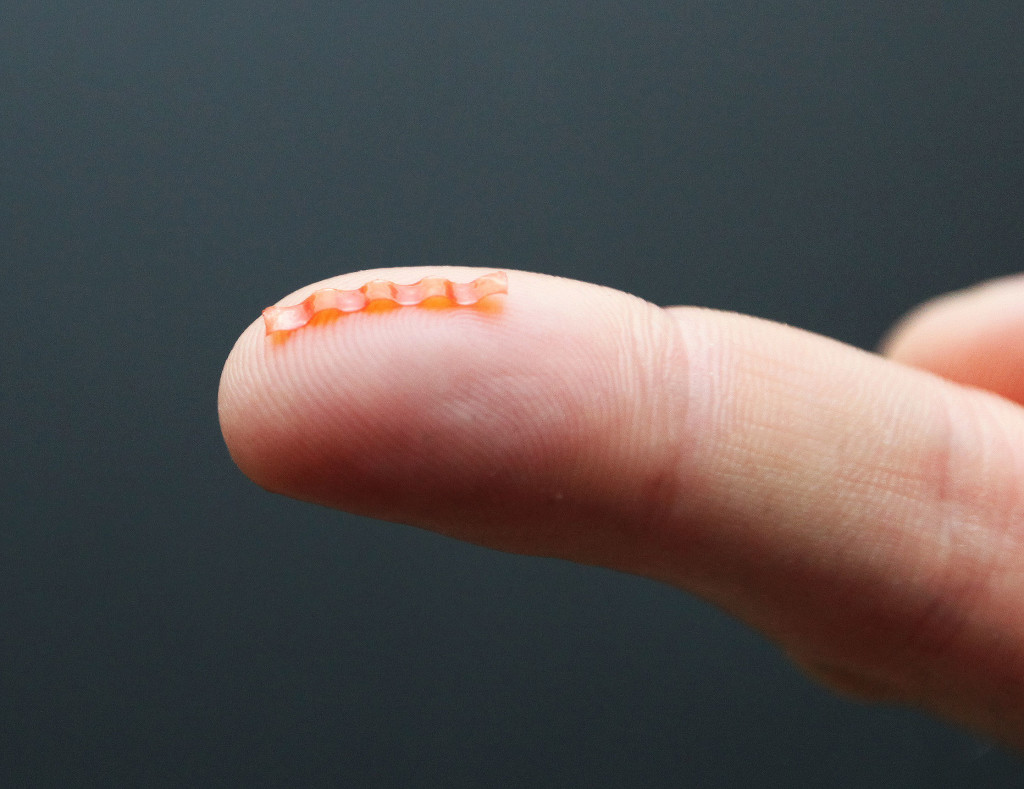
Researchers at the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw, using the liquid crystal elastomer technology, originally developed in the LENS Institute in Florence, demonstrated a bioinspired micro-robot capable of mimicking caterpillar gaits in natural scale. The 15-millimeter long soft robot harvests energy from green light and is controlled by spatially modulated laser beam. Apart from travelling on flat surfaces, it can also climb slopes, squeeze through narrow slits and transport loads.
For decades scientists and engineers have been trying to build robots mimicking different modes of locomotion found in nature. Most of these designs have rigid skeletons and joints driven by electric or pneumatic actuators. In nature, however, a vast number of creatures navigate their habitats using soft bodies — earthworms, snails and larval insects can effectively move in complex environments using different strategies. Up to date, attempts to create soft robots were limited to larger scale (typically tens of centimeters), mainly due to difficulties in power management and remote control.
Liquid Crystalline Elastomers (LCEs) are smart materials that can exhibit large shape change under illumination with visible light. With the recently developed techniques, it is possible to pattern these soft materials into arbitrary three dimensional forms with a pre-defined actuation performance. The light-induced deformation allows a monolithic LCE structure to perform complex actions without numerous discrete actuators.
Researchers from the University of Warsaw with colleagues from LESN (Italy) and Cambridge (UK) have now developed a natural-scale soft caterpillar robot with an opto-mechanical liquid crystalline elastomer monolithic design. The robot body is made of a light sensitive elastomer stripe with patterned molecular alignment. By controlling the travelling deformation pattern the robot mimics different gaits of its natural relatives. It can also walk up a slope, squeeze through a slit and push objects as heavy as ten times its own mass, demonstrating its ability to perform in challenging environments and pointing at potential future applications.
“Designing soft robots calls for a completely new paradigm in their mechanics, power supply and control. We are only beginning to learn from nature and shift our design approaches towards these that emerged in natural evolution,” says Piotr Wasylczyk, head of the Photonic Nanostructure Facility at the Faculty of Physics of the University of Warsaw, Poland, who led the project.
Researchers hope that rethinking materials, fabrication techniques and design strategies should open up new areas of soft robotics in micro- and millimeter length scales, including swimmers (both on-surface and underwater) and even fliers.
Journal reference:
Mikołaj Rogóż, Hao Zeng, Chen Xuan, Diederik Sybolt Wiersma, Piotr Wasylczyk. Light-Driven Soft Robot Mimics Caterpillar Locomotion in Natural Scale. Advanced Optical Materials, 2016; DOI:10.1002/adom.201600503
Source:
Science Daily / Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw
tags: c-Research-Innovation, robohub focus on soft robotics, soft robotics