
Robohub.org
Robots can successfully imitate human motions in the operating room
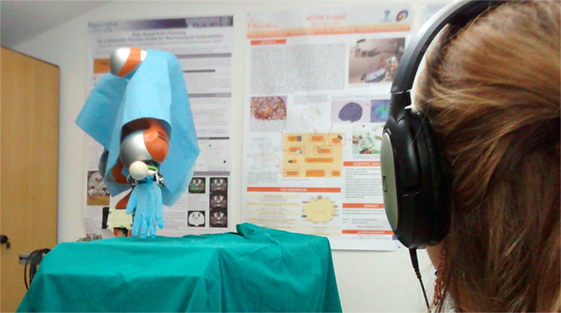
The human-like and the non-human-like trajectories were performed in a random order (10 human-like and 10 non-human-like). Photo: Courtesy of Dr. Elena De Momi, Politecnico di Milano.
By: Marcus Banks
The nursing assistant for your next trip to the hospital might be a robot. This is the implication of research recently published by Dr. Elena De Momi and colleagues in the open access journal Frontiers in Robotics and AI (Artificial Intelligence).
Dr. De Momi, of the Politecnico di Milano (Italy), led an international team that trained a robot to imitate natural human actions. De Momi’s work indicates that humans and robots can effectively coordinate their actions during high-stakes events such as surgeries.
Over time this should lead to improvements in safety during surgeries because unlike their human counterparts robots do not tire and can complete an endless series of precise movements. The goal is not to remove human expertise from the operating room, but to complement it with a robot’s particular skills and benefits.
“As a roboticist, I am convinced that robotic (co)workers and collaborators will definitely change the work market, but they won’t steal job opportunities. They will just allow us to decrease workload and achieve better performances in several tasks, from medicine to industrial applications,” De Momi explains.
To conduct their experiment De Momi’s team photographed a human being conducting numerous reaching motions, in a way similar to handing instruments to a surgeon. These camera captures were input into the neural network of the robotic arm, which is crucial to controlling movements. Next, a human operator guided the robotic arm in imitating the reaching motions that the human subject had initially performed. Although there was not a perfect overlap between the robotic and human actions, they were broadly similar.
Finally, several humans observed as the robotic arm made numerous motions. These observers determined whether the actions of the robotic arms were “biologically inspired,” which would indicate that their neural networks had effectively learned to imitate human behavior. About 70% of the time this is exactly what the human observers concluded.
These results are promising, although further research is necessary to validate or refine De Momi’s conclusions. If robotic arms can indeed imitate human behavior, it would be necessary to build conditions in which humans and robots can cooperate effectively in high-stress environments like operating rooms.
This future may not be as far away as we think. De Momi’s work is part of the growing field of healthcare robotics, which has the potential to change the way we receive health care sooner rather than later.
Read the research paper here.
If you liked this article, you may also want to read:
- Living with a prosthesis that learns: A case-study in translational medicine
- Putting humanoid robots in contact with their environment
- Robotic research: Are we applying the scientific method?
See all the latest robotics news on Robohub, or sign up for our weekly newsletter.
tags: c-Health-Medicine





