
Robohub.org
A dilemma of high-risk / high-reward
Often funding sources – the groups taking the risk – are not the beneficiaries of the rewards of the venture. Intuitive Surgical is an example.
NSF, DARPA and NASA funded a project to solve a very real problem: providing medical attention to Americans in remote places such as space, war or scientific expeditions. The initial concept was to be a telepresence project but with no known solution. That was the high-risk research project funded by the three agencies.
During the development phase, two enterprising team members, Frederic Moll and Robert Younge, concluded that true remote-presence surgery couldn’t be achieved with then-current technology but could be achieved within a controlled network,and by so doing there would be many benefits to the surgeons and patients involved. The two wrote a business plan, got venture money and proceeded to develop the system now known as the da Vinci Surgical System within a company subsequently named www.
Shortly before going public, and before getting FDA approval, Intuitive Surgical was sued for patent infringement by Computer Motion, Inc., which had its own system, the ZEUS Robotic Surgical System – a system which was already approved for use in Europe.
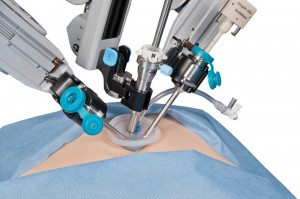
The litigation was resolved in 2003 when the two companies agreed to merge, thus ending the litigation. The ZEUS system was ultimately phased out in favor of the da Vinci system. The litigation created an active depository of intellectual properties – hundreds of patents and trade marks – that Intuitive Surgical has vigorously defended in a way that has created a competitive void in the commercialization of similar devices and systems.
Consequently Intuitive Surgical has grown to be a growth company with large profits and is listed on the NASDAQ stock exchange (NASDAQ:ISRG). But it didn’t exactly happen with the high-risk / high-reward formula. Intuitive Surgical and it’s VC backers got the reward and NSF, DARPA and NASA are still searching for their solution.
SRI and Stanford University did get money for licenses to use the technologies they developed, but not the huge rewards stemming from the successes of Intuitive Surgical.
As is often the case in startups, the solutions and products that finally emerge in the marketplace are ones that are different from those that initiated the startup. Sometimes this involves changes in funders, partners and ownership and those that reap the final rewards are often removed from the originating project.
 High risk takers are most often governmental agencies with a strategic social/political issue to resolve. Corporate R&D departments also invest in future scenarios but to a lesser extent – they most often pragmatically acquire the technology they need and rework it to fit their specific requirements.
High risk takers are most often governmental agencies with a strategic social/political issue to resolve. Corporate R&D departments also invest in future scenarios but to a lesser extent – they most often pragmatically acquire the technology they need and rework it to fit their specific requirements.
Hence the dilemma: does the initial risk taker expect to get the double reward of (1) product solution and (2) profits from their sale, or just the altruistic reward of seeing that their initial problem, for which they are risking their money, is being addressed in the broader marketplace solving the original problem, reward or not?
tags: c-Business-Finance, da Vinci, Funding, Intuitive Surgical, Robohub Focus on High-risk High-reward


