
Robohub.org
Grow a house with plant-robot hybrids
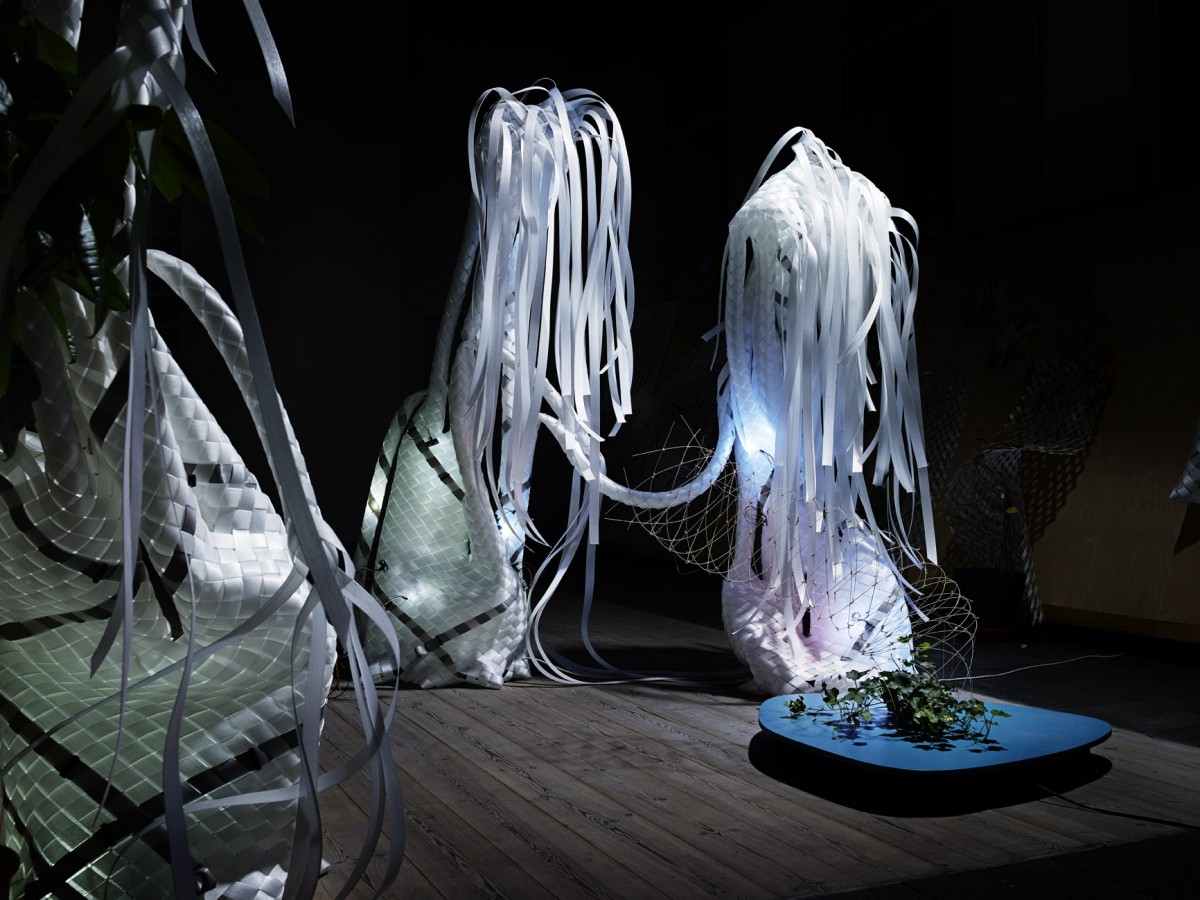

Image courtesy of flora robotica, Photo by Anders Ingvartsen, CITA
Robots and plants are being intricately linked into a new type of living technology that its creators believe could be used to grow a house.
‘The growth is for free, but we have to control the plants to grow in the shapes we want,’ explained Professor Heiko Hamann, from the University of Lübeck in Germany, who coordinates the EU-funded flora robotica project. The plants grow through a network of sensors, computers and 3D-printed robotic nodes that are connected to each other and constantly monitor the plants. The team uses a white plastic scaffolding with black strips woven into it to guide the growth. The strips contain LED lights and sensors that can cause plants to grow into pre-programed shapes.
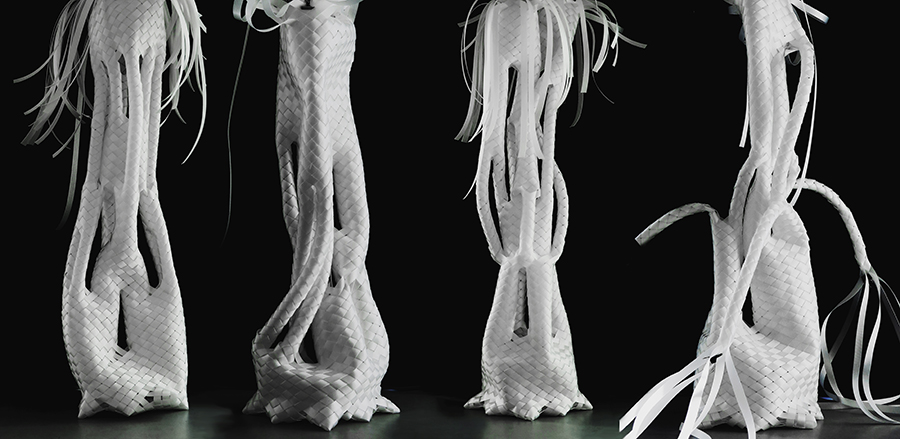
Plastic white scaffolding helps hold up plant-robot hybrids until they are strong enough to support themselves. Image courtesy of flora robotica
Once the plants are strong enough, the scaffolding is removed piece by piece and the hybrids can stand and support themselves. The idea is to create a society of plant-robot hybrids that functions as a self-organising system. As the system grows over long periods in interaction with humans, the research team hopes it will form meaningful architectural forms, including eventually a house.
Prof. Hamann believes a full house will take 40 years to grow, but his team is already starting to create parks where people can design their own plants by mixing seeds, scaffolds and electronics. The techniques required to create the plant-robot hybrids are already well advanced. ‘They can talk to each other … and they already know the pattern that they’re supposed to make, and they can decide which lights should turn on to grow the shape that you actually want,’ he said.
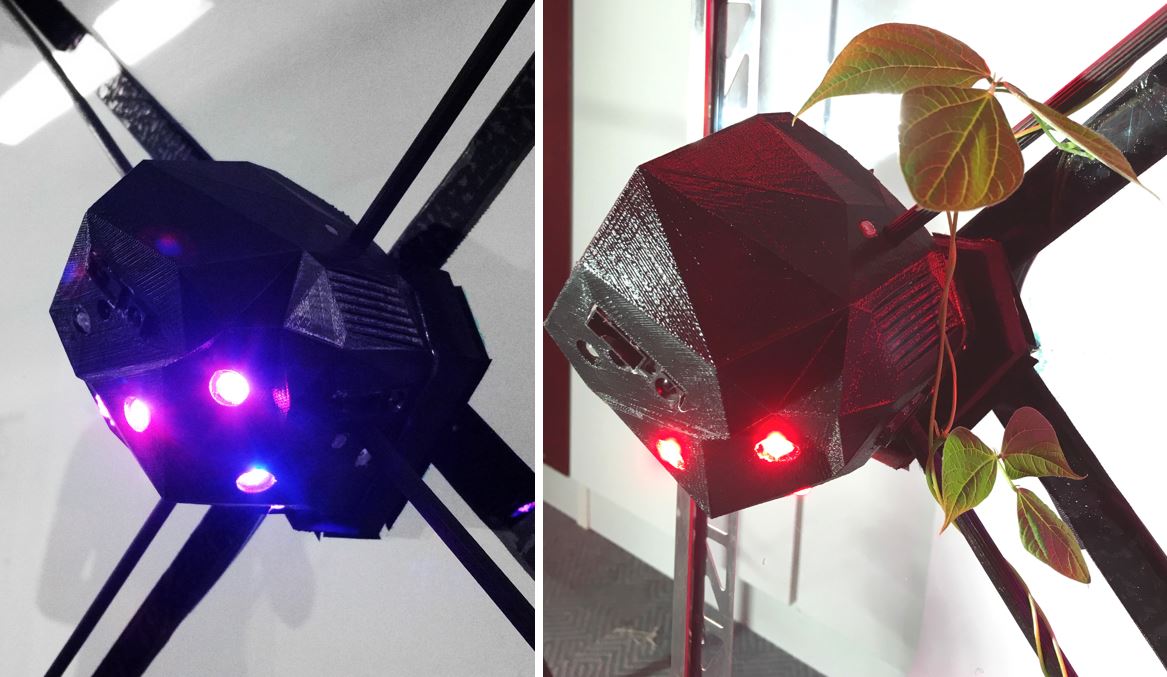

Images courtesy of flora robotica
The robots make use of the fact that plants respond differently to red and blue light. To test this out, researchers put coloured lights around bean plants and monitored their growth.
‘The blue light influences where the plant grows,’ explained Prof. Hamann.
The team is also testing out how to weave different braided structures. Some are loose and let light inside for plants to grow within the structure, while others are woven more tightly making the scaffold stronger for plants and sensors to sit outside.
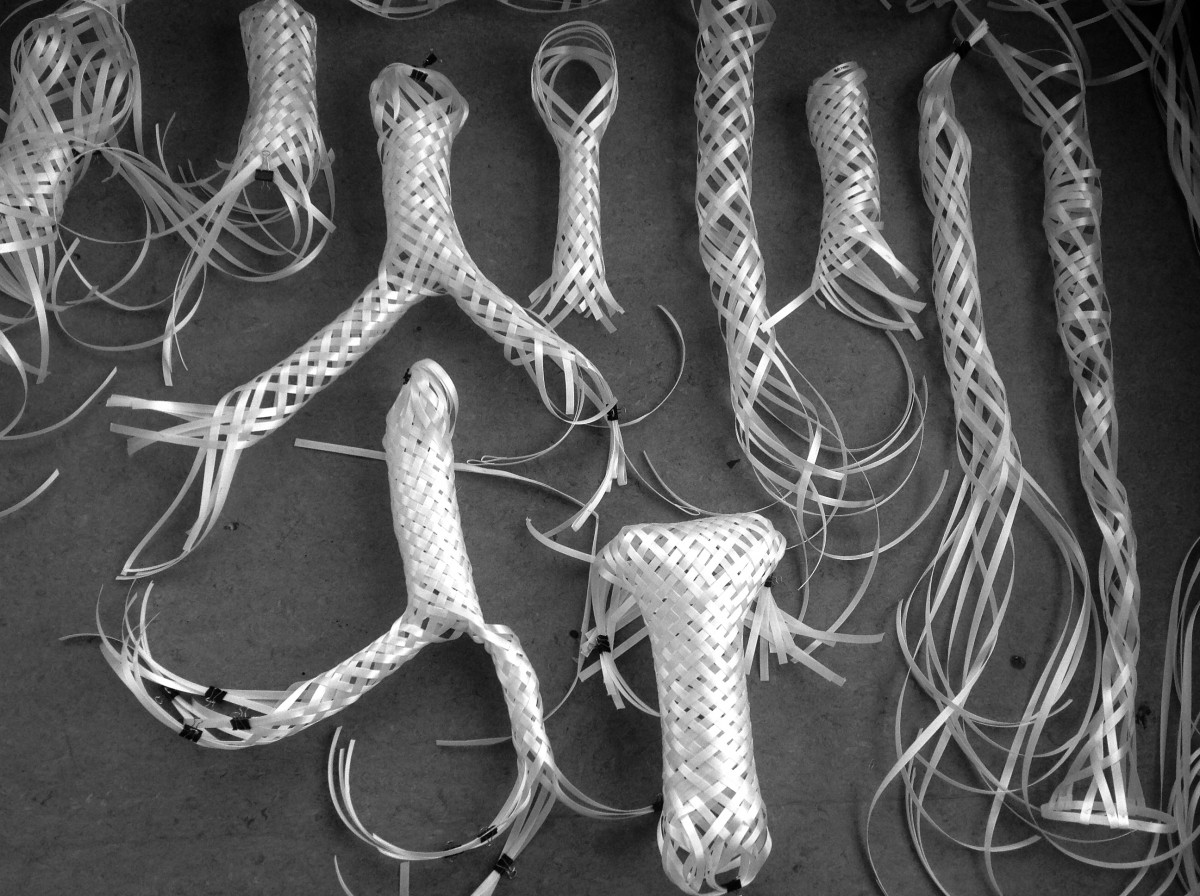
Image courtesy of flora robotica
The different tightnesses of the braids could also help researchers make bendable arms that are controlled by robots to move side to side and extend and retract – similar to the way a puppet’s arms move when someone pulls a string.

The researchers hope that the arm will be able to interact with people, for example when someone walks by. It’s part of their overall goal to ‘bring technology and nature together’. The idea is that robots will work with people around them, for example by not growing in a place where people often walk by, or telling a passer-by that a plant needs more water.
‘The plant system should interact with human beings,’ explained Prof. Hamann.

Image courtesy of flora robotica
tags: bio-inspired, c-Research-Innovation, Prototype, Research, Robotics technology





