
Robohub.org
Insect-inspired flying robot handles collisions, goes where other robots can’t
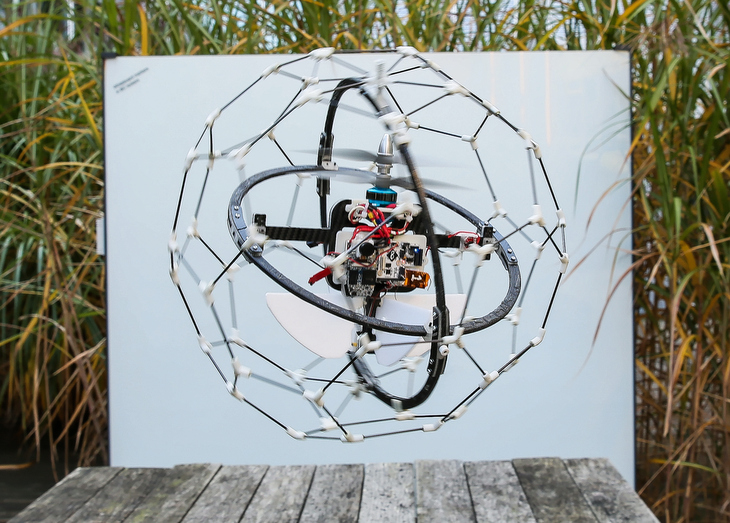
Generally, flying robots are programmed to avoid obstacles, which is far from easy in cluttered environments. At the Laboratory of Intelligent Systems, we think that flying robots should be able to physically interact with their surroundings. Take insects: they often collide with obstacles and continue flying afterwards. We thus designed GimBall, a flying robot that can collide with objects seamlessly. Thanks to a passively rotating spherical cage, it remains stable even after taking hits from all sides. This approach enables GimBall to fly in the most difficult places without complex sensors.
The concept
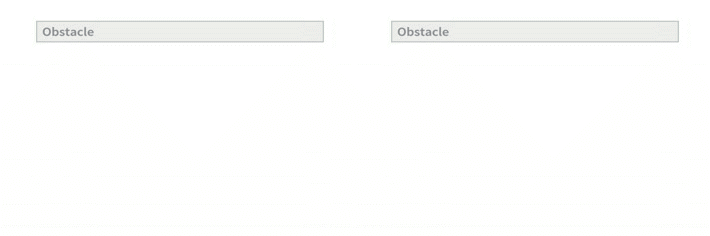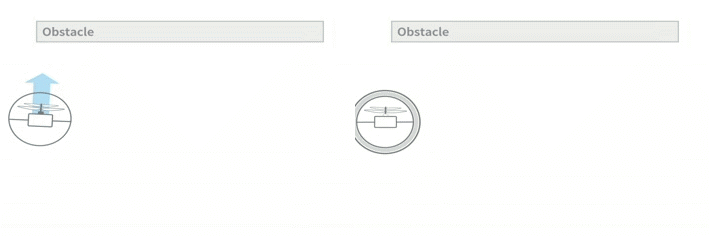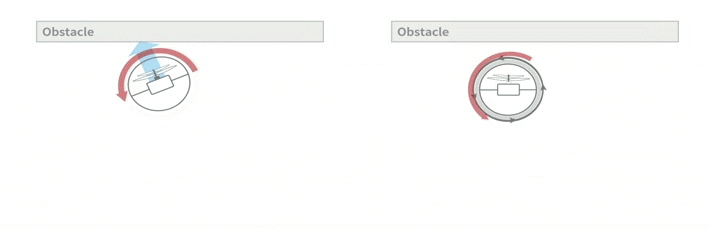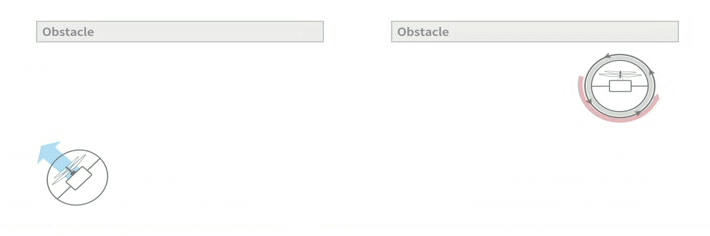
The inner frame comprises everything a flying robot needs to stabilize in flight: a coaxial motor, two control surfaces, the battery, an IMU and control electronics. In case of collision, GimBall’s spherical protective frame prevents obstacles from touching the inner frame and can passively rotate thanks to a gimbal system (hence the name). This way, the contact force does not affect the orientation of the inner frame, whose center of mass is also carefully centered. This allows the inner frame to always stay upright, and maintain the robot in stable flight.
The story
We have been designing flying robots capable of interacting with the environment for a while now. Our previous prototype, the AirBurr, was equipped with a protective cage and legs for uprighting.
This platform allowed us to realize that autonomous navigation was much simpler once you can afford collisions: advanced sensors are not required, and the obstacles can even be used to guide the robot. This idea of exploiting collisions was pushed further by integrating contact sensors to the structure itself. This way, the robot can be programmed to change direction once it detects a contact. We demonstrated that the robot could fly completely autonomously just based on tiny touch sensors (no other exteroceptive sensors whatsoever), as featured in the video below.
While the AirBurr worked well in the lab, where the environment is nicely flat and structured, we are now targeting much harder environments with the GimBall. For example, the robot could fly autonomously through a forest with a very simple strategy: fly straight. It made its way through the forest without any obstacle avoidance technique while experiencing multiple collisions.
We think that research on flying robots capable of interacting with the environment will enable new uses for UAVs. Currently, options for flight in cluttered spaces are limited, because obstacle avoidance methods cannot be trusted all the time. A robot that can survive collisions will be useful in cluttered disaster zones to find survivors or to inspect semi-collapsed buildings for example. Thanks to less stringent sensor requirements, these robots are lighter, faster and more robust than conventional platforms. Finally, they are very safe for operation close to people, since they won’t crash if you bump them and the propellers are enclosed in the protective cage.
You can find all relevant publications and more pictures or videos on our project webpage.
Coming to IROS next week? Comme see us at iRex, we’ll be running demos from Wednesday 6 to Sunday 9.
This research was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation through the National Centre of Competence in Research (NCCR) Robotics.
If you liked this article, you may also be interested in:
- Fully autonomous flapping-wing micro air vehicle weighs about as much as 4 sheets of A4 paper
- First controlled flight of an insect-sized robot
- Parrot AR.Drone app harnesses crowd power to fast-track vision learning in robotic spacecraft
- Robots Podcast: Origami robots
See all the latest robotics news on Robohub, or sign up for our weekly newsletter.
tags: Airburr, bio-inspired, c-Research-Innovation, cx-Aerial, EPFL, Flying, GimBall, Prototype, Swiss Robots





