
Robohub.org
Implantable microrobots: Manufacturing intricate biocompatible micromachines
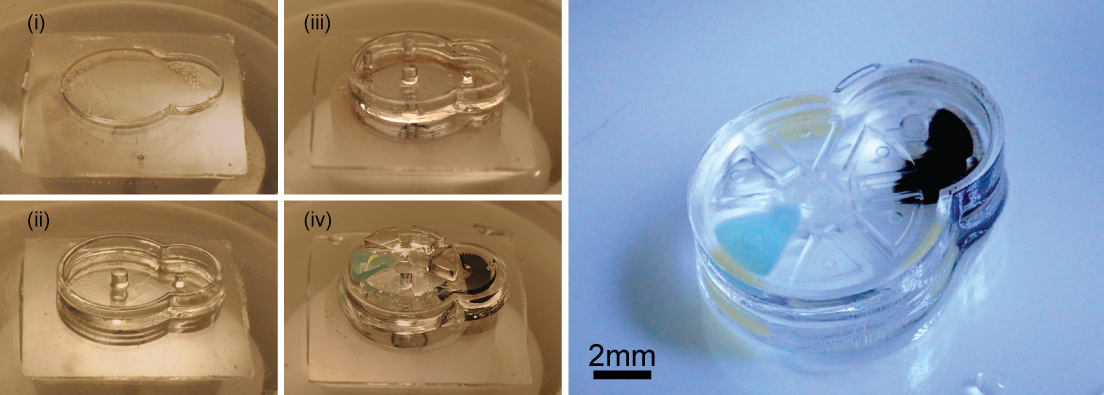
Fabrication and complete assembly of a Geneva drive device using the iMEMS method. The left panel shows the layer-by-layer fabrication of support structures and assembly of gear components. The image on the right shows the complete device after the layers have been sealed. Image: SauYin Chin, Columbia Engineering.
A team of researchers led by Biomedical Engineering Professor Sam Sia at Columbia Engineering has developed a way to manufacture microscale machines from biomaterials that can safely be implanted in the body. Working with hydrogels, which are biocompatible materials that engineers have been studying for decades, Sia has invented a new technique that stacks the soft material in layers to make devices that have three-dimensional, freely moving parts. The study, published online January 4, 2017, in Science Robotics, demonstrates a fast manufacturing method Sia calls “implantable microelectromechanical systems” (iMEMS).
By exploiting the unique mechanical properties of hydrogels, the researchers developed a “locking mechanism” for precise actuation and movement of freely moving parts, which can function as valves, manifolds, rotors, pumps, and drug delivery systems. They were able to tune the biomaterials within a wide range of mechanical and diffusive properties and to control them after implantation without a sustained power supply, such as a toxic battery. They then tested the payload delivery in a bone cancer model and found that the triggering of releases of doxorubicin from the device over 10 days showed high treatment efficacy and low toxicity, at 1/10th of the standard systemic chemotherapy dose.
“Overall, our iMEMS platform enables development of biocompatible implantable microdevices with a wide range of intricate moving components that can be wirelessly controlled on demand and solves issues of device powering and biocompatibility,” says Sia, also a member of the Data Science Institute. “We’re really excited about this because we’ve been able to connect the world of biomaterials with that of complex, elaborate medical devices. Our platform has a large number of potential applications, including the drug delivery system demonstrated in our paper which is linked to providing tailored drug doses for precision medicine.”
Most current implantable microdevices have static components rather than moving parts and, because they require batteries or other toxic electronics, have limited biocompatibility. Sia’s team spent more than eight years working on how to solve this problem. “Hydrogels are difficult to work with, as they are soft and not compatible with traditional machining techniques,” says Sau Yin Chin, lead author of the study, who worked with Sia. “We have tuned the mechanical properties and carefully matched the stiffness of structures that come in contact with each other within the device. Gears that interlock have to be stiff in order to allow for force transmission and to withstand repeated actuation. Conversely, structures that form locking mechanisms have to be soft and flexible to allow for the gears to slip by them during actuation, while at the same time they have to be stiff enough to hold the gears in place when the device is not actuated. We also studied the diffusive properties of the hydrogels to ensure that the loaded drugs do not easily diffuse through the hydrogel layers.”
The team used light to polymerize sheets of gel and incorporated a stepper mechanization to control the z-axis and pattern the sheets layer by layer, giving them three-dimensionality. Controlling the z-axis enabled the researchers to create composite structures within one layer of the hydrogel while managing the thickness of each layer throughout the fabrication process. They were able to stack multiple layers that are precisely aligned and, because they could polymerize a layer at a time, one right after the other, the complex structure was built in under 30 minutes.
Sia’s iMEMS technique addresses several fundamental considerations in building biocompatible microdevices, micromachines, and microrobots: how to power small robotic devices without using toxic batteries; how to make small biocompatible moveable components that are not silicon, which has limited biocompatibility; and how to communicate wirelessly once implanted (radio frequency microelectronics require power, are relatively large, and are not biocompatible). The researchers were able to trigger the iMEMS device to release additional payloads over days to weeks after implantation. They were also able to achieve precise actuation by using magnetic forces to induce gear movements that, in turn, bend structural beams made of hydrogels with highly tunable properties. (Magnetic iron particles are commonly used and are FDA-approved for human use as contrast agents.)
In collaboration with Francis Lee, an orthopedic surgeon at Columbia University Medical Center at the time of the study, the team tested the drug delivery system on mice with bone cancer. The iMEMS system delivered chemotherapy adjacent to the cancer, and limited tumor growth while showing less toxicity than chemotherapy administered throughout the body.
“These microscale components can be used for microelectromechanical systems, for larger devices ranging from drug delivery to catheters to cardiac pacemakers, and soft robotics,” notes Sia. “People are already making replacement tissues and now we can make small implantable devices, sensors, or robots that we can talk to wirelessly. Our iMEMS system could bring the field a step closer to developing soft miniaturized robots that can safely interact with humans and other living systems.”
The study, “Additive manufacturing of hydrogel-based materials for next-generation implantable medical devices,” was supported by an NSF CAREER award, NIH R01 grant (HL095477-05), and NSF ECCS-1509748. Chin was supported by the National Science Scholarship (PhD) awarded by the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (Singapore). The researchers have a patent pending.
If you enjoyed this article, you may also enjoy:
- The rise of China’s medical robotics sector
- Robots at your service: Empowering healthy aging at European Robotics Week, 2016
- Considering robot care, ethics & future tech at #ERW2016 European Robotics Week
- Survey: Evaluate ethics of health related privacy with care robots
- Care-O-bot 4 celebrates its premiere as a shopping assistant
- Robot companions are coming into our homes — how human should they be?
See all the latest robotics news on Robohub, or sign up for our weekly newsletter.
tags: Annoincement, bio-inspired, c-Research-Innovation, cx-Health-Medicine, Micro, Prototype, Research, Service Professional Medical Other




