
Robohub.org
Plug-and-play artificial compound eye for robotic applications
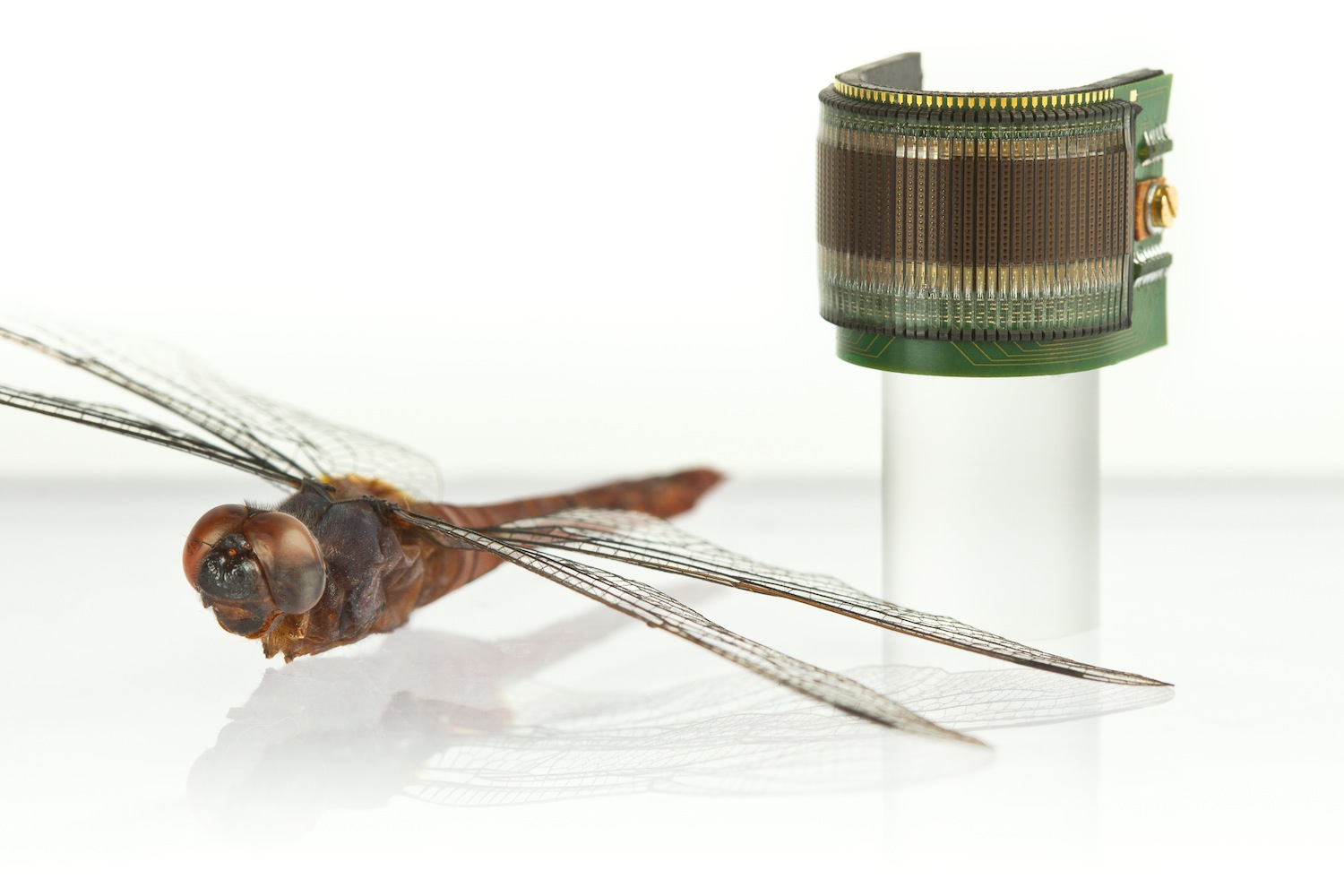

Flies have small brains that would not be able to process high-resolution images such as those that we see with our own eyes. Instead, they’ve perfected the use of compound eyes, composed of a dense mosaic of tiny eye-like structures called ommatidia. Each ommatidium consists of a microlense that focuses light from a specific section of the insect’s field of view onto an independent set of photoreceptors. Think of it as having many low-resolution cameras pointing in different directions. The result is a vision system with low spatial resolution (i.e. it can’t see details), but a wide field of view (i.e. it can see all around). By comparing information across the different ommatidia, flies can extract temporal information useful for detecting motion. This motion information, also called optic flow, is what allows flies to navigate, take-off, land and avoid obstacles while using very little processing power.
Inspired by the fly’s vision system, the Curved Artificial Compound Eye (CurvACE) published today in the prestigious journal PNAS can enable a large range of applications that require motion detection using a small plug-and-play device. As shown in the video below, you could use these sensors to control small robots navigating an environment, even in the dark, or equip a small autonomous flying robot with limited payload. Other applications include home automation, surveillance, medical instruments, prosthetic devices, and smart clothing.
The artificial compound eye features a panoramic, hemispherical field of view with a resolution identical to that of the fruitfly in less than 1 mm thickness. Additionally, it can extract images 3 times faster than a fruitfly, and includes neuromorphic photoreceptors that allow motion perception in a wide range of environments from a sunny day to moon light. To build the sensors, the researchers align an array of microlenses, an array of photodetectors, and a flexible PCB that mechanically supports and electrically connects the ensemble. The panoramic field of view is provided by dicing the rigid parts of the ommatidia, thereby allowing the mechanical bending of the sensor. The necessary components for signal readout and processing are embedded in the curvature of the sensor.
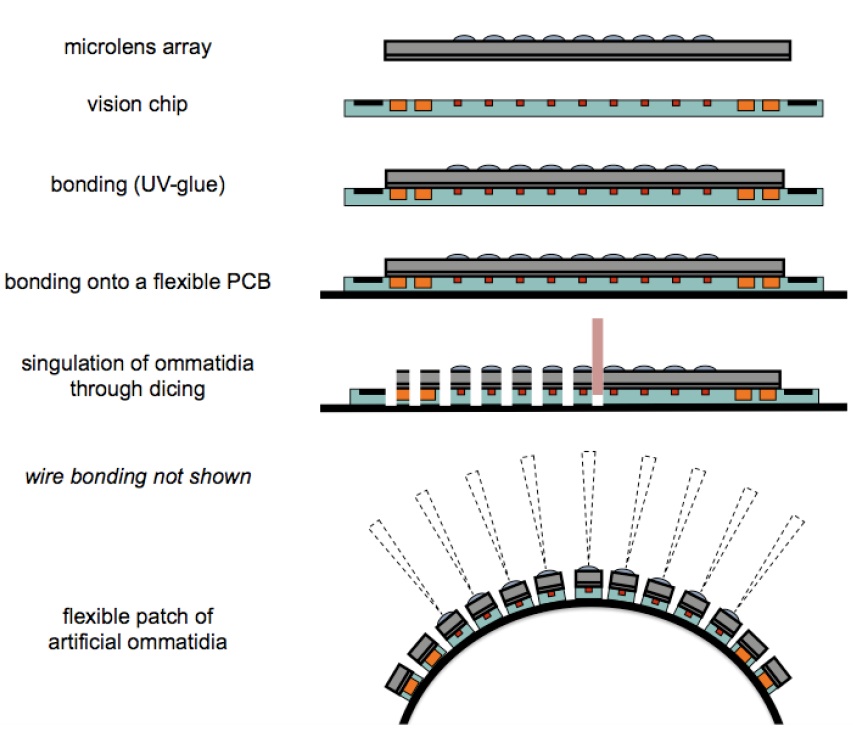
CurvACE is a European project bringing together the Laboratory of Intelligent Systems in EPFL (Switzerland), the Laboratory of Biorobotics in the University of Aix-Marseille (France), the Fraunhofer Institute of Applied Optics and Precision Engineering (Germany), and the Laboratory of Cognitive Sciences in the University of Tübingen (Germany).
Don’t miss the next ROBOTS podcast for my interview with the researchers behind this new artificial compound eye.
tags: bio-inspired, c-Research-Innovation, EPFL, Micro, review, Robotics technology, Sensing




